

Tourism: The Advantages, Disadvantages and How to Properly Travel
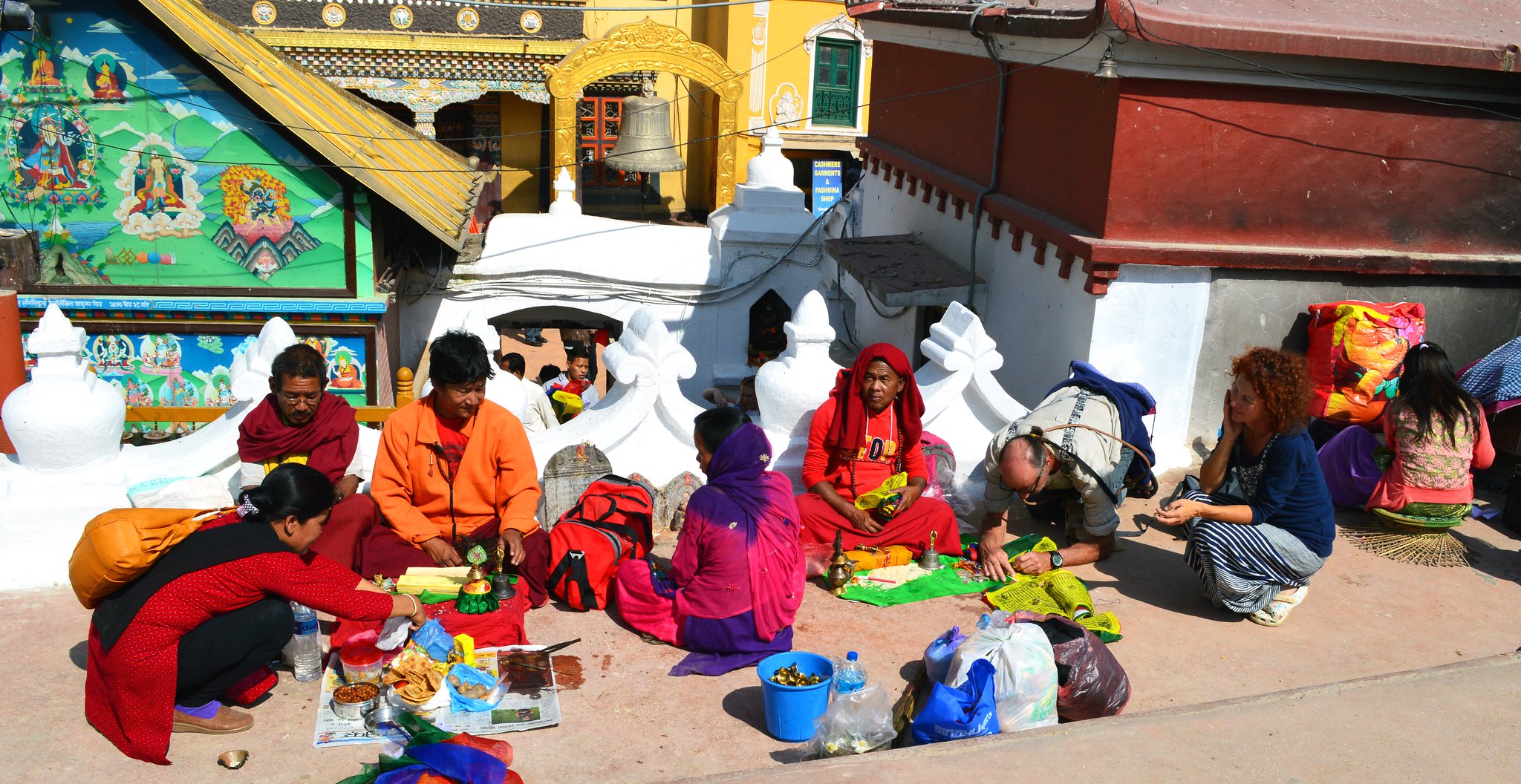

The Advantages
For developing countries, the advantages of tourism tend to be primarily monetary. A large scale tourism industry prevents larger, more harmful businesses from working off the land. Small tourist companies that reign on the land stops large capitalistic corporations from polluting the air or gentrifying people’s homes.
The tourism industry encompasses many different travel areas, which allows the majority of a country’s population to be employed . These employment places include hotels, car rental agencies, restaurants, tour companies, souvenir shops, and equipment shops, among others.
Profit earned from tourism can be reinvested into the country for better infrastructure, education, funding conservation efforts and creating more responsible ways of touring. Without tourism, many countries would not have the same level of access to education and infrastructure. Moreover, tourism allows hosts and visitors to share cultures and meet diverse groups of people. Through respectful interactions, a broader view of the world from both parties can be achieved. By reinvesting the money earned back into the country, tourism and its attractions can grow, creating a positive cycle for the country.
The Disadvantages
With the way the tourism industry is currently run, the disadvantages of tourism may greatly outweigh the advantages in a country. The first factor to take into consideration is environmental damage. When a country has a high tourist attraction, the number of people occupying a space increases immensely. As a result, the release of carbon monoxide gases can increase due to plane and car use affecting the country’s environment. Many countries with ancient ruins or natural attractions are also in danger of destruction or erosion with significant foot traffic and human interaction. Additionally, flora and fauna can decrease in areas or change their growth and migration patterns when there is an overflow of humans interact. Foot traffic and continuous touching can also slowly degrade the stability of ancient structures.
One of the advantages breached upon the sharing of cultures. While this is a great interaction of beliefs and customs, it can become destructive to a host country’s culture. One of the ways cultures can be disrespected is through the commercialization of countries’ cultures . When tourism booms, large industries swoop in and sell figures of the cultures’ icons or traditional wear, disrespecting the countries’ indigenous beliefs and can be harmful to the people living there. Moreover, poor behavior from tourists who don’t respect the spoken or unspoken codes of conduct held by indigenous peoples also undermines the sacred beliefs held within the country.
Also, for many countries, tourism is a seasonal occurrence. For people that work in the tourism industry, their jobs are only viable for a certain number of months, and after the season has ended, many are left without income. Many of these jobs also lack the benefits that other sector jobs supply. Tourism workers are often left without insurance or pension. Not to mention, foreign businesses tend to overtake the companies present in these countries, forcing small businesses to shut down. As a result, foreign businesses keep the majority of profits from tourism, while local businesses lose their income. This hurts small businesses and local economies.
As previously stated, the profit gained from tourism is often reinvested into the industry. However, with unequal infrastructure development, the tourism industry can inadvertently sustain itself without aiding a country’s other vital sectors. As such, many countries end up developing tourism hot spots while the rest of the country suffers. In these countries, there are visible socioeconomic gaps between the wealthy and the poor. Focusing mainly on the tourism industry and places of mass attraction leaves disadvantaged communities at risk of financial instability. Moreover, countries solely invested in tourism are vulnerable to quick economic falls as its working sectors are unevenly balanced. If a natural disaster, political unrest or unprecedented pandemic were to strike, the country would lose a massive income, causing an economic recession that some countries may significantly struggle to bounce back from.
Ways to Respectfully Travel
The most important step to being a respectful tourist is to be an educated tourist. Understanding and respecting the culture and the people of the country is vital. By not undermining tourism countries’ culture and beliefs, the people living there will be more welcoming to tourists, and cultures can flourish without fear of commercialization.
Being environmentally conscious is also important to the survival of these countries. Respecting a country’s land and structures preserve the countries’ beauty and keep the land clean and prepped for further development. Many countries are more environmentally strained, so reducing pollution or your carbon footprint in a foreign country can help ease the strain.
Supporting the small and local businesses found in these countries can help keep local communities employed and support the overall economy. As local businesses grow, more people will have the opportunity to be employed outside of the tourism sector, and the economy will be able to grow within itself.
By learning the advantages and disadvantages of tourism, and how one can improve the practice of traveling, the tourism industry will be able to change for the better and support the countries that host people from all over the world.
– Marlee Ingram Photo: Flickr
“The Borgen Project is an incredible nonprofit organization that is addressing poverty and hunger and working towards ending them.”
-The Huffington Post
Inside the borgen project.
- Board of Directors
Get Smarter
- Global Poverty 101
- Global Poverty… The Good News
- Global Poverty & U.S. Jobs
- Global Poverty and National Security
- Innovative Solutions to Poverty
- Global Poverty & Aid FAQ’s
Ways to Help
- Call Congress
- Email Congress
- 30 Ways to Help
- Volunteer Ops
- Internships
- The Podcast
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer

share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Tourism’s Importance for Growth Highlighted in World Economic Outlook Report
- All Regions
- 10 Nov 2023
Tourism has again been identified as a key driver of economic recovery and growth in a new report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). With UNWTO data pointing to a return to 95% of pre-pandemic tourist numbers by the end of the year in the best case scenario, the IMF report outlines the positive impact the sector’s rapid recovery will have on certain economies worldwide.
According to the World Economic Outlook (WEO) Report , the global economy will grow an estimated 3.0% in 2023 and 2.9% in 2024. While this is higher than previous forecasts, it is nevertheless below the 3.5% rate of growth recorded in 2022, pointing to the continued impacts of the pandemic and Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and from the cost-of-living crisis.
Tourism key sector for growth
The WEO report analyses economic growth in every global region, connecting performance with key sectors, including tourism. Notably, those economies with "large travel and tourism sectors" show strong economic resilience and robust levels of economic activity. More specifically, countries where tourism represents a high percentage of GDP have recorded faster recovery from the impacts of the pandemic in comparison to economies where tourism is not a significant sector.
As the report Foreword notes: "Strong demand for services has supported service-oriented economies—including important tourism destinations such as France and Spain".
Looking Ahead
The latest outlook from the IMF comes on the back of UNWTO's most recent analysis of the prospects for tourism, at the global and regional levels. Pending the release of the November 2023 World Tourism Barometer , international tourism is on track to reach 80% to 95% of pre-pandemic levels in 2023. Prospects for September-December 2023 point to continued recovery, driven by the still pent-up demand and increased air connectivity particularly in Asia and the Pacific where recovery is still subdued.
Related links
- Download the News Release on PDF
- UNWTO World Tourism Barometer
- IMF World Economic Outlook
Category tags
Related content.

International Tourism to Reach Pre-Pandemic Levels in 2024

International Tourism to End 2023 Close to 90% of Pre-P...

International Tourism Swiftly Overcoming Pandemic Downturn

Tourism on Track for Full Recovery as New Data Shows St...
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Don’t forget tourism has benefits too
Readers respond to Christopher de Bellaigue’s long read on the future of global tourism
Christopher de Bellaigue’s article ( The end of tourism? , Long read, 18 June) is interesting and insightful, but fails to point out the intrinsic value of travel. Mass tourism, apart from its economic and ecological impacts, has also implied the opportunity to access peoples, cultures and foods that we have hitherto never experienced. To travel is to live, as Hans Christian Andersen once wrote.
The chance to experience and appreciate other cultures, to understand the lives of others unlike oneself, must be seen as a public good in itself. The “end of tourism” will not mean the end of travel for the classes who can afford it, but only means the denying of the opportunity for the vast majority of the world’s people to experience the world in ways that previous generations could not have dreamed of. An end to tourism will not hinder the travel plans of the world’s richest, but will serve to insulate and harden the nativist sentiments of the more disadvantaged. Madhav Tipu Ramachandran Bengaluru, India
Tourism and globalisation is what has brought us the very knowledge and cultural understanding about all the destinations that the author talks about. Without a globally connected and travelling society there would be little awareness of other cultures, little respect for other traditions and much less intercultural exchange.
Travelling and experiencing other cultures first-hand is what makes us more open and accepting of others. It connects us to the rest of the world. Progressive politics, fighting racism and supporting migration all depend on people understanding more of other countries and cultures. Lorenz Kost Düsseldorf, Germany
I was a bit bemused that no mention was made of staying in your own country for a holiday and the impact of Covid-19 on the UK tourism industry. Lockdown has helped many of us to appreciate what we have close at hand, from our own back gardens to wildlife areas on our doorsteps.
There’s much choice for urban, countryside and seaside holidays, and such diverse beauty and culture available right here in the UK. Reopening UK-based tourism will help the economy and people’s wellbeing without impacting on the environment in the way that overseas travel does. Danielle Lowy Manchester
- Coronavirus
- Air transport
- Class issues
Most viewed
- Understanding Poverty
- Competitiveness
Tourism and Competitiveness

- Publications
The tourism sector provides opportunities for developing countries to create productive and inclusive jobs, grow innovative firms, finance the conservation of natural and cultural assets, and increase economic empowerment, especially for women, who comprise the majority of the tourism sector’s workforce. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, tourism was the world’s largest service sector—providing one in ten jobs worldwide, almost seven percent of all international trade and 25 percent of the world’s service exports —a critical foreign exchange generator. In 2019 the sector was valued at more than US$9 trillion and accounted for 10.4 percent of global GDP.
Tourism offers opportunities for economic diversification and market-creation. When effectively managed, its deep local value chains can expand demand for existing and new products and services that directly and positively impact the poor and rural/isolated communities. The sector can also be a force for biodiversity conservation, heritage protection, and climate-friendly livelihoods, making up a key pillar of the blue/green economy. This potential is also associated with social and environmental risks, which need to be managed and mitigated to maximize the sector’s net-positive benefits.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has been devastating for tourism service providers, with a loss of 20 percent of all tourism jobs (62 million), and US$1.3 trillion in export revenue, leading to a reduction of 50 percent of its contribution to GDP in 2020 alone. The collapse of demand has severely impacted the livelihoods of tourism-dependent communities, small businesses and women-run enterprises. It has also reduced government tax revenues and constrained the availability of resources for destination management and site conservation.

Naturalist local guide with group of tourist in Cuyabeno Wildlife Reserve Ecuador. Photo: Ammit Jack/Shutterstock
Tourism and Competitiveness Strategic Pillars

Our solutions are integrated across the following areas:
- Competitive and Productive Tourism Markets. We work with government and private sector stakeholders to foster competitive tourism markets that create productive jobs, improve visitor expenditure and impact, and are supportive of high-growth, innovative firms. To do so we offer guidance on firm and destination level recovery, policy and regulatory reforms, demand diversification, investment promotion and market access.
- Blue, Green and Resilient Tourism Economies. We support economic diversification to sustain natural capital and tourism assets, prepare for external and climate-related shocks, and be sustainably managed through strong policy, coordination, and governance improvements. To do so we offer support to align the tourism enabling and policy environment towards sustainability, while improving tourism destination and site planning, development, and management. We work with governments to enhance the sector’s resilience and to foster the development of innovative sustainable financing instruments.
- Inclusive Value Chains. We work with client governments and intermediaries to support Small and Medium sized Enterprises (SMEs), and strengthen value chains that provide equitable livelihoods for communities, women, youth, minorities, and local businesses.
The successful design and implementation of reforms in the tourism space requires the combined effort of diverse line ministries and agencies, and an understanding of the impact of digital technologies in the industry. Accordingly, our teams support cross-cutting issues of tourism governance and coordination, digital innovation and the use and application of data throughout the three focus areas of work.
Tourism and Competitiveness Theory of Change

Examples of our projects:
- In Indonesia , a US$955m loan is supporting the Government’s Integrated Infrastructure Development for National Tourism Strategic Areas Project. This project is designed to improve the quality of, and access to, tourism-relevant basic infrastructure and services, strengthen local economy linkages to tourism, and attract private investment in selected tourism destinations. In its initial phases, the project has supported detailed market and demand analyses needed to justify significant public investment, mobilized integrated tourism destination masterplans for each new destination and established essential coordination mechanisms at the national level and at all seventeen of the Project’s participating districts and cities.
- In Madagascar , a series of projects totaling US$450m in lending and IFC Technical Assistance have contributed to the sustainable growth of the tourism sector by enhancing access to enabling infrastructure and services in target regions. Activities under the project focused on providing support to SMEs, capacity building to institutions, and promoting investment and enabling environment reforms. They resulted in the creation of more than 10,000 jobs and the registration of more than 30,000 businesses. As a result of COVID-19, the project provided emergency support both to government institutions (i.e., Ministry of Tourism) and other organizations such as the National Tourism Promotion Board to plan, strategize and implement initiatives to address effects of the pandemic and support the sector’s gradual relaunch, as well as to directly support tourism companies and workers groups most affected by the crisis.
- In Sierra Leone , an Economic Diversification Project has a strong focus on sustainable tourism development. The project is contributing significantly to the COVID-19 recovery, with its focus on the creation of six new tourism destinations, attracting new private investment, and building the capacity of government ministries to successfully manage and market their tourism assets. This project aims to contribute to the development of more circular economy tourism business models, and support the growth of women- run tourism businesses.
- Through the Rebuilding Tourism Competitiveness: Tourism Response, Recovery and Resilience to the COVID-19 Crisis initiative and the Tourism for Development Learning Series , we held webinars, published insights and guidance notes as well as formed new partnerships with Organization of Eastern Caribbean States, United Nations Environment Program, United Nations World Tourism Organization, and World Travel and Tourism Council to exchange knowledge on managing tourism throughout the pandemic, planning for recovery and building back better. The initiative’s key Policy Note has been downloaded more than 20,000 times and has been used to inform recovery initiatives in over 30 countries across 6 regions.
- The Global Aviation Dashboard is a platform that visualizes real-time changes in global flight movements, allowing users to generate 2D & 3D visualizations, charts, graphs, and tables; and ranking animations for: flight volume, seat volume, and available seat kilometers. Data is available for domestic, intra-regional, and inter-regional routes across all regions, countries, airports, and airlines on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis from January 2020 until today. The dashboard has been used to track the status and recovery of global travel and inform policy and operational actions.

Traditional Samburu women in Kenya. Photo: hecke61/Shutterstock.
Featured Data
We-Fi WeTour Women in Tourism Enterprise Surveys (2019)
- Sierra Leone | Ghana
Featured Reports
- Destination Management Handbook: A Guide to the Planning and Implementation of Destination Management (2023)
- Blue Tourism in Islands and Small Tourism-Dependent Coastal States : Tools and Recovery Strategies (2022)
- Resilient Tourism: Competitiveness in the Face of Disasters (2020)
- Tourism and the Sharing Economy: Policy and Potential of Sustainable Peer-to-Peer Accommodation (2018)
- Supporting Sustainable Livelihoods through Wildlife Tourism (2018)
- The Voice of Travelers: Leveraging User-Generated Content for Tourism Development (2018)
- Women and Tourism: Designing for Inclusion (2017)
- Twenty Reasons Sustainable Tourism Counts for Development (2017)
- An introduction to tourism concessioning:14 characteristics of successful programs. The World Bank, 2016)
- Getting financed: 9 tips for community joint ventures in tourism . World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and World Bank, (2015)
- Global investment promotion best practices: Winning tourism investment” Investment Climate (2013)
Country-Specific
- COVID-19 and Tourism in South Asia: Opportunities for Sustainable Regional Outcomes (2020)
- Demand Analysis for Tourism in African Local Communities (2018)
- Tourism in Africa: Harnessing Tourism for Growth and Improved Livelihoods . Africa Development Forum (2014)
COVID-19 Response
- Expecting the Unexpected : Tools and Policy Considerations to Support the Recovery and Resilience of the Tourism Sector (2022)
- Rebuilding Tourism Competitiveness. Tourism response, recovery and resilience to the COVID-19 crisis (2020)
- COVID-19 and Tourism in South Asia Opportunities for Sustainable Regional Outcomes (2020)
- WBG support for tourism clients and destinations during the COVID-19 crisis (2020)
- Tourism for Development: Tourism Diagnostic Toolkit (2019)
- Tourism Theory of Change (2018)
Country -Specific
- COVID Impact Mitigation Survey Results (South Africa) (2020)
- COVID Preparedness for Reopening Survey Results (South Africa) (2020)
- COVID Study (Fiji) (2020) with IFC
Featured Blogs
- Fiona Stewart, Samantha Power & Shaun Mann , Harnessing the power of capital markets to conserve and restore global biodiversity through “Natural Asset Companies” | October 12 th 2021
- Mari Elka Pangestu , Tourism in the post-COVID world: Three steps to build better forward | April 30 th 2021
- Hartwig Schafer , Regional collaboration can help South Asian nations rebuild and strengthen tourism industry | July 23 rd 2020
- Caroline Freund , We can’t travel, but we can take measures to preserve jobs in the tourism industry | March 20 th 2020
Featured Webinars
- Destination Management for Resilient Growth . This webinar looks at emerging destinations at the local level to examine the opportunities, examples, and best tools available. Destination Management Handbook
- Launch of the Future of Pacific Tourism. This webinar goes through the results of the new Future of Pacific Tourism report. It was launched by FCI Regional and Global Managers with Discussants from the Asian Development Bank and Intrepid Group.
- Circular Economy and Tourism . This webinar discusses how new and circular business models are needed to change the way tourism operates and enable businesses and destinations to be sustainable.
- Closing the Gap: Gender in Projects and Analytics . The purpose of this webinar is to raise awareness on integrating gender considerations into projects and provide guidelines for future project design in various sectoral areas.
- WTO Tourism Resilience: Building forward Better. High-level panelists from Sri Lanka, Costa Rica, Jordan and Kenya discuss how donors, governments and the private sector can work together most effectively to rebuild the tourism industry and improve its resilience for the future.
- Tourism Watch
- [email protected]
Launch of Blue Tourism Resource Portal
What Is Sustainable Tourism and Why Is It Important?
Sustainable management and socioeconomic, cultural, and environmental impacts are the four pillars of sustainable tourism
- Chapman University
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/HaleyMast-2035b42e12d14d4abd433e014e63276c.jpg)
- Harvard University Extension School
- Sustainable Fashion
- Art & Media
What Makes Tourism Sustainable?
The role of tourists, types of sustainable tourism.
Sustainable tourism considers its current and future economic, social, and environmental impacts by addressing the needs of its ecological surroundings and the local communities. This is achieved by protecting natural environments and wildlife when developing and managing tourism activities, providing only authentic experiences for tourists that don’t appropriate or misrepresent local heritage and culture, or creating direct socioeconomic benefits for local communities through training and employment.
As people begin to pay more attention to sustainability and the direct and indirect effects of their actions, travel destinations and organizations are following suit. For example, the New Zealand Tourism Sustainability Commitment is aiming to see every New Zealand tourism business committed to sustainability by 2025, while the island country of Palau has required visitors to sign an eco pledge upon entry since 2017.
Tourism industries are considered successfully sustainable when they can meet the needs of travelers while having a low impact on natural resources and generating long-term employment for locals. By creating positive experiences for local people, travelers, and the industry itself, properly managed sustainable tourism can meet the needs of the present without compromising the future.
What Is Sustainability?
At its core, sustainability focuses on balance — maintaining our environmental, social, and economic benefits without using up the resources that future generations will need to thrive. In the past, sustainability ideals tended to lean towards business, though more modern definitions of sustainability highlight finding ways to avoid depleting natural resources in order to keep an ecological balance and maintain the quality of environmental and human societies.
Since tourism impacts and is impacted by a wide range of different activities and industries, all sectors and stakeholders (tourists, governments, host communities, tourism businesses) need to collaborate on sustainable tourism in order for it to be successful.
The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) , which is the United Nations agency responsible for the promotion of sustainable tourism, and the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) , the global standard for sustainable travel and tourism, have similar opinions on what makes tourism sustainable. By their account, sustainable tourism should make the best use of environmental resources while helping to conserve natural heritage and biodiversity, respect the socio-culture of local host communities, and contribute to intercultural understanding. Economically, it should also ensure viable long-term operations that will provide benefits to all stakeholders, whether that includes stable employment to locals, social services, or contributions to poverty alleviation.
The GSTC has developed a series of criteria to create a common language about sustainable travel and tourism. These criteria are used to distinguish sustainable destinations and organizations, but can also help create sustainable policies for businesses and government agencies. Arranged in four pillars, the global baseline standards include sustainable management, socioeconomic impact, cultural impacts, and environmental impacts.
Travel Tip:
The GSTC is an excellent resource for travelers who want to find sustainably managed destinations and accommodations and learn how to become a more sustainable traveler in general.
Environment
Protecting natural environments is the bedrock of sustainable tourism. Data released by the World Tourism Organization estimates that tourism-based CO2 emissions are forecast to increase 25% by 2030. In 2016, tourism transport-related emissions contributed to 5% of all man-made emissions, while transport-related emissions from long-haul international travel were expected to grow 45% by 2030.
The environmental ramifications of tourism don’t end with carbon emissions, either. Unsustainably managed tourism can create waste problems, lead to land loss or soil erosion, increase natural habitat loss, and put pressure on endangered species . More often than not, the resources in these places are already scarce, and sadly, the negative effects can contribute to the destruction of the very environment on which the industry depends.
Industries and destinations that want to be sustainable must do their part to conserve resources, reduce pollution, and conserve biodiversity and important ecosystems. In order to achieve this, proper resource management and management of waste and emissions is important. In Bali, for example, tourism consumes 65% of local water resources, while in Zanzibar, tourists use 15 times as much water per night as local residents.
Another factor to environmentally focused sustainable tourism comes in the form of purchasing: Does the tour operator, hotel, or restaurant favor locally sourced suppliers and products? How do they manage their food waste and dispose of goods? Something as simple as offering paper straws instead of plastic ones can make a huge dent in an organization’s harmful pollutant footprint.
Recently, there has been an uptick in companies that promote carbon offsetting . The idea behind carbon offsetting is to compensate for generated greenhouse gas emissions by canceling out emissions somewhere else. Much like the idea that reducing or reusing should be considered first before recycling , carbon offsetting shouldn’t be the primary goal. Sustainable tourism industries always work towards reducing emissions first and offset what they can’t.
Properly managed sustainable tourism also has the power to provide alternatives to need-based professions and behaviors like poaching . Often, and especially in underdeveloped countries, residents turn to environmentally harmful practices due to poverty and other social issues. At Periyar Tiger Reserve in India, for example, an unregulated increase in tourists made it more difficult to control poaching in the area. In response, an eco development program aimed at providing employment for locals turned 85 former poachers into reserve gamekeepers. Under supervision of the reserve’s management staff, the group of gamekeepers have developed a series of tourism packages and are now protecting land instead of exploiting it. They’ve found that jobs in responsible wildlife tourism are more rewarding and lucrative than illegal work.
Flying nonstop and spending more time in a single destination can help save CO2, since planes use more fuel the more times they take off.
Local Culture and Residents
One of the most important and overlooked aspects of sustainable tourism is contributing to protecting, preserving, and enhancing local sites and traditions. These include areas of historical, archaeological, or cultural significance, but also "intangible heritage," such as ceremonial dance or traditional art techniques.
In cases where a site is being used as a tourist attraction, it is important that the tourism doesn’t impede access to local residents. For example, some tourist organizations create local programs that offer residents the chance to visit tourism sites with cultural value in their own countries. A program called “Children in the Wilderness” run by Wilderness Safaris educates children in rural Africa about the importance of wildlife conservation and valuable leadership development tools. Vacations booked through travel site Responsible Travel contribute to the company’s “Trip for a Trip” program, which organizes day trips for disadvantaged youth who live near popular tourist destinations but have never had the opportunity to visit.
Sustainable tourism bodies work alongside communities to incorporate various local cultural expressions as part of a traveler’s experiences and ensure that they are appropriately represented. They collaborate with locals and seek their input on culturally appropriate interpretation of sites, and train guides to give visitors a valuable (and correct) impression of the site. The key is to inspire travelers to want to protect the area because they understand its significance.
Bhutan, a small landlocked country in South Asia, has enforced a system of all-inclusive tax for international visitors since 1997 ($200 per day in the off season and $250 per day in the high season). This way, the government is able to restrict the tourism market to local entrepreneurs exclusively and restrict tourism to specific regions, ensuring that the country’s most precious natural resources won’t be exploited.
Incorporating volunteer work into your vacation is an amazing way to learn more about the local culture and help contribute to your host community at the same time. You can also book a trip that is focused primarily on volunteer work through a locally run charity or non profit (just be sure that the job isn’t taking employment opportunities away from residents).
It's not difficult to make a business case for sustainable tourism, especially if one looks at a destination as a product. Think of protecting a destination, cultural landmark, or ecosystem as an investment. By keeping the environment healthy and the locals happy, sustainable tourism will maximize the efficiency of business resources. This is especially true in places where locals are more likely to voice their concerns if they feel like the industry is treating visitors better than residents.
Not only does reducing reliance on natural resources help save money in the long run, studies have shown that modern travelers are likely to participate in environmentally friendly tourism. In 2019, Booking.com found that 73% of travelers preferred an eco-sustainable hotel over a traditional one and 72% of travelers believed that people need to make sustainable travel choices for the sake of future generations.
Always be mindful of where your souvenirs are coming from and whether or not the money is going directly towards the local economy. For example, opt for handcrafted souvenirs made by local artisans.
Growth in the travel and tourism sectors alone has outpaced the overall global economy growth for nine years in a row. Prior to the pandemic, travel and tourism accounted for an $9.6 trillion contribution to the global GDP and 333 million jobs (or one in four new jobs around the world).
Sustainable travel dollars help support employees, who in turn pay taxes that contribute to their local economy. If those employees are not paid a fair wage or aren’t treated fairly, the traveler is unknowingly supporting damaging or unsustainable practices that do nothing to contribute to the future of the community. Similarly, if a hotel doesn’t take into account its ecological footprint, it may be building infrastructure on animal nesting grounds or contributing to excessive pollution. The same goes for attractions, since sustainably managed spots (like nature preserves) often put profits towards conservation and research.
Costa Rica was able to turn a severe deforestation crisis in the 1980s into a diversified tourism-based economy by designating 25.56% of land protected as either a national park, wildlife refuge, or reserve.
While traveling, think of how you would want your home country or home town to be treated by visitors.
Are You a Sustainable Traveler?
Sustainable travelers understand that their actions create an ecological and social footprint on the places they visit. Be mindful of the destinations , accommodations, and activities you choose, and choose destinations that are closer to home or extend your length of stay to save resources. Consider switching to more environmentally friendly modes of transportation such as bicycles, trains, or walking while on vacation. Look into supporting locally run tour operations or local family-owned businesses rather than large international chains. Don’t engage in activities that harm wildlife, such as elephant riding or tiger petting , and opt instead for a wildlife sanctuary (or better yet, attend a beach clean up or plan an hour or two of some volunteer work that interests you). Leave natural areas as you found them by taking out what you carry in, not littering, and respecting the local residents and their traditions.
Most of us travel to experience the world. New cultures, new traditions, new sights and smells and tastes are what makes traveling so rewarding. It is our responsibility as travelers to ensure that these destinations are protected not only for the sake of the communities who rely upon them, but for a future generation of travelers.
Sustainable tourism has many different layers, most of which oppose the more traditional forms of mass tourism that are more likely to lead to environmental damage, loss of culture, pollution, negative economic impacts, and overtourism.
Ecotourism highlights responsible travel to natural areas that focus on environmental conservation. A sustainable tourism body supports and contributes to biodiversity conservation by managing its own property responsibly and respecting or enhancing nearby natural protected areas (or areas of high biological value). Most of the time, this looks like a financial compensation to conservation management, but it can also include making sure that tours, attractions, and infrastructure don’t disturb natural ecosystems.
On the same page, wildlife interactions with free roaming wildlife should be non-invasive and managed responsibly to avoid negative impacts to the animals. As a traveler, prioritize visits to accredited rescue and rehabilitation centers that focus on treating, rehoming, or releasing animals back into the wild, such as the Jaguar Rescue Center in Costa Rica.
Soft Tourism
Soft tourism may highlight local experiences, local languages, or encourage longer time spent in individual areas. This is opposed to hard tourism featuring short duration of visits, travel without respecting culture, taking lots of selfies , and generally feeling a sense of superiority as a tourist.
Many World Heritage Sites, for example, pay special attention to protection, preservation, and sustainability by promoting soft tourism. Peru’s famed Machu Picchu was previously known as one of the world’s worst victims of overtourism , or a place of interest that has experienced negative effects (such as traffic or litter) from excessive numbers of tourists. The attraction has taken steps to control damages in recent years, requiring hikers to hire local guides on the Inca Trail, specifying dates and time on visitor tickets to negate overcrowding, and banning all single use plastics from the site.
Traveling during a destination’s shoulder season , the period between the peak and low seasons, typically combines good weather and low prices without the large crowds. This allows better opportunities to immerse yourself in a new place without contributing to overtourism, but also provides the local economy with income during a normally slow season.
Rural Tourism
Rural tourism applies to tourism that takes place in non-urbanized areas such as national parks, forests, nature reserves, and mountain areas. This can mean anything from camping and glamping to hiking and WOOFing. Rural tourism is a great way to practice sustainable tourism, since it usually requires less use of natural resources.
Community Tourism
Community-based tourism involves tourism where local residents invite travelers to visit their own communities. It sometimes includes overnight stays and often takes place in rural or underdeveloped countries. This type of tourism fosters connection and enables tourists to gain an in-depth knowledge of local habitats, wildlife, and traditional cultures — all while providing direct economic benefits to the host communities. Ecuador is a world leader in community tourism, offering unique accommodation options like the Sani Lodge run by the local Kichwa indigenous community, which offers responsible cultural experiences in the Ecuadorian Amazon rainforest.
" Transport-related CO 2 Emissions of the Tourism Sector – Modelling Results ." World Tourism Organization and International Transport Forum , 2019, doi:10.18111/9789284416660
" 45 Arrivals Every Second ." The World Counts.
Becken, Susanne. " Water Equity- Contrasting Tourism Water Use With That of the Local Community ." Water Resources and Industry , vol. 7-8, 2014, pp. 9-22, doi:10.1016/j.wri.2014.09.002
Kutty, Govindan M., and T.K. Raghavan Nair. " Periyar Tiger Reserve: Poachers Turned Gamekeepers ." Food and Agriculture Organization.
" GSTC Destination Criteria ." Global Sustainable Tourism Council.
Rinzin, Chhewang, et al. " Ecotourism as a Mechanism for Sustainable Development: the Case of Bhutan ." Environmental Sciences , vol. 4, no. 2, 2007, pp. 109-125, doi:10.1080/15693430701365420
" Booking.com Reveals Key Findings From Its 2019 Sustainable Travel Report ." Booking.com.
" Economic Impact Reports ." World Travel and Tourism Council .
- Regenerative Travel: What It Is and How It's Outperforming Sustainable Tourism
- How to Be a Sustainable Traveler: 18 Tips
- What Is Ecotourism? Definition, Examples, and Pros and Cons
- Some Advice on How to Travel More Intentionally
- 'The Last Tourist' Film Will Make You Approach Travel Differently
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Sustainable Travel
- Costa Rica’s Keys to Success as a Sustainable Tourism Pioneer
- What Is Community-Based Tourism? Definition and Popular Destinations
- What Is Overtourism and Why Is It Such a Big Problem?
- What Is Experiential Tourism?
- What Is Voluntourism? Does It Help or Harm Communities?
- Food Sovereignty: Definition, Principles, and Importance
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Eco Tech
- 10 Ways to Be an Eco-Conscious Tourist
- Travel + Leisure's Global Vision Awards Are a Win for the Planet
- Spain Starts a School for Shepherdesses
Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....

Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....
Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.

9 Powerful Benefits of Sustainable Tourism and Why You Should Care
August 7, 2022

Let’s talk about the benefits of sustainable tourism. No, not just the part that tries to make you feel guilty and then fob you off with a bamboo toothbrush. But real, powerful, meaningful benefits. Turns out that travel is good for the planet. Let’s go.

Table of Contents
What is the Definition of Sustainable Tourism?
Gah, sustainable tourism. It’s sexy but it sure doesn’t sound like it.
The UNWTO Definition: “Tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities”
Yet it’s more than just green travel or responsible travel or even eco-friendly travel. The emphasis on sustainability refers to lots of different, important considerations. But one of them, is that people should be having fun. Otherwise, we’re missing the point.
With that in mind, let’s talk more about some of the top benefits of sustainable tourism.
The Benefits of Sustainable Tourism
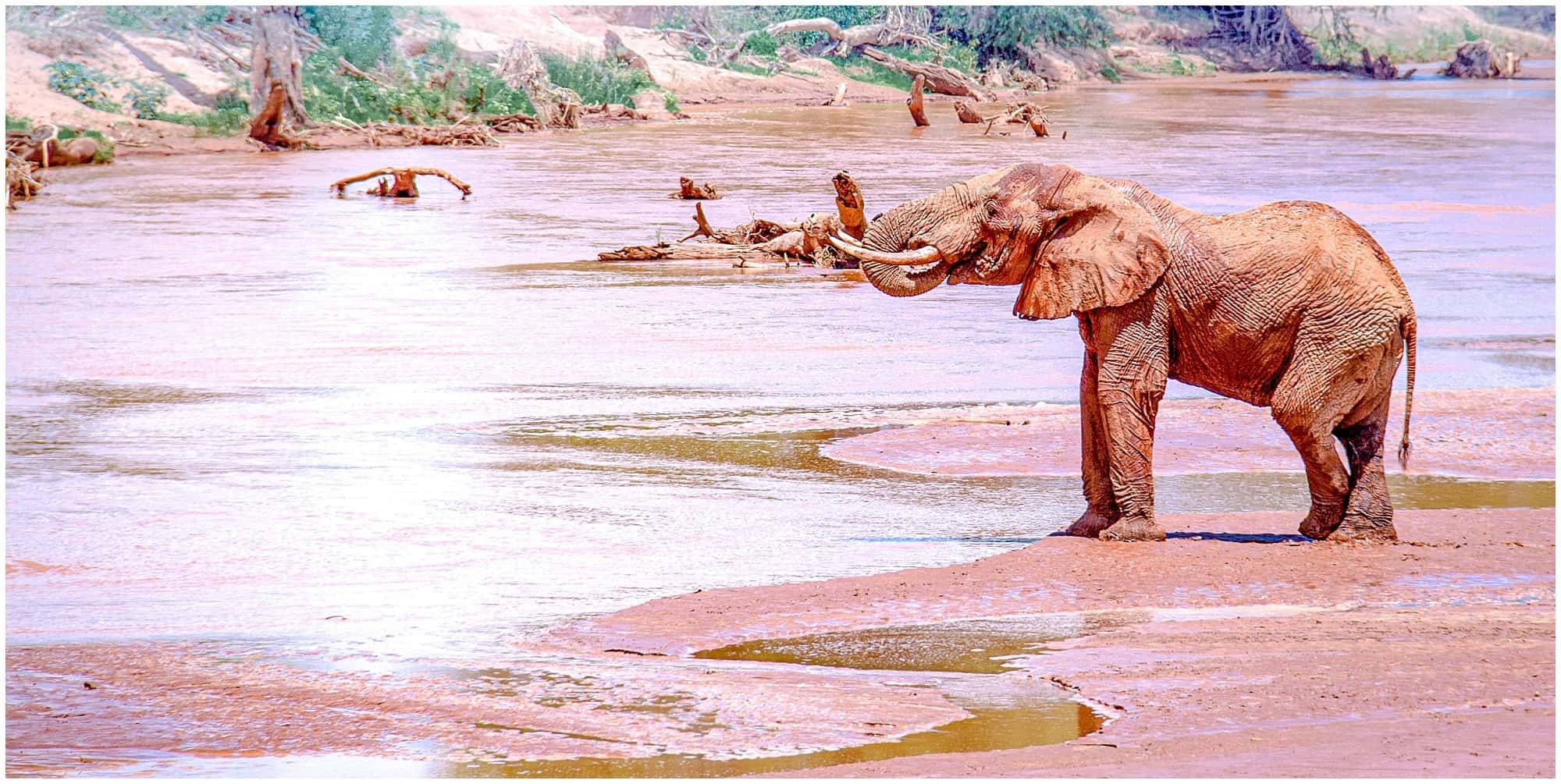

1. Sustainable Tourism Directly Helps Save Endangered Animals
What’s the most powerful way of protecting endangered animals? Making them more valuable alive than dead.
And with sustainably run wildlife encounters, that’s exactly what happens. When communities earn their living by drawing visitors to see and appreciate wildlife in their natural habitats, the pressure to poach diminishes. The benefits of sustainable tourism extend beyond the travel industry as entire regions begin to see preserving local species as economically beneficial, as well as just morally so.

2. Sustainable Tourism Protects Landscapes and Environments
Just as with endangered animals, sustainable tourism creates a massive incentive for communities to protect landscapes as well as the creatures that live within them. While areas can be fenced off by authorities simply for their own protection, one of the benefits of sustainable tourism includes an income for the people who live nearby while also financing the protection of the area in question. And it’s not just “landscapes.” Marine life and aquatic environments can also benefit from the positive impact of sustainable tourism.
Note, this is generally the opposite of overtourism.

3. Sustainable Tourism Reduces Pollution
While sustainable tourism protects against poaching and the active destruction of habitats, as mentioned above, it also helps to reduce pollution.
With extra incentives to keep local areas clean to earn an income from visitors, it is easier to to get group cooperation to reduce pollution on an individual level, and a corporate and government level.

4. Sustainable Tourism Shares Knowledge
While “bad tourism” herds people into resorts where they have no idea where they are or what local traditions look like, sustainable tourism invites visitors and residents to share their experiences, exchange knowledge and have fun.
- Recommended reading: Learning about Jordanian food in Beit Sitti

5. Sustainable Tourism Prevents Cash Crops and Protects Livelihoods
Mass industry and thoughtless mass tourism leads to cash crops and precarious livelihoods. Areas can find themselves supported by only one crop or one corporation and then it only takes one small change in circumstances, like a hurricane or corporate failure, for the entire area to struggle.
Sustainable tourism encourages a diverse approach to accommodation, food, farming and the preservation of tradition in local communities.
With smaller boutique hotels, cooking classes, agroturismo and the tours woven into the tourism industry, communities are left less at the mercy of external events and the disadvantages of cash crop economies.
- Recommended reading: The Cheese Route in Austria and What does agroturismo have to teach in Greece?


6. Sustainable Tourism is Good for Your Health
Whether we’re talking physical health or mental health, one of the benefits of sustainable tourism is wellness.
Clean air, clean water, sustainable farming practices and beautiful natural landscapes are each known to improve health on a population level.
And laughter and meeting new friends helps too. Seriously. It’s all scientifically approved!

7. Sustainable Tourism Protects and Preserves Valued Traditions
Traditional practices bind cultures together. Almost by definition, they are sustainable and have survived for centuries when we all had far less. Yet globalisation threatens many traditional practices.
In the modern world, where is the market for all the artisanal produce and practices? Responsible tourism helps to bring together traders and customers for small, traditional practices, from gin distilleries to hand-woven carpets to any and every kind of local culture and tradition.
For examples, see:
- Uncovering tradition in the highest vineyards in Europe

8. Sustainable Tourism Doesn’t Require Charity
Sometimes, the best of intentions result in the most harm. Several efforts to help alleviate the 1980s famine in east Africa, for example, resulted in harm that lasted for decades.
Sustainable travel seeks a win-win situation.
It demands a formula that works for today and tomorrow.
A method that benefits tourists and local communities, that conserves the environment and which, crucially, is both affordable and makes enough money to keep the whole show on the road.
In the words of a banker turned philanthropist.
“If we become a loss-making organisation, we are no help at all. We must be stable and sustainable. Running a business that depends on yearly grants and fundraising provides no security at all.” Jean-Marc Debricon, founder of the Green Shoots Foundation.
Truly sustainable travel should support the local economy and local people without creating a dependency on fundraising or aid.

9. Sustainable Tourism Feels Good!
Travel is one of the most joyful and rewarding things we can do with our lives on this planet. People on their deathbeds don’t wish for more time in the office or better clothes. They wish for more time with their family and their friends, and to have travelled more.
One of the many benefits of sustainable tourism is also one of the simplest: it just feels good!
In Summary: The Benefits of Sustainable Tourism
- Protects endangered animals
- Protects landscapes and marine reserves under threat
- Reduces pollution and protects natural resources
- Shares knowledge
- Protects livelihoods and brings economic benefits
- Promotes health
- Develops independence
- Feels good!
What Sustainable Tourism Is Not
Sometimes, it’s easier to understand the benefits of sustainable tourism by talking about the opposite. What sustainable tourism is not.
Not Just a “Third World” Problem
Leaving aside for a moment the terminology, sustainable tourism applies to everyone everywhere. The Palace of Versailles outside Paris needs to manage the principles of sustainable tourism just as much as the Amazon rainforest does.
Not Paternalistic
It’s not about “rich white saviours” deciding what’s best for other people and their land. It’s about everyone working together.
Not Just Being Green
Ecotourism or green travel makes protecting the environment the main concern. Sustainable tourism goes further than that. It looks at protecting people, their culture and their future as well as their past. It also focuses on the traveller having a good time in whichever way that feels meaningful to them.
Why? Because…
It needs to make a profit to be economically sustainable.
Here’s the sustainable part. It has to make money. It cannot be a setup that relies on donations, which could stop at any time, or that relies on the traveller feeling good about feeling bad.
Some industries can just about pull that off. But travel cannot because…
“Travel is my one time to relax and take a break, goddammit!”
Not A Chore
Tourism has to be sustainable. Which means that it has to be manageable (and I’d wager pleasurable) to the traveller as well as the host community. That’s something that green travel and ethical travel and ecotourism occasionally lose sight of.
Responsible travel is almost the same thing. But it doesn’t sound much fun, does it?! What happened to taking a break from some of our responsibilities for a short while?!
And finally, we can all be very responsible for a short period of time. But is there a system in place that makes being responsible sustainable? That’s the key question.
In Summary: What Sustainable Tourism Is Not
- For “third world” countries
- About “being green”
- “White saviours” dictating terms
- No fun for the traveller!
FAQs About Sustainable Tourism
Who benefits from sustainable tourism?
Everyone. Both locals and travellers and people who never visit the destination.
What is sustainable tourism?
It’s a model of tourism which benefits both people and places, as well as the environment and is economically sustainable on its own.
Why is sustainable tourism difficult to achieve?
I’m not convinced that it is, with the right mindset. But there is a temptation to cut corners and exploit natural resources for the fastest or cheapest result instead of the most beneficial one.
What are the benefits of responsible tourism?
All of the above!
Sustainable Living: The Key Takeaway…
We can’t wait until we’re perfect to start doing something better.
More on Sustainable Travel
- Start here: how to be a responsible tourist
- Is dark tourism ethical? What you need to know.
- Get inspired by this collection of the best sustainable travel blogs.
- The unmistakable emotional meaning of home
- Why you need to know about the cork trees in Portugal
- The importance of doing nothing
- How to find the most ethical travel destinations
- 15 sustainable beach tips for your next trip to the sea
- Five Ways Travel Can Help the Planet – rethinking Earth Day
- Voluntourism – the questions you should ask by Uncornered Market
5 thoughts on “9 Powerful Benefits of Sustainable Tourism and Why You Should Care”
The positive of sustainable tourism is to ensure that development is a positive experience for local people, tourism companies, and tourists themselves. I don’t know about before reading your article. Thank you so much for sharing such a valuable information.
Many efforts at sustainability focus on the environment, some on the residents. But for true success, we need to consider all three components. Thanks for stopping by!
Sustainable tourism is the key to establishing the balance between development and nature. It is indeed true that it helps protect endangered animals and birds, protects landscapes and promotes a healthy lifestyle. One such example is the Khonoma Village of Nagaland in India. The villagers were once hunters but now is mainly known for their preservation efforts, ecotourism and sustainable tourism
Thanks for the recommendation! Hope to check it out one day.
You’re welcome Abi. Dzulekie is another village near Khonoma known for the same.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Pros and Cons of Tourism
Be it Niagara Falls, The Grand Canyon, or the Amazon Rainforest, these places have numerous reasons to attract tourists every year. Tourists love to visit such spots looking for fun, amusement, and even finding peace of mind. Tourism has turned into a thriving industry in many countries. Governments and local communities reap the benefits of tourism in many different ways. But those advantages come with certain risks as well. However, like everything else, there are pros and cons of tourism . You should be taking a closer look at the good and the bad of tourism before you set a vacation schedule alone or with your friends and families.
What are the Pros of Tourism?
In 2021, tourism to Grand Canyon National Park made a significant contribution of $710 million to the local economy, reports National Park Service.
1. Economic Boost
Tourism is a significant contributor to the economy of a country. By attracting tourists, nations can create sustainable revenue streams, generate job opportunities, and boost growth across several sectors. According to a report by NPS, the park welcomed approximately 4.5 million visitors to the Grand Canyon, spending an estimated $710 million in the surrounding gateway regions.
2. Cultural Exchange
Travel can bring people together and provide a unique opportunity to share ideas and experiences. Travelers often have an open mind about different cultures and customs, so they are eager to explore new places. This type of exchange can break down cultural barriers between countries by allowing each party to understand the other's culture better. This exchange of cultural values can be counted as one of the major advantages of tourism.
3. Environmental Conservation
All natural heritages are tourist spots, and people come to admire the view. One of the significant advantages of tourism is that it can help protect and preserve the environment. Local governments can invest the revenue generated by tourism for the betterment of environmentally sensitive regions and areas with fragile ecosystems.
4. Improved Infrastructure is Among the Pros of Tourism
With the influx of tourists, countries can consider upgrading their infrastructure to accommodate visitors' needs. This includes constructing new airports, roads, accommodations, and public facilities such as parks and museums. This positive change can be felt both by the tourists and the inhabitants.
5. Global Recognition
Tourism is an essential part of many countries economies, and it can also provide significant global recognition for the destination. A well-designed tourism strategy that attracts a high volume of international visitors can bring in foreign money, create jobs, and help to develop infrastructure. It also raises awareness about an area, leading to increased interest from the rest of the world.
What are the Cons of Tourism?
Besides the positive changes, tourism also has its share of downsides. Most of the cons of the tourism industry are associated with the misuse of natural resources. Some of the other problems with tourism include:
1. Environmental Damage
Tourism can lead to environmental damage in many ways. For example, it can impact water resources through increased water and wastewater production demand. It can also add to pollution by generating emissions from transportation as visitors travel around the area. Additionally, tourists may increase pressure on local land resources, leading to deforestation and loss of habitats for native species.
2. Displaced Communities
Tourism often brings economic benefits to local communities. Still, when done in a way that does not consider the local community's needs and aspirations, it can cause displacement. Communities may be displaced from their traditional lands or homes, pushing them away from the resources they need for subsistence. This can be particularly detrimental if these resources are already scarce or difficult to access.
3. Cultural Erosion
Cultural Erosion is one of the most dreaded cons of tourism. A tourist destination with a distinct local culture is prone to changes due to the influx of tourists. The more tourism activities are higher the chances of community displacement.
This phenomenon is often compounded by the fact that many tourists come from cultures very different to those of the local community, and their presence can lead to a sudden change in cultural values. This rapid transition can significantly damage a community as its members may no longer feel represented or respected.
4. Economic Dependence
The COVID-19 pandemic best explains how tourism can suddenly burden an economy. As the pandemic wiped out all income for many countries' businesses, many had to rely heavily on government support and bailouts as their primary sources of revenue. This has resulted in rising debts due to emergency aid distributions and other fiscal measures associated with relief during this crisis.
5. Overcrowding
Visiting a particular area can harm the environment and local culture as tourism grows. One of the main disadvantages of tourism is overcrowding, which can strain resources, increase pollution, and damage natural habitats.
Overcrowding can decrease the quality of life for residents, as tourists take up public space and resources. It can also affect the health and safety of visitors who may be exposed to increased levels of crime or air pollution.
Conclusion on the Pros and Cons of Tourism
The pros and cons of tourism are complex if you evaluate them thoroughly. It is easy to see that people benefit from increased access to new cultures, experiences, and destinations.
On the other hand, there are real risks associated with tourist activities like over-tourism and the destruction of natural spaces. Therefore, it's up to individuals to assess these impacts on their own terms. It's up to every citizen to become responsible travelers who understand tourism's positive and negative effects.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the cons of tourism.
Tourism frequently exerts excessive strain on natural resources due to overconsumption, particularly in areas with limited resources. It places immense pressure on local land utilization, resulting in soil erosion, heightened pollution levels, loss of natural habitats, and increased jeopardy for endangered species.
What are the pros of tourism?
It fosters job creation, bolsters the local economy, facilitates infrastructure development, preserves the natural environment and cultural heritage, and works towards alleviating poverty and inequality.
What are the social benefits of tourism?
Tourism brings forth numerous social benefits, showcasing its positive impacts on society. These encompass the preservation of local culture and heritage, the fostering of vibrant communities, the provision of essential social services, the promotion of cultural and artistic commerce, the revitalization of customs and art forms, as well as the safeguarding of our precious heritage.
Who does tourism help?
Tourists contribute to the local economy by spending their money, leading to job creation and economic growth. This support is particularly crucial for small businesses, which often struggle to generate substantial profits.
What's your reaction?
Quick links.
- » Home
- » About us
- » Contact us
- » Post Article
- » Privacy policy
- » Terms and Conditions
- » Health and Wellness
- » Education and Communication
- » Computers and Electronics
- » Personal Care and Style
- » Travel Updates and Tourism Guide
- » Finance and Business Sector
- » Food and Entertainment
- » Home and Garden
- » Automobiles Sector

Encyclopedia of Tourism pp 1–2 Cite as
Comparative Advantage in Tourism
- Jie Zhang 3 &
- Camilla Jensen 4
- Living reference work entry
- Latest version View entry history
- First Online: 08 October 2022
16 Accesses
The principle of comparative advantage was introduced by David Ricardo in response to Adam Smith’s principle of absolute advantage. Comparative advantage in an activity (such as tourism) is defined as the ability to produce or service at a lower relative opportunity cost.
Comparative advantage in tourism describes a nation or a destination that can win competitiveness from its factor endowment, for example, sun, sea, sand, and natural scenery. These nations or destinations are not necessarily the best in the world at anything, but this does not prevent them from producing and engaging in tourism trade, hence the principle of comparative advantage.
Some scholars use competitiveness and comparative advantage interchangeably. For example, where comparative advantages “constitute the resources available to a destination, competitive advantages relate to a destination’s ability to use these resources effectively in the long-term” (Crouch and Ritchie 1999 : 143). In other words, comparative...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Crouch, G., and J. Ritchie. 1999. Tourism, competitiveness, and social prosperity. Journal of Business Research 44 (3): 137–152.
Article Google Scholar
———. 2012. Tourism and competitiveness . London: Edward Elgar.
Book Google Scholar
Fuchs, M., W. Höpken, and M. Lexhagen. 2014. Big data analytical for knowledge generation in tourism destinations – A case from Sweden. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management 3: 198–209.
Jensen, C., and J. Zhang. 2013. Trade in tourism services: Explaining tourism trade and the impact of the general agreement on trade in service on the gains from trade. The Journal of International Trade and Economic Development 22: 398–429.
Xie, S. 2019. Why comparative advantage is a problematic guide to practical policy. Economic Affairs 39 (2): 243–250.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Regional Tourism Research, Nexø, Denmark
Social Sciences and Business, Roskilde University, Roskilde, Denmark
Camilla Jensen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jie Zhang .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Hospitality Leadership, University of Wisconsin-Stout, Menomonie, WI, USA
Jafar Jafari
School of Hotel and Tourism Management, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Honggen Xiao
Section Editor information
Department of Marketing, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand
Juergen Gnoth
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Zhang, J., Jensen, C. (2022). Comparative Advantage in Tourism. In: Jafari, J., Xiao, H. (eds) Encyclopedia of Tourism. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_599-2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_599-2
Received : 25 May 2021
Accepted : 07 July 2022
Published : 08 October 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-01669-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-01669-6
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Business and Management Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
Chapter history
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_599-2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01669-6_599-1
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Travel, Tourism & Hospitality ›
- Leisure Travel
Impact of technology on travel and tourism - statistics & facts
What are the main technology trends in travel and tourism, travel apps: two countries dominate the market, key insights.
Detailed statistics
Revenue of Amadeus 2010-2022
Amadeus: number of bookings 2010-2022
Revenue of Sabre Corp. worldwide 2012-2023
Company Insights High-Growth Companies Asia-Pacific
- Great Deals E-Commerce Corporation
- Spofeed Co., Ltd.
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Current statistics on this topic.
Online Travel Market
Most downloaded travel apps worldwide 2022, by aggregated downloads
IT Services
Tour Operators & Travel Agencies
Travel agencies and tour operators using cloud computing services EU 2016-2021
Related topics
- Online travel market
- Digitalization of the travel industry
- Digitalization of the hospitality industry worldwide
Online travel trends
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) use in travel and tourism
- Travel and tourism in the metaverse
- Mobile travel trends
Online travel companies
- Booking Holdings Inc.
- Expedia Group, Inc.
- Trip.com Group
- Tripadvisor
Recommended statistics
Global distribution systems (gdss).
- Basic Statistic Revenue of Amadeus 2010-2022
- Basic Statistic Revenue of Amadeus 2010-2022, by segment
- Basic Statistic Amadeus: number of bookings 2010-2022
- Basic Statistic Revenue of Sabre Corp. worldwide 2012-2023
- Basic Statistic Revenue of Sabre Corp. worldwide 2019-2023, by segment
- Premium Statistic Revenue of Travelport worldwide 2010-2022
- Basic Statistic Revenue of Travelport 2013-2018, by segment
Revenue of Amadeus worldwide from 2010 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Revenue of Amadeus 2010-2022, by segment
Revenue of Amadeus worldwide in 2022, by business segment (in million euros)
Number of travel bookings made using the Amadeus distribution platform from 2010 to 2022 (in millions)
Revenue of Sabre Corp. worldwide from 2012 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Revenue of Sabre Corp. worldwide 2019-2023, by segment
Revenue of Sabre Corp. worldwide from 2019 to 2023, by business segment (in billion U.S. dollars)
Revenue of Travelport worldwide 2010-2022
Revenue of Travelport Worldwide Limited worldwide from 2010 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Revenue of Travelport 2013-2018, by segment
Revenue of Travelport worldwide from 2013 to 2018, by business segment (in million U.S. dollars)
Travel apps
- Premium Statistic Revenue of the travel apps industry worldwide 2017-2027
- Premium Statistic Travel apps revenue in selected countries worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Most downloaded travel apps worldwide 2022, by aggregated downloads
- Premium Statistic Most downloaded online travel agency apps worldwide 2022, by aggregated downloads
- Premium Statistic Average number of reviews of travel and tourism apps worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Average number of ratings of travel and tourism apps worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Average retention rate of travel and tourism apps worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Leading travel apps in the U.S. 2022, by market share
- Premium Statistic Leading travel apps in Europe 2022, by market share
Revenue of the travel apps industry worldwide 2017-2027
Revenue of the travel apps market worldwide from 2017 to 2027 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Travel apps revenue in selected countries worldwide 2022
Revenue of travel apps in selected countries worldwide in 2022 (in million U.S. dollars)
Most downloaded travel apps worldwide in 2022, by aggregated number of downloads (in millions)
Most downloaded online travel agency apps worldwide 2022, by aggregated downloads
Most downloaded online travel agency apps worldwide in 2022, by aggregated number of downloads (in millions)
Average number of reviews of travel and tourism apps worldwide 2022
Average number of reviews of travel, tourism, and hospitality apps worldwide in 2022
Average number of ratings of travel and tourism apps worldwide 2022
Average number of ratings of travel, tourism, and hospitality apps worldwide in 2022
Average retention rate of travel and tourism apps worldwide 2022
Average retention rate of travel, tourism, and hospitality apps worldwide in 2022
Leading travel apps in the U.S. 2022, by market share
Market share of leading travel apps in the United States in 2022
Leading travel apps in Europe 2022, by market share
Market share of leading travel apps in Europe in 2022
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Premium Statistic Number of companies using ChatGPT within their business 2023, by industry
- Premium Statistic Share of travel firms that implemented AI strategies worldwide 2021, by AI maturity
- Premium Statistic AI-influenced revenue share of travel companies worldwide 2018-2024
- Premium Statistic Travelers expecting to use AI to plan trips in 2033 worldwide 2022, by aspect
- Premium Statistic Expected usage of ChatGPT to plan next trip in the U.S. 2023
- Premium Statistic U.S. adults that thought a Chat-GPT text on travel was AI/human-made 2023
- Basic Statistic Interest in AI-related products among U.S. adults 2023
Number of companies using ChatGPT within their business 2023, by industry
Amount of companies using ChatGPT in their business function in 2023, by industry
Share of travel firms that implemented AI strategies worldwide 2021, by AI maturity
Share of travel companies that implemented Artificial Intelligence (AI) strategies worldwide as of September 2021, by maturity of AI strategies
AI-influenced revenue share of travel companies worldwide 2018-2024
Share of travel companies' revenue that was influenced by Artificial Intelligence (AI) worldwide in 2018 and 2021, with a forecast for 2024
Travelers expecting to use AI to plan trips in 2033 worldwide 2022, by aspect
Share of travelers that would trust using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to plan travel in 2033 worldwide as of August 2022, by travel aspect
Expected usage of ChatGPT to plan next trip in the U.S. 2023
Likelihood of using ChatGPT in the process of planning the next trip among respondents in the United States as of April 2023
U.S. adults that thought a Chat-GPT text on travel was AI/human-made 2023
Share of adults that believed a ChatGPT-generated text about travel was made by an Artificial Intelligence (AI) or a human in the United States as of March 2023
Interest in AI-related products among U.S. adults 2023
Share of adults in the United States who are interested in artificial intelligence (AI) related products as of February 2023
Metaverse and extended reality (XR)
- Basic Statistic Leading business sectors already investing in the metaverse 2022
- Premium Statistic U.S teens and adults on enhanced experiences in the metaverse 2022
- Premium Statistic Interest in metaverse travel activities of Gen Z in the U.S. and the UK 2022
- Premium Statistic Interest in AR in the U.S. 2022, by use case
- Premium Statistic Interest in VR in the U.S. 2022, by use case
Leading business sectors already investing in the metaverse 2022
Leading business sectors worldwide that have already invested in the metaverse as of March 2022
U.S teens and adults on enhanced experiences in the metaverse 2022
Experiences expected to be better in a virtual or metaverse environment according to teens and adults in the United States as of May 2022
Interest in metaverse travel activities of Gen Z in the U.S. and the UK 2022
Interest in metaverse travel activities of Gen Z in the United States and the United Kingdom (UK) as of February 2022
Interest in AR in the U.S. 2022, by use case
Interest in augmented reality (AR) in the United States as of October 2022, by use case
Interest in VR in the U.S. 2022, by use case
Interest in virtual reality (VR) in the United States as of October 2022, by use case
Use of technology
- Premium Statistic Travelers' expected use of selected planning tools for trips in 2033 worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Expected comfort level with selected payment methods for trips in 2033 worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Global consumer and merchant acceptance of crypto payments 2021, by industry
- Basic Statistic Popular goods and services to buy with crypto 2022, by gender and income group
- Premium Statistic Travel agencies and tour operators using cloud computing services EU 2016-2021
Travelers' expected use of selected planning tools for trips in 2033 worldwide 2022
Share of travelers expecting to use selected planning tools for trips in 2033 worldwide as of August 2022
Expected comfort level with selected payment methods for trips in 2033 worldwide 2022
Share of travelers expecting to be comfortable in using selected payment methods for trips in 2033 worldwide as of August 2022
Global consumer and merchant acceptance of crypto payments 2021, by industry
Willingness to use/accept cryptocurrencies for payments by consumers/merchants across various industries worldwide as of 2021
Popular goods and services to buy with crypto 2022, by gender and income group
Most popular goods and services bought by consumers worldwide when using cryptocurrencies for online shopping in 2022, by gender and income group
Use of cloud computing services among travel agencies, tour operators, and related activities in the European Union (EU 27) from 2016 to 2021, by cloud service
Further reports Get the best reports to understand your industry
Get the best reports to understand your industry.
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)

13 Social impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Understanding the social impacts of tourism is vital to ensuring the sustainable management of the tourism industry. There are positive social impacts of tourism, demonstrating benefits to both the local community and the tourists. There are also negative social impacts of tourism.
In this article I will explain what the most common social impacts of tourism are and how these are best managed. At the end of the post I have also included a handy reading list for anybody studying travel and tourism or for those who are interested in learning more about travel and tourism management.
The social impacts of tourism
Preserving local culture, strengthening communities, provision of social services, commercialisation of culture and art, revitalisation of culture and art, preservation of heritage, social change, globalisation and the destruction of preservation and heritage, loss of authenticity , standardisation and commercialisation, culture clashes, tourist-host relationships, increase in crime, gambling and moral behaviour, social impacts of tourism: conclusion, social impacts of tourism- further reading.
Firstly, we need to understand what is meant by the term ‘social impacts of tourism’. I have covered this in my YouTube video below!
To put it simply, social impacts of tourism are;
“The effects on host communities of direct and indirect relations with tourists , and of interaction with the tourism industry”
This is also often referred to as socio-cultural impacts.
Tourism is, at its core, an interactive service. This means that host-guest interaction is inevitable. This can have significant social/socio-cultural impacts.
These social impacts can be seen as benefits or costs (good or bad). I will explain these below.

Positive social impacts of tourism
There are many social benefits of tourism, demonstrating positive social impacts. These might include; preserving the local culture and heritage; strengthening communities; provision of social services; commercialisation of culture and art; revitalisation of customs and art forms and the preservation of heritage.

It is the local culture that the tourists are often coming to visit.
Tourists visit Beijing to learn more about the Chinese Dynasties. Tourists visit Thailand to taste authentic Thai food. Tourists travel to Brazil to go to the Rio Carnival, to mention a few…
Many destinations will make a conserved effort to preserve and protect the local culture. This often contributes to the conservation and sustainable management of natural resources, the protection of local heritage, and a renaissance of indigenous cultures, cultural arts and crafts.
In one way, this is great! Cultures are preserved and protected and globalisation is limited. BUT, I can’t help but wonder if this is always natural? We don’t walk around in Victorian corsets or smoke pipes anymore…
Our social settings have changed immensely over the years. And this is a normal part of evolution! So is it right that we should try to preserve the culture of an area for the purposes of tourism? Or should we let them grow and change, just as we do? Something to ponder on I guess…
Tourism can be a catalyst for strengthening a local community.
Events and festivals of which local residents have been the primary participants and spectators are often rejuvenated and developed in response to tourist interest. I certainly felt this was the way when I went to the Running of the Bulls festival in Pamplona, Spain. The community atmosphere and vibe were just fantastic!

The jobs created by tourism can also be a great boost for the local community. Aside from the economic impacts created by enhanced employment prospects, people with jobs are happier and more social than those without a disposable income.
Local people can also increase their influence on tourism development, as well as improve their job and earnings prospects, through tourism-related professional training and development of business and organisational skills.
Read also: Economic leakage in tourism explained

The tourism industry requires many facilities/ infrastructure to meet the needs of the tourist. This often means that many developments in an area as a result of tourism will be available for use by the locals also.
Local people often gained new roads, new sewage systems, new playgrounds, bus services etc as a result of tourism. This can provide a great boost to their quality of life and is a great example of a positive social impact of tourism.
Tourism can see rise to many commercial business, which can be a positive social impact of tourism. This helps to enhance the community spirit as people tend to have more disposable income as a result.
These businesses may also promote the local cultures and arts. Museums, shows and galleries are fantastic way to showcase the local customs and traditions of a destination. This can help to promote/ preserve local traditions.

Some destinations will encourage local cultures and arts to be revitalised. This may be in the form of museum exhibitions, in the way that restaurants and shops are decorated and in the entertainment on offer, for example.
This may help promote traditions that may have become distant.
Many tourists will visit the destination especially to see its local heritage. It is for this reason that many destinations will make every effort to preserve its heritage.
This could include putting restrictions in place or limiting tourist numbers, if necessary. This is often an example of careful tourism planning and sustainable tourism management.
This text by Hyung You Park explains the principles of heritage tourism in more detail.
Negative social impacts of tourism
Unfortunately, there are a large number of socio-cultural costs on the host communities. These negative social impacts include; social change; changing values; increased crime and gambling; changes in moral behaviour; changes in family structure and roles; problems with the tourist-host relationship and the destruction of heritage.

Social change is basically referring to changes in the way that society acts or behaves. Unfortunately, there are many changes that come about as a result of tourism that are not desirable.
There are many examples throughout the world where local populations have changed because of tourism.
Perhaps they have changed the way that they speak or the way that they dress. Perhaps they have been introduced to alcohol through the tourism industry or they have become resentful of rich tourists and turned to crime. These are just a few examples of the negative social impacts of tourism.
Read also: Business tourism explained: What, why and where

Globalisation is the way in which the world is becoming increasingly connected. We are losing our individuality and gaining a sense of ‘global being’, whereby we are more and more alike than ever before.
Globalisation is inevitable in the tourism industry because of the interaction between tourists and hosts, which typically come from different geographic and cultural backgrounds. It is this interaction that encourage us to become more alike.
Here are some examples:
- When I went on the Jungle Book tour on my travels through Goa, the tourists were giving the Goan children who lived in the area sweets. These children would never have eaten such sweets should they not have come into contact with the tourists.
- When I travelled to The Gambia I met a local worker (known as a ‘ bumster ‘) who was wearing a Manchester United football top. When I asked him about it he told me that he was given the top by a tourist who visited last year. If it was not for said tourist, he would not have this top.
- In Thailand , many workers have exchanged their traditional work of plowing the fields to work in the cities, in the tourism industry. They have learnt to speak English and to eat Western food. If it were not for the tourists they would have a different line of work, they would not speak English and they would not choose to eat burger and chips for their dinner!
Many people believe globalisation to be a bad thing. BUT, there are also some positives. Think about this…
Do you want an ‘authentic’ squat toilet in your hotel bathroom or would you rather use a Western toilet? Are you happy to eat rice and curry for breakfast as the locals would do or do you want your cornflakes? Do you want to struggle to get by when you don’t speak the local language or are you pleased to find somebody who speaks English?
When we travel, most tourists do want a sense of ‘familiar’. And globalisation helps us to get that!
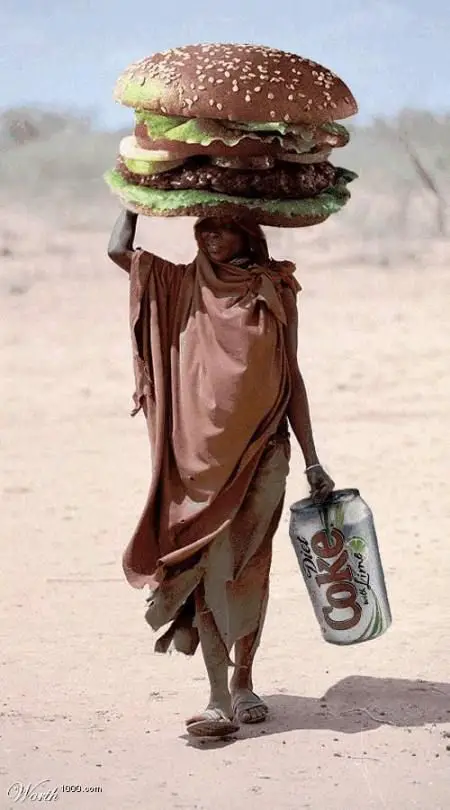

You can learn more about globalisation in this post- What is globalisation? A simple explanation .

Along similar lines to globalisation is the loss of authenticity that often results from tourism.
Authenticity is essentially something that is original or unchanged. It is not fake or reproduced in any way.
The Western world believe that a tourist destination is no longer authentic when their cultural values and traditions change. But I would argue is this not natural? Is culture suppose to stay the same or it suppose to evolve throughout each generation?
Take a look at the likes of the long neck tribe in Thailand or the Maasai Tribe in Africa. These are two examples of cultures which have remained ‘unchanged’ for the sole purpose of tourism. They appear not to have changed the way that they dress, they way that they speak or the way that they act in generations, all for the purpose of tourism.
To me, however, this begs the question- is it actually authentic? In fact, is this not the exact example of what is not authentic? The rest of the world have modern electricity and iPhones, they watch TV and buy their clothes in the nearest shopping mall. But because tourists want an ‘authentic’ experience, these people have not moved on with the rest of the world, but instead have remained the same.
I think there is also an ethical discussion to be had here, but I’ll leave that for another day…
You can learn more about what is authenticity in tourism here or see some examples of staged authenticity in this post.
Read also: Environmental impacts of tourism
Similarly, destinations risk standardisation in the process of satisfying tourists’ desires for familiar facilities and experiences.
While landscape, accommodation, food and drinks, etc., must meet the tourists’ desire for the new and unfamiliar, they must at the same time not be too new or strange because few tourists are actually looking for completely new things (think again about the toilet example I have previously).
Tourists often look for recognisable facilities in an unfamiliar environment, like well-known fast-food restaurants and hotel chains. Tourist like some things to be standardised (the toilet, their breakfast, their drinks, the language spoken etc), but others to be different (dinner options, music, weather, tourist attractions etc).
Do we want everything to become ‘standardised’ though? I know I miss seeing the little independent shops that used to fill the high streets in the UK. Now it’s all chains and multinational corporations. Sure, I like Starbucks (my mug collection is coming on quite nicely!), but I also love the way that there are no Starbucks in Italy. There’s something great about trying out a traditional, yet unfamiliar coffee shop, or any independant place for that matter.
I personally think that tourism industry stakeholders should proceed with caution when it comes to ‘standardisation’. Sure, give the tourists that sense of familiar that they are looking for. But don’t dilute the culture and traditions of the destination that they are coming to visit, because if it feels too much like home….. well, maybe they will just stay at home next time? Just a little something to think about…

On a less philosophical note, another of the negative social impacts of tourism is that it can have significant consequences is culture clashes.
Because tourism involves movement of people to different geographical locations cultural clashes can take place as a result of differences in cultures, ethnic and religious groups, values, lifestyles, languages and levels of prosperity.
The attitude of local residents towards tourism development may unfold through the stages of euphoria, where visitors are very welcome, through apathy, irritation and potentially antagonism when anti-tourist attitudes begin to grow among local people. This is represented in Doxey’s Irritation Index, as shown below.
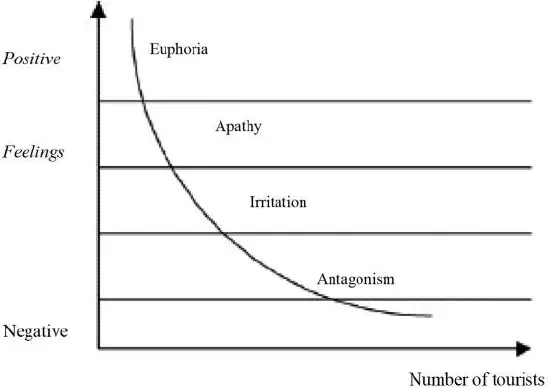
Culture clashes can also be exasperated by the fundamental differences in culture between the hosts and the tourists.
There is likely to be economic inequality between locals and tourists who are spending more than they usually do at home. This can cause resentment from the hosts towards the tourists, particularly when they see them wearing expensive jewellery or using plush cameras etc that they know they can’t afford themselves.
Further to this, tourists often, out of ignorance or carelessness, fail to respect local customs and moral values.
Think about it. Is it right to go topless on a beach if within the local culture it is unacceptable to show even your shoulders?
There are many examples of ways that tourists offend the local population , often unintentionally. Did you know that you should never put your back to a Buddha? Or show the sole of your feet to a Thai person? Or show romantic affection in public in the Middle East?
A little education in this respect could go a long way, but unfortunately, many travellers are completely unaware of the negative social impacts that their actions may have.
The last of the social impacts of tourism that I will discuss is crime, gambling and moral behaviour. Crime rates typically increase with the growth and urbanisation of an area and the growth of mass tourism is often accompanied by increased crime.
The presence of a large number of tourists with a lot of money to spend and often carrying valuables such as cameras and jewellery increases the attraction for criminals and brings with it activities like robbery and drug dealing.
Although tourism is not the cause of sexual exploitation, it provides easy access to it e.g. prostitution and sex tourism . Therefore, tourism can contribute to rises in the numbers of sex workers in a given area. I have seen this myself in many places including The Gambia and Thailand .
Lastly, gambling is a common occurrence as a result of tourism. Growth of casinos and other gambling facilities can encourage not only the tourists to part with their cash, but also the local population .
As I have demonstrated in this post, there are many social impacts of tourism. Whilst some impacts are positive, most unfortunately are negative impacts.
Hopefully this post on the social impacts of tourism has helped you to think carefully about the impacts that your actions may have on the local community that you are visiting. I also hope that it has encouraged some deeper thinking with regards to issues such as globalisation, authenticity and standardisation.
If you are interested in learning more about topics such as this subscribe to my newsletter ! I send out travel tips, discount coupons and some material designed to get you thinking about the wider impacts of the tourism industry (like this post)- perfect for any tourism student or keen traveller!
As you can see, the social impacts of tourism are an important consideration for all industry stakeholders. Do you have any comments on the social impacts of tourism? Leave your comments below.
If you enjoyed this article on the social impacts of tourism, I am sure that you will love these too-
- Environmental impacts of tourism
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
Liked this article? Click to share!
Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Tourism Industry
Introduction, background information, technology in the industry, benefits of technology in the tourism industry, negative impact of technology in tourism industry.
Examining all the possible advantages and disadvantages of technology in the tourism industry has become a topic of interest for numerous people in the field. It’s not a secret that the Internet and different information systems have transformed the hospitality sphere.
Were these changes welcomed and embraced? What is the negative impact of technology on the tourism industry? Does it exist at all?
Technology is paramount to the success of the industry. Yet, as it turns out, the Internet and other digital perks of the modern world have both benefits and flaws. In this essay, the advantages and disadvantages of technology in the hospitality industry are explored.
The hospitality and tourism industry is one of the best-performing industries, both at regional/domestic and international levels. According to the Tourism World Council (2004), the tourism industry contributes to around 10% of GDP in the world.
This rate is expected to increase by the year 2014 (World Travel and Tourism Council 2004). The force behind this rapid growth is the adoption of information technology in its management and operations.
Many businesses in hospitality and tourism incorporate information technology in their businesses, thus standing a good chance of reaping huge returns of the same (Garzotto et al. 2004).
Computerized reservation systems are an example of an information technology system used in this sector to reach the target customers.
Before the advancement of technology, it was very difficult for the tourist and hospitality industry to market its services to its customers. It was also very expensive because customers are always physically apart, miles away, for instance.
However, the coming of information technology has eased the transaction of business besides boosting the customer base. The fact that people are able to communicate and interact with one another in different regions has made it easier and cheap to market their products and services.
In the past, inter-organizational system, which connected organizations, was the most popular form of IT. However, because of high costs, many businesses could not meet the cost of using it (Chih-Yao 2011, p. 1986).
The emergence of global distribution systems allowed easy connection and communication across borders. This allowed a fast transfer of information that helped to boost the industry in terms of the number of bookings.
Global distribution was a form of inter-organizational system that emerged from computer reservation systems that helped to integrate information from the airline. These integrations boosted the tourism industry since customers were able to make their reservations at one common marketplace.
These systems were used in the 1960s, and their integration into the modern computer was impossible. The advancement of technology has seen the emergence of the Internet and the World Wide Web, which have transformed the way people interact and or do their businesses (Cristiana 2008, p. 345).
Businesses market their hospitality services and tourism products through the Internet. This platform has connected the world. It has turned it into a global village. People can interact in different locations in real-time.
They can share their views and opinions without having to meet physically. Technology has led to the development of different forms or platforms that enable interconnections.
Nowadays, social media such as MySpace, Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and many others are sources of information that both the tourism and hospitality industry have used to reach customers across the globe leading to an influx of tourists hence boosting the level of their income (Alexis, & Buhalis 2007, p. 389).
Clayton and Criscuolo (2002) argue that technology through the Internet has brought about various changes in how people carry out their businesses.
The changes include providing an avenue through which ideas can be transformed into marketable innovation to be transmitted later to a wider market at low costs of accessing these markets and searching for buyers.
It allows easier access to the market offering new products. It has changed the way information is shared between individuals and organizations (p. 14). The benefits of technology in the hospitality and tourism industry are enormous.
The benefits of IT are manifested almost in every aspect of our lives. The Internet has become an important part of people’s lives. People are able to share information in their remote locations through personal computers, fax machines, cell phones, emails, and the Internet in real-time (Cristiana 2008, p. 346).
The capability that has come with technology has been manifested in major sectors of economies. The hospitality and tourism sector is one of the sectors that require adequate marketing across the globe.
With the Internet in place, this has been achieved with ease and at low costs. The business has hosted different sites that they use to advertise their products and services to the entire world. They are able to tailor the needs of the customers accordingly.
Another advantage of technology is that it has facilitated globalization. The world has been constricted into one small village. People are connected through Internet networks and social media. Information is transmitted at a faster rate with just one click of a mouse.
The hospitality industry and tourism have used this opportunity to share ideas on various businesses. It has also helped to bring together people separated by geographical location and those from different cultures.
Since this industry depends on information, this technology has added a boost because people are able to access information about the locations that they can visit and spend their leisure time and holidays relaxing.
According to Cristiana (2008), many people in the USA use the Internet to book their trips to various destinations (p. 344). The rate is increasing every day. For instance, it is estimated that more than 75 million people who travel across the globe use the Internet to get information on their destinations.
They, therefore, use the Internet to book, check and compare prices, and schedule their traveling to various tourist destinations. Many people who travel across their borders spend their time and or are accommodated by the hospitality industry. Therefore, they contribute a lot to the industry.
Some travel for leisure. They, therefore, pay the host country foreign exchange for them to be hosted or to travel across the country visiting any area of attraction like game reserves and game parks. The number of bookings increased to double digits between 1996 and 2006.
The growth was high in 2001 at 58% and 25% in 2002 (Cristiana 2008, p. 344). Many online travelers say that they use the Internet to get updates or information on their destinations and any other logistics about their traveling (Cristiana 2008, p. 344).
Therefore, they transact their businesses through the Internet. For instance, they book the places of visit upon landing at their destination in advance. This shows how technology has transformed the industry.
In the past, it was very difficult and costly to travel because of the numerous tedious paperwork processes that people went through. When they reach their destinations, they do not have to look for accommodation.
Therefore, technology has taken this a notch higher, as everything is done in the comfort of the houses (Dis 2010, p. 9).
A study carried out on online travelers showed that the majority of people traveling did so for pleasure, vacation/holiday, personal purposes, and business (Cristiana 2008, p. 347).
Technology has enabled people to search for their directions, maps for directions, accommodation/hospitality facilities, schedules, airfare, and the amount of money to be spent for a tour. These logistics are available on the Internet. It has become an essential medium of budgeting and choice-making.
This is with regard to the places or locations that a person wants to visit. The availability of this information on the Internet, for example, tourist attractions sites, tourist attraction scenes, and features, create a platform for persuading people to travel and experience them.
Therefore, the Internet has contributed to the increased booking and tourist visits, explaining the increase in the industry’s gross domestic product (Cristiana 2008, p. 344).
Technology has evolved at a faster rate making it even possible to access the Internet through cell phones. People across the globe are able to access information on their phones, even to the extent of communicating with one another. This platform has enabled the hospitability industry and tourist industry to market their products on the Internet.
People traveling for leisure or any other reason are always in touch with their family members and friends. This has contributed to the increased travel across borders by many people (Cristiana 2008, p. 348).
According to Jungsun and Hardin (2010), social media, Facebook and MySpace host many users (p. 735). It is estimated that around 360 million people visited and used the media in 2007 for their interaction and other purposes (Jungsun & Hardin 2010, p. 735).
The media is used for sharing ideas and keeping in touch with people across the country. Therefore, they provide a good platform for businesses to market their products and services. The hospitality and tourism industry has the potential to use such media to reach out to many potential visitors.
People will get information about tourist destinations and some of the hospitality services provided through such media. Therefore, they can contribute greatly to the success of the hospitality and tourism industry. However, technology has had a negative impact on this industry.
Technology has some challenges. According to Jungsun and Hardin (2010), the virtual world presents challenges of maintenance and follow-up (p. 735). It requires a lot of investment in Internet use in terms of updating the links and responding to many blogs that are sent.
People or potential visitors may change their minds or plan to travel to a particular destination if their queries are not answered on time (Jungsun & Hardin 2010, p. 735). Another challenge is the increased risk of cybercrime and hacking.
Some people may gain entrance to a system hosted on the Internet to gain access to any information that may be confidential. Such individuals may falsify the information hence leading to misrepresentation and loss of customers.
Furthermore, the number of visitors that visit the website may not be enough as expected. This causes a huge loss since the company may not be able to raise enough revenue hence affecting the level of income of the company.
One of the disadvantages that technology has brought to the industry is that it has caused unemployment. Many people who worked in the hotels as managers, waiters, and cooks, as well as those in the tourist industry, such as tour guides, lost their jobs to cut the cost and by utilizing the Internet.
The creation of jobs in these industries has also reduced because most of the marketing and advertising is done through the Internet. Privacy has also been affected by the coming up of the Internet.
People have improvised ways of hacking or gaining into the websites of organizations to steal important information. This exposes the company to risk (Zipf 2002, p. 57).
Proliferation has increased on the Internet. Many tourist websites are available on the Internet. This is a challenge, especially for small and medium tourist enterprises that possess inadequate skills and knowledge in website efficiency.
This proliferation is a sign that there is a lack of organization in the market that is already saturated. Many of these websites are not familiar to the clients. This becomes difficult for potential customers to locate them and even to have confidence in them to the extent of using them.
Intermediaries that are used to link customers to various businesses provide another challenge on the Internet. They are paid for their services hence leading to low profits, revenue, and homogeneity of the websites (Alexis & Buhalis 2007, p. 389).
Therefore, in conclusion, technology has contributed greatly to the success of the hospitality and tourism industry across the globe. Countries that have positively embraced technology in their operations have benefited in terms of increased revenue.
The potential of this technology is exorbitant. However, it requires people who have vast knowledge and expertise on how it operates to manage it well and to reap its overwhelming potential.
On the other hand, technology has rendered many people jobless. This has affected their living standards since they depend on their jobs as their source of livelihood. However, its benefits surpass the negatives, as revealed in the paper.
Alexis, P. & Buhalis, D. 2007, ‘ Exploring the information and communication technologies revolution and visioning the future of tourism, travel and hospitality industries, 6th e-tourism futures forum: ICT revolutionising tourism 26–27 March 2007 , Guildford’, International Journal of Tourism Research, vol. 9 I no.5, pp. 385-387.
Chih-Yao, L. 2011, ‘The Integration and Development of the Leisure and Hospitality Information System Module with the Embedded Technology,’ International Journal on Computer Science & Engineering , vol. 3 no. 5, pp. 1986-1994.
Cristiana, P. 2008, ‘The tourism industry and the use of internet’, Annals of the University of Oradea, Economic Science Series, vol. 17 no. 2, pp. 344-347.
Clayton, T. & Criscuolo, C. 2002, Electronic commerce and business change, National Statistics . Web.
Dis, T. 2010, ‘Information and Communication Technologies in the Hospitality Industry’, Hosteur , vol. 19 no. 1, pp. 9-11.
Garzotto, F. et al. 2004, Ubiquitous access to cultural tourism portals’, paper presented to Database and Expert Systems Applications, 15th International Workshop on (DEXA’04), Zaragoza, Spain.
Jungsun, K. & Hardin, A. 2010, ‘The Impact of Virtual Worlds on Word-of-Mouth: improving Social Networking and Services cape in the Hospitality Industry,’ Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management , vol. 19 no. 7, pp. 735-753.
World Travel and Tourism Council 2004, Progress and priorities 2004/2005, World Travel and Tourism Council . Web.
Zipf, A. 2002, ‘Adaptive context-aware mobility support for tourists,’ IEEE Intelligent Systems , vol. 17 no. 6, pp. 57-59.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 28). Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Tourism Industry. https://ivypanda.com/essays/how-technology-is-changing-the-hospitality-and-tourism-industry-advantages-and-disadvantages/
"Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Tourism Industry." IvyPanda , 28 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/how-technology-is-changing-the-hospitality-and-tourism-industry-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Tourism Industry'. 28 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Tourism Industry." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/how-technology-is-changing-the-hospitality-and-tourism-industry-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
1. IvyPanda . "Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Tourism Industry." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/how-technology-is-changing-the-hospitality-and-tourism-industry-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Advantages and Disadvantages of Technology in Tourism Industry." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/how-technology-is-changing-the-hospitality-and-tourism-industry-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
- Destination Marketing and Destination Management in Tourism
- Traveling, Its Advantages and Disadvantages Essay
- Tourism Destination Competitiveness
- Tourism Destination Management and Development
- Integrity in the Hospitality Industry
- Dark Tourism as a Contemporary Issue in Hospitality
- Eco Tourism and Hospitality Industry
- Improving Tourism Destinations Competitiveness
- Issues in Tourism and Hospitality Industry Essay
- Tourism Destination Evaluation on Iraq
- VisitBritain: Britain’s National Tourism Agency
- Final report on Travel
- Travel Agent in the Leisure Industry
- Transplant Tourism as an aspect of Medical Tourism
- Information Systems in Tourism Industry: Essay Example

CT leans on March Madness to launch a $1.8 million tourism campaign

Connecticut has launched its 2024 spring and summer tourism campaign. The “Make It Here” campaign takes advantage of UConn’s national prominence during March Madness, the annual NCAA college basketball tournament.
"There is no better opportunity to showcase the state," said Governor Ned Lamont at a tourism conference organized by the Department of Economic and Community Development at the Bushnell Center for the Performing Arts in Hartford.
“This is two weeks where the whole country is talking about Connecticut. They are talking about UConn. They are talking about basketball. But they are talking about Connecticut,” he said.
Anthony Anthony, the state’s chief marketing officer, said the DECD has targeted UConn games for the launch of its campaign.
“We bought specifically commercial time during the UConn Husky games to show our commercial, the “Make it Here." So, national championship, make it here baby!” said Anthony.
Connecticut’s $1.8 million campaign runs from April 1 to Labor Day. It spotlights hundreds of businesses statewide, ranging from hotels and restaurants to cultural attractions, theaters, wineries, breweries and state parks.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Advantages of Tourism. Tourism is a huge industry. It not only creates jobs, but also fosters economic development in different areas of the world. It has many advantages such as boosting the economy and giving the destination a sense of place. Tourism also helps preserve natural resources and cultural traditions.
From the economic advantages that tourism brings to host communities to the enjoyment that tourism brings to the tourists themselves, there is no disputing the value of this industry. The importance of tourism can be viewed from two perspectives: the tourism industry and the tourist. In this article I will explain how both the industry and the ...
The contribution of tourism to economic well-being depends on the quality and the revenues of the tourism offer. UN Tourism assists destinations in their sustainable positioning in ever more complex national and international markets. As the UN agency dedicated to tourism, UN Tourism points out that particularly developing countries ...
The Advantages. For developing countries, the advantages of tourism tend to be primarily monetary. A large scale tourism industry prevents larger, more harmful businesses from working off the land. Small tourist companies that reign on the land stops large capitalistic corporations from polluting the air or gentrifying people's homes.
Benefits and threats of travel and tourism in a globalized cultural context. When we chose the theme for this special issue: "Benefits and threats of travel and tourism in a globalized context", no one foresaw how current and appropriate this topic would be. Indeed, due to the global nature of our interconnected world, a virus abruptly ...
10 Nov 2023. Tourism has again been identified as a key driver of economic recovery and growth in a new report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). With UNWTO data pointing to a return to 95% of pre-pandemic tourist numbers by the end of the year in the best case scenario, the IMF report outlines the positive impact the sector's rapid ...
An end to tourism will not hinder the travel plans of the world's richest, but will serve to insulate and harden the nativist sentiments of the more disadvantaged. Tourism and globalisation is ...
The tourism sector is an important foreign exchange earner and provides opportunities for developing countries to create productive and inclusive jobs, grow innovative firms, finance the conservation of natural and cultural assets, and increase economic empowerment, especially for women and youth, who comprise the majority of the tourism sector's workforce.
Competitive advantage has a long history of application in industrial studies relating to competition and competitiveness at the company or firm level. Its introduction to tourism and destination management started after the publication of The Competitive Advantage of Nations (Porter 1990 ). At the industry level, competitive advantage is used ...
In relation to tourism and destination management, competitive advantage deals with the ability to use a destination's resources efficiently and effectively over the long term (Crouch and Ritchie 1999 ). A number of researchers have provided inputs into the understanding of destination competitiveness (Tsai et al. 2009 ).
Competitive advantage has a long history of application in industrial studies relating to com-petition and competitiveness at the company or firm level. Its application to tourism and destina-tion management started after Porter's (1990) The Competitive Advantage of Nations. At the industry level, competitive advantage is used to
Abstract. This study investigates the determinants of competitive advantages in tourism services for the EU-28 countries over the period 2000-2013. After having extended the Balassa methodology to measure competitive advantages, a dynamic panel data model is implemented to explain their drivers. The econometric analysis indicates that ...
Sustainable competitive advantage in tourism organizations: A strategic model. It is argued that an understanding of the11 characteristics identified are pivotal to strategic decision making in tourism organizations (Stage 4). Individually and collectively the characteristics have implications for the way in which resources and capabilities are ...
Sustainable tourism considers its current and future economic, social, and environmental impacts by addressing the needs of its ecological surroundings and the local communities. This is achieved ...
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
The Advantages of Tourism. Economic. It brings in money. This is probably the main advantage of tourism and the reason why it has been promoted so extensively, especially in developing countries. The income generated can make up a significant proportion of both private, local, and national incomes. Opportunities.
Note, this is generally the opposite of overtourism. Sustainable tourism keeps fresh air…fresh. 3. Sustainable Tourism Reduces Pollution. While sustainable tourism protects against poaching and the active destruction of habitats, as mentioned above, it also helps to reduce pollution.
One of the significant advantages of tourism is that it can help protect and preserve the environment. Local governments can invest the revenue generated by tourism for the betterment of environmentally sensitive regions and areas with fragile ecosystems. 4. Improved Infrastructure is Among the Pros of Tourism.
Comparative advantage in an activity (such as tourism) is defined as the ability to produce or service at a lower relative opportunity cost. Comparative advantage in tourism describes a nation or a destination that can win competitiveness from its factor endowment, for example, sun, sea, sand, and natural scenery.
Development of the Private Sector. Negative economic impacts of tourism. Leakage. Infrastructure cost. Increase in prices. Economic dependence of the local community on tourism. Foreign Ownership and Management. Economic impacts of tourism: Conclusion. Further reading on the economic impacts of tourism.
One of the most recent technology trends shaping the tourism market is the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the travel industry. Although AI adoption is still in its early stages, many key ...
Negative social impacts of tourism. Social Change. Globalisation and the Destruction of Preservation and Heritage. Loss of Authenticity. Standardisation and Commercialisation. Culture clashes. Tourist-host relationships. Increase in crime, gambling and moral behaviour. Social impacts of tourism: Conclusion.
This study investigates the impact of green HRM (GHRM) on green competitive advantage (GCA), examining the mediating role of eco-innovation and the moderating role of green psychological climate (GPC). The study surveyed 472 fulltime employees in five-star hotels and travel agencies, developing and testing a five-hypothesis research model using PLS-SEM. Results revealed that GHRM positively ...
One of the disadvantages that technology has brought to the industry is that it has caused unemployment. Many people who worked in the hotels as managers, waiters, and cooks, as well as those in the tourist industry, such as tour guides, lost their jobs to cut the cost and by utilizing the Internet.
Connecticut has launched its 2024 spring and summer tourism campaign. The "Make It Here" campaign takes advantage of UConn's national prominence during March Madness, the annual NCAA college ...
Wednesday, 27 Mar 2024. Communications Office. For the second year in a row, homeowners in Prince William County interested in solar energy can take advantage of the Solarize Virginia Program, which helps make the transition to solar easier and more affordable. By registering for the program, homeowners can receive a free solar satellite ...