

The Ages of Exploration
Christopher columbus, age of discovery.
Quick Facts:
He is credited for discovering the Americas in 1492, although we know today people were there long before him; his real achievement was that he opened the door for more exploration to a New World.
Name : Christopher Columbus [Kri-stə-fər] [Kə-luhm-bəs]
Birth/Death : 1451 - 1506
Nationality : Italian
Birthplace : Genoa, Italy

Christopher Columbus leaving Palos, Spain
Christopher Columbus aboard the "Santa Maria" leaving Palos, Spain on his first voyage across the Atlantic Ocean. The Mariners' Museum 1933.0746.000001
Introduction We know that In 1492, Columbus sailed the ocean blue. But what did he actually discover? Christopher Columbus (also known as (Cristoforo Colombo [Italian]; Cristóbal Colón [Spanish]) was an Italian explorer credited with the “discovery” of the Americas. The purpose for his voyages was to find a passage to Asia by sailing west. Never actually accomplishing this mission, his explorations mostly included the Caribbean and parts of Central and South America, all of which were already inhabited by Native groups.
Biography Early Life Christopher Columbus was born in Genoa, part of present-day Italy, in 1451. His parents’ names were Dominico Colombo and Susanna Fontanarossa. He had three brothers: Bartholomew, Giovanni, and Giacomo; and a sister named Bianchinetta. Christopher became an apprentice in his father’s wool weaving business, but he also studied mapmaking and sailing as well. He eventually left his father’s business to join the Genoese fleet and sail on the Mediterranean Sea. 1 After one of his ships wrecked off the coast of Portugal, he decided to remain there with his younger brother Bartholomew where he worked as a cartographer (mapmaker) and bookseller. Here, he married Doña Felipa Perestrello e Moniz and had two sons Diego and Fernando.
Christopher Columbus owned a copy of Marco Polo’s famous book, and it gave him a love for exploration. In the mid 15th century, Portugal was desperately trying to find a faster trade route to Asia. Exotic goods such as spices, ivory, silk, and gems were popular items of trade. However, Europeans often had to travel through the Middle East to reach Asia. At this time, Muslim nations imposed high taxes on European travels crossing through. 2 This made it both difficult and expensive to reach Asia. There were rumors from other sailors that Asia could be reached by sailing west. Hearing this, Christopher Columbus decided to try and make this revolutionary journey himself. First, he needed ships and supplies, which required money that he did not have. He went to King John of Portugal who turned him down. He then went to the rulers of England, and France. Each declined his request for funding. After seven years of trying, he was finally sponsored by King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain.
Voyages Principal Voyage Columbus’ voyage departed in August of 1492 with 87 men sailing on three ships: the Niña, the Pinta, and the Santa María. Columbus commanded the Santa María, while the Niña was led by Vicente Yanez Pinzon and the Pinta by Martin Pinzon. 3 This was the first of his four trips. He headed west from Spain across the Atlantic Ocean. On October 12 land was sighted. He gave the first island he landed on the name San Salvador, although the native population called it Guanahani. 4 Columbus believed that he was in Asia, but was actually in the Caribbean. He even proposed that the island of Cuba was a part of China. Since he thought he was in the Indies, he called the native people “Indians.” In several letters he wrote back to Spain, he described the landscape and his encounters with the natives. He continued sailing throughout the Caribbean and named many islands he encountered after his ship, king, and queen: La Isla de Santa María de Concepción, Fernandina, and Isabella.
It is hard to determine specifically which islands Columbus visited on this voyage. His descriptions of the native peoples, geography, and plant life do give us some clues though. One place we do know he stopped was in present-day Haiti. He named the island Hispaniola. Hispaniola today includes both Haiti and the Dominican Republic. In January of 1493, Columbus sailed back to Europe to report what he found. Due to rough seas, he was forced to land in Portugal, an unfortunate event for Columbus. With relations between Spain and Portugal strained during this time, Ferdinand and Isabella suspected that Columbus was taking valuable information or maybe goods to Portugal, the country he had lived in for several years. Those who stood against Columbus would later use this as an argument against him. Eventually, Columbus was allowed to return to Spain bringing with him tobacco, turkey, and some new spices. He also brought with him several natives of the islands, of whom Queen Isabella grew very fond.
Subsequent Voyages Columbus took three other similar trips to this region. His second voyage in 1493 carried a large fleet with the intention of conquering the native populations and establishing colonies. At one point, the natives attacked and killed the settlers left at Fort Navidad. Over time the colonists enslaved many of the natives, sending some to Europe and using many to mine gold for the Spanish settlers in the Caribbean. The third trip was to explore more of the islands and mainland South America further. Columbus was appointed the governor of Hispaniola, but the colonists, upset with Columbus’ leadership appealed to the rulers of Spain, who sent a new governor: Francisco de Bobadilla. Columbus was taken prisoner on board a ship and sent back to Spain.
On his fourth and final journey west in 1502 Columbus’s goal was to find the “Strait of Malacca,” to try to find India. But a hurricane, then being denied entrance to Hispaniola, and then another storm made this an unfortunate trip. His ship was so badly damaged that he and his crew were stranded on Jamaica for two years until help from Hispaniola finally arrived. In 1504, Columbus and his men were taken back to Spain .
Later Years and Death Columbus reached Spain in November 1504. He was not in good health. He spent much of the last of his life writing letters to obtain the percentage of wealth overdue to be paid to him, and trying to re-attain his governorship status, but was continually denied both. Columbus died at Valladolid on May 20, 1506, due to illness and old age. Even until death, he still firmly believed that he had traveled to the eastern part of Asia.
Legacy Columbus never made it to Asia, nor did he truly discover America. His “re-discovery,” however, inspired a new era of exploration of the American continents by Europeans. Perhaps his greatest contribution was that his voyages opened an exchange of goods between Europe and the Americas both during and long after his journeys. 5 Despite modern criticism of his treatment of the native peoples there is no denying that his expeditions changed both Europe and America. Columbus day was made a federal holiday in 1971. It is recognized on the second Monday of October.

- Fergus Fleming, Off the Map: Tales of Endurance and Exploration (New York: Grove Press, 2004), 30.
- Fleming, Off the Map , 30
- William D. Phillips and Carla Rahn Phillips, The Worlds of Christopher Columbus (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1993), 142-143.
- Phillips and Phillips, The Worlds of Christopher Columbus , 155.
- Robin S. Doak, Christopher Columbus: Explorer of the New World (Minneapolis: Compass Point Books, 2005), 92.
- Original "EXPLORATION through the AGES" site
- The Mariners' Educational Programs


By AD. F. Bandelier Transcribed by Janet van Heyst Dedicated in honor of Fr. Moses M. Nagy, O. Cist.
(Italian CRISTOFORO COLOMBO; Spanish CRISTOVAL COLON.) Born at Genoa, or on Genoese territory, probably 1451; died at Valladolid, Spain, 20 May 1506.
The early age at which he began his career as a sailor is not surprising for a native of Genoa, as the Genoese were most enterprising and daring seamen. Columbus is said in his early days to have been a corsair, especially in the war against the Moors, themselves merciless pirates. He is also supposed to have sailed as far south as the coast of Guinea before he was sixteen years of age. Certain it is that while quite young he became a thorough and practical navigator, and later acquired a fair knowledge of astronomy. He also gained a wide acquaintance with works on cosmography such as Ptolemy and the “Imago Mundi” of Cardinal d’Ailly, besides entering into communication with the cosmographers of his time. The fragment of a treatise written by him and called by his son Fernando “The Five Habitable Zones of the Earth” shows a degree of information unusual for a sailor of his day. As in the case of most of the documents relating to the life of Columbus the genuineness of the letters written in 1474 by Paolo Toscanelli, a renowned physicist of Florence, to Columbus and a member of the household of King Alfonso V of Portugal, has been attacked on the ground of the youth of Columbus, although they bears signs of authenticity. The experiences and researches referred to fit in satisfactorily with the subsequent achievements of Columbus. For the rest, the early part of Columbus’s life is interwoven with incidents, most of which are unsupported by evidence, though quite possible. His marriage about 1475 to a Portuguese lady whose name is given sometimes as Doña Felipa Moniz and sometimes as Doña Felipa Perestrella seems certain.
Columbus seems to have arrived in Portugal about 1471, although 1474 is also mentioned and supported by certain indications. He vainly tried to obtain the support of the King of Portugal for his scheme to discover the Far East by sailing westward, a scheme supposed to have been suggested by his brother Bartholomew, who is said to have been earning a livelihood at Lisbon by designing marine charts. Columbus went to Spain in 1485, and probably the first assistance he obtained there was from the Duke of Medina Celi, Don Luis de la Cerda, for whom he performed some services that brought him a compensation of 3000 maravedis in May, 1487. He lived about two years at the home of the duke and made unsuccessful endeavors to interest him in his scheme of maritime exploration. His attempts to secure the help of the Duke of Medina Sidonia were equally unproductive of results. No blame attaches to the noblemen for declining to undertake an enterprise which only rulers of nations could properly carry out. Between 1485 and 1488 Columbus began his relations with Doña Beatriz Enriquez de Arana, or Harana, of a good family of the city of Cordova, from which sprang his much beloved son Fernando, next to Christopher and his brother Bartholomew the most gifted of the Colombos.
Late in 1485 or early in 1486, Columbus appeared twice before the court to submit his plans and while the Duke of Medina Celi may have assisted him to some extent, the chief support came from the royal treasurer, Alonzo de Quintanilla, Friar Antonio de Marchena (confounded by Irving with Father Perez of La Rábida), and Diego de Deza, Bishop of Placencia. Columbus himself declared that these two priests were always his faithful friends. Marchena also obtained for him the valuable sympathy of Cardinal Gonzalez de Mendoza. Through the influence of these men the Government appointed a junta or commission of ecclesiastics that met at Salamanca late in 1486 or early in 1487, in the Dominican convent of San Esteban to investigate the scheme, which they finally rejected. The commission had no connection with the celebrated University of Salamanca, but was under the guidance of the prior of Prado. It seems that Columbus gave but scant and unsatisfactory information to the commission, probably through fear that his ideas might be improperly made use of and he be robbed of the glory and advantages that he expected to derive from his project. This may account for the rejection of his proposals. The prior of Prado was a Hieronymite, while Columbus was under the especial protection of the Dominicans. Among his early friends in Spain was Luis de Santangel, whom Irving calls “receiver of the ecclesiastical revenues of Aragon”, and who afterwards advanced to the queen the funds necessary for the first voyage. If Santangel was receiver of the church revenues and probably treasurer and administrator, it was the Church that furnished the means (17,000 ducats) for the admiral’s first voyage.
It would be unjust to blame King Ferdinand for declining the proposals of Columbus after the adverse report of the Salamanca commission, which was based upon objections drawn from Seneca and Ptolemy rather than upon the opinion of St. Augustine in the “De Civitate Dei”. The king was then preparing to deal the final blow to Moorish domination in Spain after the struggle of seven centuries, and his financial resources were taxed to the utmost. Moreover, he was not easily carried away by enthusiasm and, though we now recognize the practical value of the plans of Columbus, at the close of the fifteenth century it seemed dubious, to say the least, to a cool-headed ruler, wont to attend first to immediate necessities. The crushing of the Moorish power in the peninsula was then of greater moment than the search after distant lands for which, furthermore, there were not the means in the royal treasury. Under these conditions Columbus, always in financial straits himself and supported by the liberality of friends, bethought himself of the rulers of France and England. In 1488 his brother Bartholomew, as faithful as sagacious, tried to induce one or the other of them to accept the plans of Christopher, but failed. The idea was too novel to appeal to either. Henry VII of England was too cautious to entertain proposals from a comparatively unknown seafarer of a foreign nation, and Charles VIII of France was too much involved in Italian affairs. The prospect was disheartening. Nevertheless, Columbus, with the assistance of his friends, concluded to make another attempt in Spain. He proceeded to court again in 1491, taking with him his son Diego. The court being then in camp before Granada, the last Moorish stronghold, the time could not have been more inopportune. Another junta was called before Granada while the siege was going on, but the commission again reported unfavourably. This is not surprising, as Ferdinand of Aragon could not undertake schemes that would involve a great outlay, and divert his attention from the momentous task he was engaged in. Columbus always directed his proposals to the king and as yet the queen had taken no official notice of them, as she too was heart and soul in the enterprise destined to restore Spain wholly to Christian rule.
The junta before Granada took place towards the end of 1491, and its decision was such a blow to Columbus that he left the court and wandered away with his boy. Before leaving, however, he witnessed the fall of Granada, 2 January, 1492. His intention was to return to Cordova and then, perhaps, to go to France. On foot and reduced almost to beggary, he reached the Dominican convent of La Rábida probably in January, 1492. The prior was Father Juan Perez, the confessor of the queen, frequently confounded with Fray Antonio Marchena by historians of the nineteenth century, who also erroneously place the arrival of Columbus at La Rábida in the early part of his sojourn in Spain. Columbus begged the friar who acted as door-keeper to let his tired son rest at the convent over night. While he was pleading his cause the prior was standing near by and listening. Something struck him in the appearance of this man, with a foreign accent, who appeared to be superior to his actual condition. After providing for his immediate wants Father Perez took him to his cell, where Columbus told him all his aspirations and blighted hopes. The result was that Columbus and his son stayed at the convent as guests and Father Perez hurried to Santa Fe near Granada, for the purpose of inducing the queen to take a personal interest in the proposed undertaking of the Italian navigator.
Circumstances had changed with the fall of Granada, and the Dominican’s appeal was favourably received by Isabella who, in turn, influenced her husband. Columbus was called to court at once, and 20,000 maravedis were assigned him out of the queen’s private resources that he might appear in proper condition before the monarch. Some historians assert that Luis de Santangel decided the queen to espouse the cause of Columbus, but the credit seems rather to belong to the prior of La Rábida. The way had been well prepared by the other steadfast friends of Columbus, not improbably Cardinal Mendoza among others. At all events negotiations progressed so rapidly that on 17 April the first agreement with the Crown was signed, and on 30 April the second. Both show an unwise liberality on the part of the monarchs, who made the highest office in what was afterwards the West Indies hereditary in the family of Columbus. Preparations were immediately begun for the equipment of the expedition. The squadron with which Columbus set out on his first voyage consisted of three vessels–the Santa Maria, completely decked, which carried the flag of Columbus as admiral, the Pinta, and the Niña, both caravels, i.e. undecked, with cabins and forecastles. These three ships carried altogether 120 men. Two seamen of repute, Martín Alonso Pinzon and his brother Vicente Yanez Pinzon, well-to-do-residents of Palos commanded, the former the Pinta. the latter the Niña, and experienced pilots were placed on both ships. Before leaving, Columbus received the Sacraments of Penance and Holy Eucharist, at the hands (it is stated) of Father Juan Perez, the officers and crews of the little squadron following his example. On 3 August, 1492, the people of Palos with heavy hearts saw them depart on an expedition regarded by many as foolhardy.
Las Casas claims to have used the journal of Columbus’s first voyage, but he admits that he made an abridged copy of it. What and how much he left out, of course, is not known. But it is well to bear in mind that the journal, as published, is not the original in its entirety. The vessels touched at the Canaries, and then proceeded on the voyage. Conditions were most favourable. Hardly a wind ruffled the waters of the ocean. The dramatic incident of the mutiny, in which the discouragement of the crews is said to have culminated before land was discovered, is a pure invention. That there was dissatisfaction and grumbling at the failure to reach land seems to be certain, but no acts of insubordination are mentioned either by Columbus, his commentator Las Casas, or his son Fernando. Perhaps the most important event during the voyage was the observation, 17 September, by Columbus himself, of the declination of the magnetic needle, which Las Casas attributes to a motion of the polar star. The same author intimates that two distinct journals were kept by the admiral, “because he always represented [feigned] to the people that he was making little headway in order that the voyage should not seem long to them, so that he kept a record by two routes, the shorter being the fictitious one, and the longer the true one”. He must therefore either have kept two log-books, or he must have made two different entries in the same book. At any rate Las Casas seems to have had at his command both sets of data, since he gives them almost from day to day. This precautionary measure indicates that Columbus feared insubordination and even revolt on the part of the crews, but there is no evidence that any mutiny really broke out. Finally, at ten o’clock, p.m., 11 October, Columbus himself described a light which indicated land and was so recognized by the crew of his vessel. It reappeared several times, and Columbus felt sure that the shores so eagerly expected were near. At 2 a.m. on 12 October the land was seen plainly by one of the Pinta’s crew, and in the forenoon Columbus landed on what is now called Watling’s Island in the Bahama group, West Indies. The discoverers named the island San Salvador. The Indians inhabiting it belonged to the widespread Arawak stock and are said to have called the island Guanahani. Immediately after landing Columbus took possession of the island for the Spanish sovereigns.
The results of the first voyage, aside from the discovery of what the admiral regarded as being approaches to India and China, may be summed up as follows: partial recognition of the Bahamas; the discovery and exploration of a part of Cuba, and the establishment of a Spanish settlement on the coast of what is now the Island of Haiti or Santo Domingo. Cuba Columbus named Juana, and Santo Domingo, Hispaniola.
It was on the northern coast of the large island of Santo Domingo that Columbus met with the only serious mishap of the first voyage. Having established the nucleus of the first permanent Spanish settlement in the Indies, he left about three score men to hold it. The vicinity was comparatively well peopled by natives, Arawaks like those of the Bahamas, but slightly more advanced in culture. A few days previous to the foundation Martin Alonso Pinzon disappeared with the caravel Pinta which he commanded and only rejoined the admiral on 6 January, 1493, an act, to say the least, of disobedience, if not of treachery. The first settlement was officially established on Christmas Day, 1492, and hence christened “La Navidad”. On the same day the admiral’s ship ran aground. It was a total loss, and Columbus was reduced for the time being to the Niña, as the Pinta had temporarily deserted. Happily the natives were friendly. After ensuring, as well as he might, the safety of the little colony by the establishment of friendly relations with the Indians, Columbus left for Spain, where, after weathering a frightful storm during which he was again separated from the Pinta, he arrived at Palos, 15 March, 1493.
From the journal mentioned we also gather (what is not stated in the letters of Columbus) that while on the northern shores of Santo Domingo (Hispaniola) the admiral “learned that behind the Island Juana [Cuba] towards the South, there is another large island in which there is much more gold. They call that island Yamaye. . . . And that the island Española or the other island Yamaye was near the mainland, ten days distant by canoe, which might be sixty or seventy leagues, and that there the people were clothed [dressed]”. Yamaye is Jamaica, and the mainland alluded to as sixty or seventy leagues distant to the south (by south the west is meant), or 150 to 175 English miles (the league, at that time, being counted at four millas of 3000 Spanish feet), was either Yucatan or Honduras. Hence the admiral brought the news of the existence of the American continent to Europe as early as 1493. That he believed the continent to be Eastern Asia does not diminish the importance of his information.
Columbus had been careful to load his ship with all manner of products of the newly discovered countries and he also took some of the natives. Whether, among the samples of the vegetable kingdom, tobacco was included, is not yet satisfactorily ascertained. Nor is it certain that, when upon his return he presented himself to the monarchs at Barcelona, an imposing public demonstration took place in his honour. That he was received with due distinction at court and that he displayed the proofs of his discovery can not be doubted. The best evidence of the high appreciation of the King and Queen of Spain is the fact, that the prerogatives granted to him were confirmed, and everything possible was done to enable him to continue his explorations. The fact that Columbus had found a country that appeared to be rich in precious metals was of the utmost importance. Spain was poor, having been robbed, ages before, of its metallic wealth by the Romans. As gold was needed the discovery of a new source of that precious metal made a strong impression on the people of Spain, and a rush to the new regions was inevitable.
Columbus started on his second voyage to the Indies from Cadiz, 25 September, 1493, with three large vessels and thirteen caravels, carrying in all about 1500 men. On his first trip, he had heard about other, smaller islands lying some distance south of Hispaniola, and said to be inhabited by ferocious tribes who had the advantage over the Arawaks of being intrepid seafarers, and who made constant war upon the inhabitants of the Greater Antilles and the Bahamas, carrying off women and children into captivity. They were believed to practice cannibalism. These were the Caribs and the reports about them were true, outside of some exaggerations and fables like the story of the Amazons. Previous to the arrival of Columbus the Caribs had driven the Arawaks steadily north, depopulated some of the smaller islands, and were sorely pressing the people of Hispaniola, parts of Cuba, Porto Rico, and even Jamaica. Columbus wished to learn more about these people. The helpless condition of the Arawaks made him eager to protect them against their enemies. The first land sighted, 3 November, was the island now known as Dominica, and almost at the same time that of Marie Galante was discovered. Geographically the second voyage resulted in the discovery of the Caribbean Islands (including the French Antilles), Jamaica, and minor groups. Columbus having obtained conclusive evidence of the ferocious customs of the Caribs, regarded them as dangerous to the settlements he proposed to make among the Arawaks and as obstacles to the Christianization and civilization of these Indians. The latter he intended to make use of as labourers, as he soon perceived that for some time to come European settlers would be too few in numbers and too new to the climate to take advantage of the resources of the island. The Caribs he purposed to convert eventually, but for the time being they must be considered as enemies, and according to the customs of the age, their captors had the right to reduce them to slavery. The Arawaks were to be treated in a conciliatory manner, as long as they did not show open hostility. Before long, however, there was a change in these relations.
After a rapid survey of Jamaica, Columbus hastened to the northern coast of Haiti, where he had planted the colony of La Navidad. To his surprise the little fort had disappeared. There were to be seen only smouldering ruins and some corpses which were identified as Spanish. The natives, previously so friendly, were shy, and upon being questioned were either mute or contradictory in their replies. It was finally ascertained that another tribe, living farther inland and hostile to those on the coast, had fallen upon the fort, killed most of the inmates and burnt most of the buildings. Those who escaped had perished in their flight. But it also transpired that the coast people themselves had taken part in the massacre. Columbus, while outwardly on good terms with them, was on his guard and, in consequence of the aversion of his people to a site where only disaster had befallen them, moved some distance farther east and established on the coast the larger settlement of Isabella. This stood ten leagues to the east of Cape Monte Cristo, where the ruins are still to be seen.
The existence of gold on Haiti having been amply demonstrated on the first voyage, Columbus inaugurated a diligent search for places where it might be found. The gold trinkets worn by the Indians were washings or placeres, but mention is also made, on the first voyage, of quartz rock containing the precious metal. But it is likely that the yellow mineral was iron pyrites, probably gold-bearing but, in the backward state of metallurgy, worthless at the time. Soon after the settlement was made at Isabella the colonists began to complain that the mineral wealth of the newly discovered lands had been vastly exaggerated and one, who accompanied the expedition as expert in metallurgy, claimed that the larger nuggets held by the natives had been accumulated in the course of a long period of time. This very sensible supposition was unjustly criticized by Irving, for since Irving’s time it has been clearly proved that pieces of metal of unusual size and shape were often kept for generations by the Indians as fetishes.
A more important factor which disturbed the Spanish was the unhealthiness of the climate. The settlers had to go through the slow and often fatal process of acclimatization. Columbus himself suffered considerably from ill-health. Again, the island was not well provided with food suitable for the newcomers. The population, notwithstanding the exaggerations of Las Casas and others, was sparse. Isabella with its fifteen hundred Spanish immigrants was certainly the most populous settlement. At first there was no clash with the natives, but parties sent by Columbus into the interior came in contact with hostile tribes. For the protection of the colonists Columbus built in the interior a little fort called Santo Tomas. He also sent West Indian products and some Carib prisoners back to Spain in a vessel under the command of Antonio de Torres. Columbus suggested that the Caribs be sold as slaves in order that they might be instructed in the Christian Faith. This suggestion was not adopted by the Spanish monarchs, and the prisoners were treated as kindly in Spain as the friendly Arawaks who had been sent over.
The condition of affairs on Hispaniola (Haiti) was not promising. At Isabella and on the coast there was grumbling against the admiral, in which the Benedictine Father Buil (Boil) and the other priests joined, or which, at least, they did not discourage. In the interior there was trouble with the natives. The commander at Santo Tomas, Pedro Margarite, is usually accused of cruelty to the Indians, but Columbus himself in his Memorial of 30 January, 1494, commends the conduct of that officer. However, he had to send him reinforcements, which were commanded by Alonzo de Ojeda.
Anxiously following up his theory that the newly discovered islands were but outlying posts of Eastern Asia and that further explorations would soon lead him to the coast of China or to the Moluccas, Columbus, notwithstanding the precarious condition of the colony, left it in charge of his brother Diego and four counsellors (one of whom was Father Buil), and with three vessels set sail towards Cuba. During his absence of five months he explored parts of Cuba, discovered the Isle of Pines and several groups of smaller islands, and made the circuit of Jamaica, landing there almost every day. When he returned to Isabella (29 September, 1494), he was dangerously ill and in a stupor. Meanwhile his brother Bartholomew had arrived from Spain with a small squadron and supplies. He proved a welcome auxiliary to the weak Diego, but could not prevent serious trouble. Margarite, angered by interference with his administration in the interior, returned to the coast, and there was joined by Father Buil and other malcontents. They seized the three caravels that had arrived under the command of Bartholomew Columbus, and set sail in them for Spain to lay before the Government what they considered their grievances against Columbus and his administration.
That there was cause for complaint there seems to be no doubt, but it is almost impossible now to determine who was most at fault, Columbus or his accusers. He was certainly not as able an administrator as he was a navigator. Still, taking into consideration the difficulties, the novelty of the conditions, and the class of men Columbus had to handle, and placing over against this what he had already achieved on Haiti, there is not so much ground for criticism. The charges of cruelty against the natives are based upon rather suspicious authority, Las Casas being the principal source. There were errors and misdeeds on both sides, which, however, might not have brought about a crisis had not disappointment angered the settlers, who had based their expectations on the glowing reports of Columbus himself, and disposed them to attribute all their troubles to their opponents.
TBC – Before the return of Columbus to Isabella, Ojeda had repulsed an attempt of the natives to surprise Santo Tomas. Thereupon the Indians of various tribes of the interior now formed a confederation and threatened Isabella. Columbus, however, on his return, with the aid of firearms, sixteen horses, and about twenty blood-hounds easily broke up the Indian league. Ojeda captured the leader, and the policy of kindness hitherto pursued towards the natives was replaced by repression and chastisement. According to the customs of the times the prisoners of war were regarded as rebels, reduced to slavery, and five hundred of these were sent to Spain to be sold. It is certain that the condition of the Indians became much worse thereafter, that they were forced into unaccustomed labours, and that their numbers began to diminish rapidly. That these harsh measures were authorized by Columbus there can be no doubt.
While the Spanish monarchs in their dispatches to Columbus continued to show the same confidence and friendliness they could not help hearing the accusations made against him by Father Buil, Pedro Margarite, and the other malcontents, upon their return to Spain. It was clear that there were two factions among the Spaniards in Haiti, one headed by the admiral, the other composed of perhaps a majority of the settlers including ecclesiastics. Still the monarchs enjoined the colonists by letter to obey Columbus in everything and confirmed his authority and privileges. The incriminations, however, continued, and charges were made of nepotism and spoliation if royal revenue. There was probably some foundation for these charges, though also much wilful misrepresentation. Unable to ascertain the true condition of affairs, the sovereigns finally decided to send to the Indies a special commissioner to investigate and report. Their choice fell upon Juan de Aguado who had gone with Columbus on his first voyage and with whom he had always been on friendly terms. Aguado arrived at Isabella in October, 1495, while Columbus was absent on a journey of exploration across the island. No clash appears to have occurred between Aguado and Bartholomew Columbus, who was in charge of the colony during his brother’s absence, much less with the admiral himself upon the latter’s return. Soon after, reports of important gold discoveries came from a remote quarter of the island accompanied by specimens. The arrival of Aguado convinced Columbus of the necessity for his appearance in Spain and that new discoveries of gold would strengthen his position there. So he fitted out two ships, one for himself and one for Aguado, placing in them two hundred dissatisfied colonists, a captive Indian chief (who died on the voyage), and thirty Indian prisoners, and set sail for Spain on 10 March, 1496, leaving his brother Bartholomew at Isabella as temporary governor. As intercourse between Spain and the Indies was now carried on at almost regular intervals. Bartholomew was in communication with the mother country and was at least tacitly recognized as his brother’s substitute in the government of the Indies. Columbus reached Cadiz 11 June, 1496.
The story of his landing is quite dramatic. He is reported to have gone ashore, clothed in the Franciscan garb, and to have manifested a dejection which was wholly uncalled for. His health, it is true, was greatly impaired, and his companions bore the marks of great physical suffering. The impression created by their appearance was of course not favourable and tended to confirm the reports of the opponents of Columbus about the nature of the new country. This, as well as the disappointing results of the search for precious metals, did not fail to have its influence. The monarchs saw that the first enthusiastic reports had been exaggerated, and that the enterprise while possibly lucrative in the end, would entail large expenditures for some time to come. Bishop Fonseca, who was at the head of colonial affairs, urged that great caution should be exercised. What was imputed to Bishop Fonseca as jealousy was only the sincere desire of an honest functionary to guard the interests of the Crown without blocking the way of an enthusiastic but somewhat visionary genius who had been unsuccessful as an administrator. Later expressions (1505) of Columbus indicate that the personal relations to Fonseca were at the time far from unfriendly. But the fact that Columbus had proposed the enslaving of American natives and actually sent a number of them over to Spain had alienated the sympathy of the queen to a certain degree, and thus weakened his position at court.
Nevertheless, it was not difficult for Columbus to organize a third expedition. Columbus started on his third voyage from Seville with six vessels on 30 May, 1498. He directed his course more southward than before, owing to reports of a great land lying west and south of the Antilles and his belief that it was the continent of Asia. He touched at the Island of Madeira, and later at Gomera, one of the Canary Islands, whence he sent to Haiti three vessels. Sailing southward, he went to the Cape Verde Islands and, turning thence almost due west, arrived on 31 July 1498, in sight of what is now the Island of Trinidad which was so named by him. Opposite, on the other side of a turbulent channel, lay the lowlands of north-eastern South America. Alarmed by the turmoil caused by the meeting of the waters of the Orinoco (which empties through several channels into the Atlantic opposite Trinidad) with the Guiana current, Columbus kept close to the southern shore of Trinidad as far as its south-western extremity, where he found the water still more turbulent. He therefore gave that place the name of Boca del Drago, or Dragon’s Mouth. Before venturing into the seething waters Columbus crossed over to the mainland and cast anchor. He was under the impression that this was an island, but a vast stream of fresh water gave evidence of a continent. Columbus landed, he and his crew being thus the first Europeans to set foot on South American soil. The natives were friendly and gladly exchanged pearls for European trinkets. The discovery of pearls in American waters was important and very welcome.
A few days later, the admiral, setting sail again, was borne by the currents safely to the Island of Margarita, where he found the natives fishing for pearls, of which he obtained three bags by barter.
Some of the letters of Columbus concerning his third voyage are written in a tone of despondency. Owing to his physical condition, he viewed things with a discontent far from justifiable. And, as already said, his views of the geographical situation were somewhat fanciful. The great outpour opposite Trinidad he justly attributed to the emptying of a mighty river coming from the west, a river, so large that only a continent could afford its space. In this he was right, but in his eyes that continent was Asia, and the sources of that river must be on the highest point of the globe. He was confirmed in this idea by his belief that Trinidad wasnearer the Equator than it actually is and that near the Equator the highest land on earth should be found. He thought also that the sources of the Orinoco lay in the Earthly Paradise and that the great river was one of the four streams that according to Scripture flowed from the Garden of Eden. He had no accurate knowledge of the form of the earth, and conjectured that it was pear-shaped.
On 15 August, fearing a lack of supplies, and suffering severely from what his biographers call gout and from impaired eyesight, he left his new discoveries and steered for Haiti. On 19 August he sighted that island some distance west of where the present capital of the Republic of Santo Domingo now stands. During his absence his brother Bartholomew had abandoned Isabella and established his head-quarters at Santo Domingo so called after his father Domenico. During the absence of Columbus events on Haiti had been far from satisfactory. His brother Bartholomew, who was then known as the adelantado, had to contend with several Indian outbreaks, which he subdued partly by force, partly by wise temporizing. These outbreaks were, at least in part, due to a change in the class of settlers by whom the colony was reinforced. The results of the first settlement far from justified the buoyant hopes based on the exaggerated reports of the first voyage, and the pendulum of public opinion swung back to the opposite extreme. The clamour of opposition to Columbus in the colonies and the discouraging reports greatly increased in Spain the disappointment with the new territorial acquisitions. That the climate was not healthful seemed proved by the appearance of Columbus and his companions on his return from the second voyage. Hence no one was willing to go to the newly discovered country, and convicts, suspects, and doubtful characters in general who were glad to escape the regulations of justice were the only reinforcements that could be obtained for the colony on Hispaniola. As a result there were conflicts with the aborigines, sedition in the colony, and finally open rebellion against the authority of the adelantado and his brother Diego. Columbus and his brothers were Italians, and this fact told against them among the malcontents and lower officials, but that it influenced the monarchs and the court authorities is a gratuitous charge.
As long as they had not a common leader Bartholomew had little to fear from the malcontents, who separated from the rest of the colony, and formed a settlement apart. They abused the Indians, thus causing almost uninterrupted trouble. However, they soon found a leader in the person of one Roldan, to whom the admiral had entrusted a prominent office in the colony. There must have been some cause for complaint against the government of Bartholomew and Diego, else Roldan could not have so increased the number of his followers as to make himself formidable to the brothers, undermining their authority at their own head-quarters and even among the garrison of Santo Domingo. Bartholomew was forced to compromise on unfavourable terms. So, when the admiral arrived from Spain he found the Spanish settlers on Haiti divided into two camps, the stronger of which, headed by Roldan, was hostile to his authority. That Roldan was an utterly unprincipled man, but energetic and above all, shrewd and artful, appears from the following incident. Soon after the arrival of Columbus the three caravels he had sent from Gomera with stores and ammunition struck the Haitian coast where Roldan had established himself. The latter represented to the commanders of the vessels that he was there by Columbus’s authority and easily obtained from them military stores as well as reinforcements in men. On their arrival shortly afterward at Santo Domingo the caravels were sent back to Spain by Columbus. Alarmed at the condition of affairs and his own importance, he informed the monarchs of his critical situation and asked for immediate help. Then he entered into negotiations with Roldan. The latter not only held full control in the settlement which he commanded, but had the sympathy of most of the military garrisons that Columbus and his brothers relied upon as well as the majority of the colonists. How Columbus and his brother could have made themselves so unpopular is explained in various ways. There was certainly much unjustifiable ill will against them, but there was also legitimate cause for discontent, which was adroitly exploited by Roldan and his followers.
Seeing himself almost powerless against his opponents on the island, the admiral stooped to a compromise. Roldan finally imposed his own conditions. He was reinstated in his office and all offenders were pardoned; and a number of them returned to Santo Domingo. Columbus also freed many of the Indian tribes from tribute, but in order still further to appease the former mutineers, he instituted the system of repartimientos, by which not only grants of land were made to the whites, but the Indians holding these lands or living on them were made perpetual serfs to the new owners, and full jurisdiction over life and property of these Indians became vested in the white settlers. This measure had the most disastrous effect on the aborigines, and Columbus has been severely blamed for it, but he was then in such straits that he had to go to any extreme to pacify his opponents until assistance could reach him from Spain. By the middle of the year 1500 peace apparently reigned again in the colony, though largely at the expense of the prestige and authority of Columbus.
Meanwhile reports and accusations had reached the court of Spain from both parties in Haiti. It became constantly more evident that Columbus was no longer master of the situation in the Indies, and that some steps were necessary to save the situation. It might be said that the Court had merely to support Columbus whether right or wrong. But the West Indian colony had grown, and its settlers had their connections and supporters in Spain, who claimed some attention and prudent consideration. The clergy who were familiar with the circumstances through personal experience for the most part disapproved of the management of affairs by Columbus and his brothers. Queen Isabella’s irritation at the sending of Indian captives for sale as slaves had by this time been allayed by a reminder of the custom then in vogue of enslaving captive rebels or prisoners of war addicted to specially inhuman customs, as was the case with the Caribs. Anxious to be just, the monarchs decided upon sending to Haiti an officer to investigate and to punish all offenders. This visitador was invested with full power, and was to have the same authority as the monarchs themselves for the time being, superseding Columbus himself, though the latter was the Viceroy of the Indies. The visita was a mode of procedure employed by the Spanish monarchs for the adjustment of critical matters, chiefly in the colonies. The visitador was selected irrespective of rank or office, solely from the standpoint of fitness, and not infrequently his mission was kept secret from the viceroy or other high official whose conduct he was sent to investigate; there are indications that sometimes he had summary power over life and death. A visita was a much dreaded measure, and for very good reasons.
The investigation in the West Indies was not called a visita at the time, but such it was in fact. The visitador chosen was Francisco de Bobadilla, of whom both Las Casas and Oviedo (friends and admirers of Columbus) speak in favourable terms. His instructions were, as his office required, general and his faculties, of course, discretionary; there is no need of supposing secret orders inimical to Columbus to explain what afterwards happened. The admiral was directed, in a letter addressed to him and entrusted to Bobadilla, to turn over to the latter, at least temporarily, the forts and all public property on the island. No blame can be attached to the monarchs for this measure. After an experiment of five years the administrative capacity of Columbus had failed to prove satisfactory. Yet, the vice-regal power had been vested in him as an hereditary right. To continue adhering to that clause of the original contract was impracticable, since the colony refused to pay heed to Columbus and his orders. Hence the suspension of the viceregal authority of Columbus was indefinitely prolonged, so that the office was reduced to a mere title and finally fell into disuse. The curtailment of revenue resulting from it was comparatively small, as all the emoluments proceeding from his other titles and prerogatives were left untouched. The tale of his being reduced to indigence is a baseless fabrication.
A man suddenly clothed with unusual and discretionary faculties is liable to be led astray by unexpected circumstances and tempted to go to extremes. Bobadilla had a right to expect implicit obedience to royal orders on the part of all and, above all, from Columbus as the chief servant of the Crown. When on 24 August, 1500, Bobadilla landed at Santo Domingo and demanded of Diego Columbus compliance with the royal orders, the latter declined to obey until directed by the admiral who was then absent. Bobadilla, possibly predisposed against Columbus and his brothers by the reports of others and by the sight of the bodies of Spaniards dangling from gibbets in full view of the port, considered the refusal of Diego as an act of direct insubordination. The action of Diego was certainly unwise and gave colour to an assumption that Columbus and his brothers considered themselves masters of the country. This implied rebellion and furnished a pretext to Bobadilla for measures unjustifiably harsh. As visitador he had absolute authority to do as he thought best, especially against the rebels, of whom Columbus appeared in his eyes as the chief.
Within a few days after the landing of Bobadilla, Diego and Bartholomew Columbus were imprisoned and put in irons. The admiral himself, who returned with the greatest possible speed, shared their fate. The three brothers were separated and kept in close confinement, but they could hear from their cells the imprecations of the people against their rule. Bobadilla charged them with being rebellious subjects and seized their private property to pay their personal debts. He liberated prisoners, reduced or abolished imposts, in short did all he could to place the new order of things in favourable contrast to the previous management. No explanation was offered to Columbus for the harsh treatment to which he was subjected, for a visitador had only to render account to the king or according to his special orders. Early in October, 1500, the three brothers, still in fetters, were placed on board ship, and sent to Spain, arriving at Cadiz at the end of the month. Their treatment while aboard seems to have been considerate; Villejo, the commander, offered to remove the manacles from Columbus’s hands and relieve him from the chains, an offer, however, which Columbus refused to accept. It seems, nevertheless, that he did not remain manacled, else he could not have written the long and piteous letter to the nurse of Prince Juan, recounting his misfortunes on the vessel. He dispatched this letter to the court at Granada before the reports of Bobadilla were sent.
The news of the arrival of Columbus as a prisoner was received with unfeigned indignation by the monarchs, who saw that their agent Bobadilla had abused the trust placed in him. The people also saw the injustice, and everything was done to relieve Columbus from his humiliating condition and assure him of the royal favour, that is, everything except to reinstate him as Governor of the Indies. This fact is mainly responsible for the accusation of duplicity and treachery which is made against King Ferdinand. Critics overlook the fact that in addition to the reasons already mentioned no new colonists could be obtained from Spain, if Columbus were to continue in office, and that the expedient of sending convicts to Haiti had failed disastrously. Moreover, the removal of Columbus was practically implied in the instructions and powers given to Bobadilla, and the conduct of the admiral during Aguado’s mission left no room for doubt that he would submit to the second investigation. He would have done so, but Bobadilla, anxious to make a display and angered at the delay of Diego Columbus, exceeded the spirit of his instructions, expecting thereby to rise in royal as well as in popular favour.
In regard to the former he soon found out his mistake. His successor in the governorship of Haiti was soon appointed in the person of Nicolas de Ovando. Bobadilla was condemned to restore to Columbus the property he had sequestered, and was recalled. The largest fleet sent to the Indies up to that time sailed under Ovando on 13 February, 1502. It is not without significance that 2500 people, some of high rank, flocked to the vessels that were to transport the new governor to the Indies. This shows that with the change in the administration of the colony faith in its future was restored among the Spanish people. By this time the mental condition of Columbus had become greatly impaired. While at court for eighteen months vainly attempting to obtain the restoration to a position for which he was becoming more and more unfitted, he was planning new schemes. Convinced that his third voyage had brought him nearer to Asia, he proposed to the monarchs a project to recover the Holy Sepulchre by the western route, that would have led him across South America to the Pacific Ocean. He fancied that the large river he had discovered west of Trinidad flowed in a direction opposite to its real course, and thought that by following it he could reach the Red Sea and thence cross over to Jerusalem. So preoccupied was he with these ideas that he made arrangements for depositing part of his revenue with the bank of Genoa to be used in the reconquest of the Holy Land. This alone disposes of the allegations that Columbus was left without resources after his liberation from captivity. He was enabled to maintain a position at court corresponding to his exalted rank, and favours and privileges were bestowed on both of his sons. The project of testing the views of Columbus in regard to direct communication with Asia was seriously considered, and finally a fourth voyage of exploration at the expense of the Spanish Government was conceded to Columbus. That there were some misgivings in regard to his physical and mental condition is intimated by the fact that he was given as companions his brother Bartholomew, who had great influence with him, and his favourite son Fernando. Four vessels carrying, besides these three and a representative of the Crown to receive any treasure that might be found, about 150 men, set sail from San Lucar early in May, 1502. Columbus was enjoined not to stop at Haiti, a wise measure, for had the admiral landed there so soon after the arrival of Ovando, there would have been danger of new disturbances. Disobeying these instructions, Columbus attempted to enter the port of Santo Domingo, but was refused admission. He gave proof of his knowledge and experience as a mariner by warning Ovando of an approaching hurricane, but was not listened to. He himself sheltered his vessels at some distance from the harbour. The punishment for disregarding the friendly warning came swiftly; the large fleet which had brought Ovando over was, on sailing for Spain, overtaken by the tempest, and twenty ships were lost, with them Bobadillo, Roldan, and the gold destined for the Crown. The admiral’s share of the gold obtained on Haiti, four thousand pieces directly sent to him by his representative on the island, was not lost, and on being delivered in Spain, was not confiscated. Hence it is difficult to see how Columbus could have been in need during the last years of his life.
The vessels of Columbus having suffered comparatively little from the tempest, he left the coast of Haiti in July, 1502, and was carried by wind and current to the coast of Honduras. From 30 July, 1502, to the end of the following April he coasted Central America beyond Colon to Cape Tiburon on the South American Continent. On his frequent landings he found traces of gold, heard reports of more civilized tribes of natives farther inland, and persistent statements about another ocean lying west and south of the land he was coasting, the latter being represented to him as a narrow strip dividing two vast seas. The mental condition of Columbus, coupled with his physical disabilities, prevented him from interpreting these important indications otherwise than as confirmations of his vague theories and fatal visions. Instead of sending an exploring party across the isthmus to satisfy himself of the truth of these reports, he accepted this testimony to the existence of a sea beyond, which he firmly believed to be the Indian Ocean, basing his confidence on a dream in which he had seen a strait he supposed to be the Strait of Malacca. As his crews were exasperated by the hardships and deceptions, his ships worn-eaten, and he himself emaciated, he turned back towards Haiti with what he thought to be the tidings of a near approach to the Asiatic continent. It had been a disastrous voyage; violent storms continually harassed the little squadron, two ships had been lost, and the treasure obtained far from compensated for the toil and the suffering endured. This was all the more exasperating when it became evident that a much richer reward could be obtained by penetrating inland, to which, however, Columbus would not or perhaps could not consent.
On 23 June, 1503, Columbus and his men, crowded on two almost sinking caravels, finally landed on the inhospitable coast of Jamaica. After dismantling his useless craft, and using the material for temporary shelter, he sent a boat to Haiti to ask for assistance and to dispatch thence to Spain a vessel with a pitiful letter giving a fantastic account of his sufferings which in itself gave evidence of an over-excited and disordered mind.
Ovando to whom Columbus’s request for help was delivered at Jaragua (Haiti) cannot be acquitted of unjustifiable delay in sending assistance to the shipwrecked and forsaken admiral. There is no foundation for assuming that he acted under the orders or in accordance with the wishes of the sovereigns. Columbus had become useless, the colonists in Haiti would not tolerate his presence there. The only practical course was to take him back to Spain directly and remove him forever from the lands the discovery of which had made him immortal. In spite of his many sufferings, Columbus was not utterly helpless. His greatest trouble came from the mutinous spirit of his men who roamed about, plundering and maltreating the natives, who, in consequence, became hostile and refused to furnish supplies. An eclipse of the moon predicted by Columbus finally brought them to terms and thus prevented starvation. Ovando, though informed of the admiral’s critical condition, did nothing for his relief except to permit Columbus’s representative in Haiti to fit out a caravel with stores at the admiral’s expense and send it to Jamaica; but even this tardy relief did not reach Columbus until June, 1504. He also permitted Mendez, who had been the chief messenger of Columbus to Haiti, to take passage for Spain, where he was to inform the sovereigns of the admiral’s forlorn condition. There seems to be no excuse for the conduct of Ovando on this occasion. The relief expedition finally organized in Haiti, after a tedious and somewhat dangerous voyage, landed the admiral and his companions in Spain, 7 November, 1504.
A few weeks later Queen Isabella died, and grave difficulties beset the king. Columbus, now in very feeble health, remained at Seville until May, 1505, when he was at last able to attend court at Valladolid. His reception by the king was decorous, but without warmth. His importunities to be restored to his position as governor were put off with future promises of redress, but no immediate steps were taken. The story of the utter destitution in which the admiral is said to have died is one of the many legends with which his biography has been distorted. Columbus is said to have been buried at Valladolid. His son Diego is authority for the statement that his remains were buried in the Carthusian Convent of Las Cuevas, Seville, within three years after his death. According to the records of the convent, the remains were given up for transportation to Haiti in 1536, though other documents placed this event in 1537. It is conjectured, however, that the removal did not take place till 1541, when the Cathedral of Santo Domingo was completed, though there are no records of this entombment. When, in 1795, Haiti passed under French control, Spanish authorities removed the supposed remains of Columbus to Havana. On the occupation of Cuba by the United States they were once more removed to Seville (1898).
Columbus was unquestionably a man of genius. He was a bold, skilful navigator, better acquainted with the principles of cosmography and astronomy than the average skipper of his time, a man of original ideas, fertile in his plans, and persistent in carrying them into execution. The impression he made on those with whom he came in contact even in the days of his poverty, such as Fray Juan Perez, the treasurer Luis de Santangel, the Duke of Medina Sidonia, and Queen Isabella herself, shows that he had great powers of persuasion and was possessed of personal magnetism. His success in overcoming the obstacles to his expeditions and surmounting the difficulties of his voyages exhibit him as a man of unusual resources and of unflinching determination.
Columbus was also of a deeply religious nature. Whatever influence scientific theories and the ambition for fame and wealth may have had over him, in advocating his enterprise he never failed to insist on the conversion of the pagan peoples that he would discover as one of the primary objects of his undertaking. Even when clouds had settled over his career, after his return as a prisoner from the lands he had discovered, he was ready to devote all his possessions and the remaining years of his life to set sail again for the purpose of rescuing Christ’s Sepulchro from the hands of the infidel.
OTHER MEMBERS OF THE COLUMBUS FAMILY
Other members of the Columbus family also acquired fame:
Diego, the first son of Christopher and heir to his titles and prerogatives, was born at Lisbon, 1476, and died at Montalvan, near Toledo, 23 February, 1526. He was made a page to Queen Isabella in 1492, and remained at court until 1508. Having obtained confirmation of the privileges originally conceded to his father (the title of viceroy of the newly discovered countries excepted) he went to Santo Domingo in 1509 as Admiral of the Indies and Governor of Hispaniola. The authority of Diego Velazquez as governor, however, had become too firmly established, and Diego was met by open and secret opposition, especially from the royal Audiencia. Visiting Spain in 1520 he was favourably received and new honours bestowed upon him. However, in 1523, he had to return again to Spain to answer charges against him. The remainder of his life was taken up by the suit of the heirs of Columbus against the royal treasury, a memorable legal contest only terminated in 1564. Diego seems to have been a man of no extraordinary attainments, but of considerable tenacity of character.
Ferdinand, better known as Fernando Colon, second son of Christopher, by Doña Beatriz Enriquez, a lady of a noble family of Cordova in Spain, was born at Cordova, 15 August, 1488; died at Seville, 12 July 1539. As he was naturally far more gifted than his half-brother Diego, he was a favourite with his father, whom he accompanied on the last voyage. As early as 1498 Queen Isabella had made him one of her pages and Columbus in his will (1505) left him an ample income, which was subsequently increased by royal grants. Fernando had decided literary tastes and wrote well in Spanish. While it is stated that he wrote a history of the West Indies, there are now extant only two works by him: “Descripción y cosmografía de España”, a detailed geographical itinerary begun in 1517, published at Madrid in the “Boletin de la Real Sociedad geográfica” (1906-07); and the life of the admiral, his father, written about 1534, the Spanish original of which has been lost. It was published in an Italian translation by Ulloa in 1571 as “Vita dell’ ammiraglio”, and re-translated into Spanish by Barcia. “Historiadores primitivos de Indias” (Madrid, 1749). As might be expected this biography is sometimes partial, though Fernando often sides with the Spanish monarchs against his father. Of the highest value is the report by Fray Roman Pane on the customs of the Haitian Indians which is incorporated into the text. (See ARAWAKS.) Fernando left to the cathedral chapter of Seville a library of 20,000 volumes, a part of which still exists and is known as the Biblioteca Columbina.
Bartholomew
Bartholomew, elder brother of Christopher, born possibly in 1445 at Genoa; died at Santo Domingo, May, 1515. Like Christopher he became a seafarer at an early age. After his attempts to interest the Kings of France and England in his brother’s projects, his life was bound up with that of his brother. It was during his time that bloodhounds were introduced into the West Indies. He was a man of great energy and some military talent, and during Christopher’s last voyage took the leadership at critical moments. After 1506 he probably went to Rome and in 1509 back to the West Indies with his nephew Diego.
Diego, younger brother of Christopher and his companion on the second voyage, born probably at Genoa; died at Santo Domingo after 1509. After his release from chains in Spain (1500) he became a priest and returned to the West Indies in 1509.
The tract of CHRISTOPHER COLUMBUS, De prima in mari Indico lustratione, was published with the Bellum Christianorum principum of ROBERT ABBOT OF SAINT-REMI (Basle, 1533).–Codice diplomatico-Colombo-Americano, ossia Raccolia di documenti spettanti a Cr. Col., etc. (Genoa, 1823); ANON., Cr. Col. aiutato dei minorite nella scoperta del nuovo mondo (Genoa, 1846); SANGUINETTI, Vita di Colombo (Genoa, 1846); BOSSI, Vita di Cr. Col. (Milan, 1818); SPOTORNO, Della origine e della patria di Cr. Col. (Geonoa, 1819); NAVARRETE, Coleccion de los viajes y descubrimientas. . .desde fines del siglo XV (Madrid, 1825), I, II; AVEZAC-MACAYA, Annee veritable de la naissance de Chr. Col. (Paris, 1873); ROSELLY DE LORGNES, Vie et voyages de Chr. Col. (Paris, 1804), from which was compiled by BARRY, Life of Chr. Col. (New York, 1869); COLUMBUS, FERDINAND, French tr. by MULLER, Hist. de la vie et des decouvertes de Chr. Col. (Paris, s.d.); MAJOR (tr.), Select Letters of Chr. Col. (London, 1847 and 1870); HARRISSE, Fernando Colon historiador de du padre (Seville, 1871); VIGNAUD, La maison d’Alba et les archives colombiennes (Paris, 1901); l’HAGON, La Patria dr Colon segun los documentos de las ordenes militares (Madrid, 1892); UZIELLO in Congresso geografico italiano; Atti for April, 1901, Tascanelli, Colombo e Vespucci (Milan, 1902); WINSOR, Christopher Columbus (Boston, 1891); ADAMS, Christopher Columbus, in Makers of America (New York, 1892); DURO, Colon y la Historia Postuma (Madrid, 1885); THACHER, Christopher Columbus: His Life, His Work, His Remains (3 vols., New York, 1903-1904); IRVING, Life and Voyages of Christopher Columbus (3 vols., New York, 1868); PETER MARTYR, Dr orbe nova (Alcala, 1530); LAS CASAS, Historia de las Indias in Documentas para la historia de Espana; OVIEDO, Hist. general (Madrid, 1850). The last three authors had personal intercourse with Columbus, and their works are the chief source of information concerning him. CLARKE, Christopher Columbus in The Am. Cath. Quart. Rev. (1892); SHEA, Columbus, This Century’s Estimate of His Life and Work (ibid.); U.S. CATH. HIST. SOC., The Cosmographier Introductio of Martin Waldseemuller (New York, 1908).
The Catholic Encyclopedia, Volume IV Copyright © 1908 by Robert Appleton Company Online Edition Copyright © 1999 by Kevin Knight Nihil Obstat. Remy Lafort, Censor Imprimatur. +John M. Farley, Archbishop of New York

- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
The Ships of Christopher Columbus Were Sleek, Fast—and Cramped
By: Dave Roos
Updated: July 28, 2023 | Original: October 9, 2019

On August 3, 1492, Christopher Columbus and his crew set sail from the port of Palos in southern Spain on three vessels: la Santa Clara (Niña), la Pinta and la Santa Gallega (Santa Maria). Two of the ships, the Niña and Pinta, were tiny by today’s standards—only 50 to 70 feet from bow to stern—but prized for their speed and maneuverability. The Santa Maria, Columbus’s flagship, was a larger, heavier cargo ship.
For 35 days, Columbus and his crew of 86 Spanish sailors sailed westward searching for a passage to China and India. With the men close to mutiny against their “foreign” captain, Columbus was about to turn back when the cry went out at 2 a.m. on October 12 that land had been sighted .
Columbus hadn’t found a western route to India, of course, but his success in crossing the Atlantic was due in large part to the ships he chose for the perilous voyage, particularly the diminutive Niña and Pinta, which were a speedy type of ship called a caravel.
When the royal decree went out in 1492 from Queen Isabella of Spain to fund Columbus’s first voyage, it read , “By these presents, we dispatch the noble man Christoforus Colón with three equipped caravels over the Ocean Seas toward the regions of India for certain reasons and purposes.”

Caravels Were Cutting Edge in the 15th Century
Though only two of Columbus’s ships ended up being caravels, Isabella’s decree speaks to the popularity of the vessel during the 15th-century “ Age of Discovery .” Starting with Portuguese explorations of the African coast in the mid-1400s, caravels were prized for their sleek, lightweight hull and their uncanny ability to sail into the wind.
Luis Filipe Viera de Castro, a nautical archeologist at Texas A&M University, says that the earlier Portuguese caravels, known as the caravela latina , were rigged with lateen (triangular) sails that hung at 45-degree angle to the deck.
“Lateen sails are […] almost like wings,” says Castro. “You can point the bow of the caravel with an angle of just 20 degrees off the wind and still get enough lift on the outer edge of the sail to propel forward.”
The lateen-rigged caravels were critical in the Portuguese voyages to sub-Saharan African, where strong coastal winds blow north to south. The versatile caravel could speed south along the coast and easily return to shore against the wind.
For Columbus’s maiden journey, he used a Spanish update to the caravel known as the caravela redonda , a three-masted ship where the first two masts were rigged with conventional square sails for open-ocean speed, and a third was rigged with a lateen sail for coastal maneuverability. That rigging combination made ships like the Niña and the Pinta some of the best sailing vessels of their time.
In addition to their versatile rigging options, 15th-century caravels moved the rudder to the rear center of the ship. In the 14th-century caravels popular in the Mediterranean, the rudder was still on the side, says Castro, like Viking ships. The new position allowed for far greater control.
Small Ships Offered Advantages—But Also Discomforts
Small caravels like the Niña and Pinta could only carry between 40 and 50 tons and were crewed by fewer than 30 sailors each. Their lightweight design and rounded bottom meant that they rode high in the water. This proved critical when Columbus needed to navigate the shallow island coastlines near modern-day Cuba.
The bulkier Santa Maria, which was a 110-ton cargo ship called a nau , ran aground on Christmas Day 1492 and had to be abandoned.
Yet the main advantage of the Spanish caravel, namely its compact size, was also its greatest disadvantage. Life aboard a short ship like the Niña or Pinta would have been absurdly crowded and uncomfortable.
Unlike the Santa Maria, which at least had tiny cabins where sailors could sleep between eight-hour shifts, the Niña and Pinta had a single small deck at the rear of the ship with only one cramped cabin reserved for the captain.
“If you’re a sailor on a caravel, you’re living on the deck and sleeping on the deck,” says Marc Nucup, public historian at The Mariners’ Museum in Newport News, Virginia. “You’re trying to stay out of the way of the sailors who are working. There’s almost no private space.”
Work was relentless on any 15th-century ship. The 20 sailors on the Niña and the 26 crewing the Pinta would have been constantly engaged with adjusting the rigging, trimming the sails, inspecting for leaks and plugging them with spongy scraps of old rope called oakum.
“Cathedrals, castles and ships—those were the most complicated things that humans had built up until that time,” says Nucup. “There was always something to do.”
The round-the-clock workload meant that even if you were off-duty, good luck trying to sleep on the deck while the other sailors stomped around you. Hammocks weren’t yet in use on ships in the 15th century, says Nucup.

Food Aboard Ships Was Dry and Often Filled With Maggots
And then there was the food. Columbus stocked a full year’s worth of food for the journey, not knowing how long it would be before they could return to Spain. For food to last at sea, it needed to be dry. Staples included dried and salted anchovies and cod, pickled or salted beef and pork, dried grains like chickpeas, lentils and beans, and, of course, hardtack biscuits.
The word biscuit comes from the Latin bis coctus for “twice-baked.” The hardtack biscuits “enjoyed” by Columbus’s crew would have been prepared by baking a hockey puck of flour and water multiple times, then crushing it into tiny pieces, reconstituting it with water and baking it again. Hardtack biscuits were so rock solid that they could only be eaten if softened with water or dipped in the communal slurry served every meal in a large wooden trough.
Yet tooth-breaking, dry biscuits were still preferable to those that had been spoiled by exposure to water in their storage barrel. Ferdinand Columbus, the explorer’s 14-year-old son, reported on the conditions on Columbus’s fourth voyage to the Americas.
"What with the heat and dampness, our ship biscuit had become so wormy that, God help me, I saw many who waited for darkness to eat porridge made of it, that they might not see the maggots,” wrote young Ferdinand, “and others were so used to eating them that they didn't even trouble to pick them out because they might lose their supper had they been so fastidious."

HISTORY Vault: Columbus the Lost Voyage
Ten years after his 1492 voyage, Columbus, awaiting the gallows on criminal charges in a Caribbean prison, plotted a treacherous final voyage to restore his reputation.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
The First New World Voyage of Christopher Columbus (1492)
European Exploration of the Americas
Spencer Arnold/Getty Images
- Ph.D., Spanish, Ohio State University
- M.A., Spanish, University of Montana
- B.A., Spanish, Penn State University
How was the first voyage of Columbus to the New World undertaken, and what was its legacy? Having convinced the King and Queen of Spain to finance his voyage, Christopher Columbus departed mainland Spain on August 3, 1492. He quickly made port in the Canary Islands for a final restocking and left there on September 6. He was in command of three ships: the Pinta, the Niña, and the Santa María. Although Columbus was in overall command, the Pinta was captained by Martín Alonso Pinzón and the Niña by Vicente Yañez Pinzón.
First Landfall: San Salvador
On October 12, Rodrigo de Triana, a sailor aboard the Pinta, first sighted land. Columbus himself later claimed that he had seen a sort of light or aura before Triana did, allowing him to keep the reward he had promised to give to whoever spotted land first. The land turned out to be a small island in the present-day Bahamas. Columbus named the island San Salvador, although he remarked in his journal that the natives referred to it as Guanahani. There is some debate over which island was Columbus’ first stop; most experts believe it to be San Salvador, Samana Cay, Plana Cays or Grand Turk Island.
Second Landfall: Cuba
Columbus explored five islands in the modern-day Bahamas before he made it to Cuba. He reached Cuba on October 28, making landfall at Bariay, a harbor near the eastern tip of the island. Thinking he had found China, he sent two men to investigate. They were Rodrigo de Jerez and Luis de Torres, a converted Jew who spoke Hebrew, Aramaic, and Arabic in addition to Spanish. Columbus had brought him as an interpreter. The two men failed in their mission to find the Emperor of China but did visit a native Taíno village. There they were the first to observe the smoking of tobacco, a habit which they promptly picked up.
Third Landfall: Hispaniola
Leaving Cuba, Columbus made landfall on the Island of Hispaniola on December 5. Indigenous people called it Haití but Columbus referred to it as La Española, a name which was later changed to Hispaniola when Latin texts were written about the discovery. On December 25, the Santa María ran aground and had to be abandoned. Columbus himself took over as captain of the Niña, as the Pinta had become separated from the other two ships. Negotiating with the local chieftain Guacanagari, Columbus arranged to leave 39 of his men behind in a small settlement, named La Navidad .
Return to Spain
On January 6, the Pinta arrived, and the ships were reunited: they set out for Spain on January 16. The ships arrived in Lisbon, Portugal, on March 4, returning to Spain shortly after that.
Historical Importance of Columbus' First Voyage
In retrospect, it is somewhat surprising that what is today considered one of the most important voyages in history was something of a failure at the time. Columbus had promised to find a new, quicker route to the lucrative Chinese trade markets and he failed miserably. Instead of holds full of Chinese silks and spices, he returned with some trinkets and a few bedraggled Indigenous people from Hispaniola. Some 10 more had perished on the voyage. Also, he had lost the largest of the three ships entrusted to him.
Columbus actually considered the Indigenous people his greatest find. He thought that a new trade of enslaved people could make his discoveries lucrative. Columbus was hugely disappointed a few years later when Queen Isabela, after careful thought, decided not to open the New World to the trading of enslaved people.
Columbus never believed that he had found something new. He maintained, to his dying day, that the lands he discovered were indeed part of the known Far East. In spite of the failure of the first expedition to find spices or gold, a much larger second expedition was approved, perhaps in part due to Columbus’ skills as a salesman.
Herring, Hubert. A History of Latin America From the Beginnings to the Present. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1962
Thomas, Hugh. "Rivers of Gold: The Rise of the Spanish Empire, from Columbus to Magellan." 1st edition, Random House, June 1, 2004.
- La Navidad: First European Settlement in the Americas
- The Second Voyage of Christopher Columbus
- Explorers and Discoverers
- The Road to the American Revolution
- Amerigo Vespucci, Explorer and Navigator
- The Untold History of Native American Enslavement
- The Early American Colonial Regions
- History of the Plymouth Colony
- The Mayflower Compact of 1620
- Facts About the Jamestown Colony
- American Revolution: Battle of Nassau
- American Revolution: The Boston Massacre
- Check Your Knowledge: A 'New World' Discovered
- The Albany Plan of Union
- Chart of the 13 Original Colonies
- The Original 13 U.S. States
- Art History
- U.S. History
Christopher Columbus

But does everyone actually know Christopher Columbus’ actual life and struggles? Here is a brief look at some of the important highlights of his life, making him one of the greatest navigators and explorers of all time.
The Migrant Italian
Nobody would have thought that the son of a cheese maker and wool weaver would literally discover a lot of new places about the world. Cristoforo Colombo (Latinized as Christopher Columbus) regularly assisted his father Domenico in running the trade they had in their hometown of Genoa (despite coming from the beaches of Liguria) in Italy, along with his brothers Giacomo and Giovani Pellegrino . Their life could have been normal all throughout, until Domenico decided to migrate to Savona. He owned a tavern and called the new place their home in 1470.
The trade-oriented Christopher, however, went back to Genoa three years later to serve as an apprentice to three famous Italian families, namely the Centurione, the Spinola, and the Di Negro. And because of their trade activities, he was sent to many places around Europe, like Bristol, England, Ireland, and Lisbon in Portugal.
In the course of these travels, he fell in love with and married Filipa Moniz Perestrelo, the daughter of the famous Bartolomeo Perestrelo of Portugal. In 1479, they had their first and only son Diego, and after spending some time with his infant, Christopher Columbus set sail again to the Portuguese trading posts along Guinea as well as the surrounding islands.
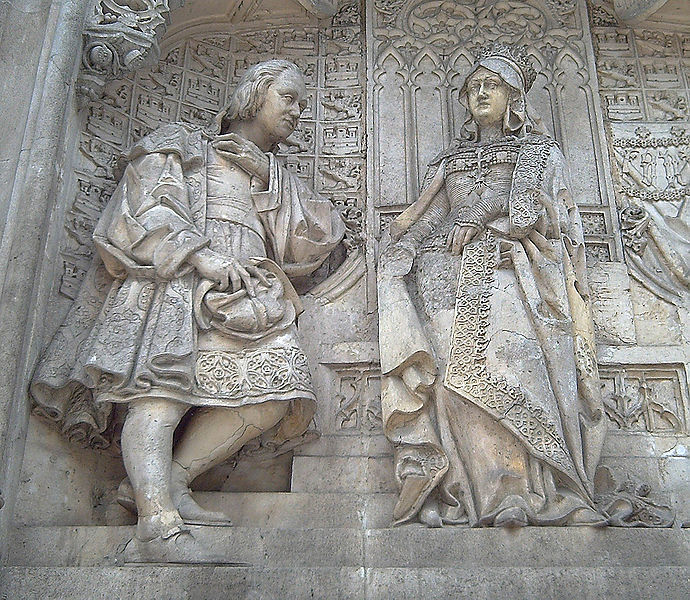
However, in 1485, the path of love took a different course, as it was said that Christopher either left his wife or heard about the death of Filipa. Either way, he found a new lover in Beatriz de Arana, a 20-year old orphan who became his mistress two years later.
Knowledge is the Key
During his work as an apprentice, he was able to extensively read various languages, including Latin, and read books discussing subject matters like astronomy, geometry, history, and trading.
One important thing that he came across in the course of all these is his readings on Greek and Roman geometry which played with the possibility of the roundness of the earth, instead of the widely accepted flatness of it. This has been backed up by his own experience as a trade apprentice, who observed the directions of the winds along the sea, as well as his skill in cartography. He found the theory to be plausible, as he pondered on his experiences and the possible explanation offered for it using Ptolemy’s geometrics.
Eventually, his curiosity and drive for knowledge was fueled, and this pushed him to do that which would surprise the rulers of Europe at that time.
The Four Voyages
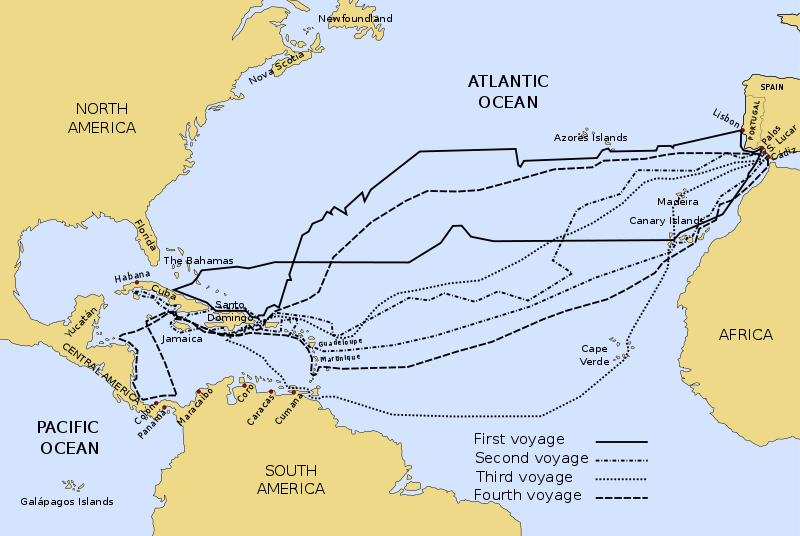
Grounded in his belief of this possibility, he went on to propose his ideas to John II of Portugal by finding the Western route to the orient. Unfortunately, he was denied by John, on the grounds that his estimated distance was way shorter than what was usual.
Being rejected by Portugal, he took his research and findings at Genoa and England to prove them, but was rejected again. He then went straight to Spain to ask for an audience with Ferdinand and Isabella, the King and Queen of Spain. After his conversation with them, the Spanish Crown granted him funds for the sake of occupying lands in the Orient as part of the Spanish colonies.
First Voyage
Finally, it was only in 1492 that Columbus was able to leave Cadiz, Spain with three ships, the Gallega, Pinta and Santa Clara. His mission now was to occupy land, and as a reward, he will stand as the governor of those territories.

After staying for a few days, Columbus eventually moved towards Cuba and Hispaniola, reaching the La Navidad as shelter. In there, he was able to come across the Samana Peninsula, which he named as the “Bay of Arrows,” because the hostile Ciguayo tribesmen used their arrows to resist Columbus’ fleet.
Fortunately, Christopher Columbus’ men were able to resist them, and taking about 20 tribesmen as proof to the Spanish Crown, they took off and returned to Palos, Spain on March 15, 1943.
Second Voyage
His report on the voyage alongside his proofs impressed Ferdinand and Isabella, granting him another chance to expand the Spanish colonies in a second voyage. This one left Cadiz in September 1493, and he now had 17 ships with about 1,000 men for purposes of colonization and conversion into Christianity. The men were promised riches and abundance once they transferred these lands to the Spanish government.
A month later, after a stopover at the Canary Islands for replenishment of supplies and ship repairs (which he had also done in the first voyage), he set off again, but this time, he took a more southwestern route.
For this voyage, Columbus’ objective was to discover and claim the islands near Cuba. Influenced by his religiosity and his desire to convert natives into the Christian religion, he named these islands after various Christian saints and patrons. Some of these included the Santa Maria de Guadalupe, and further north, there were Montserrat, St. Kitts, Nevis, and Saint Croix, after the Holy Cross where Christ was crucified.
After these islands, he landed at Puerto Rico , rescuing two Spanish men found to be castrated by the natives. He also headed back and looked at how Cuba and Jamaica were doing, before retracing his path in Hispaniola back to Spain.
Third Voyage
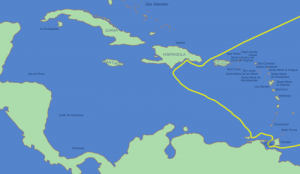
His success in discovering new lands and claiming them for the Spanish Crown made him more well-known everywhere, and more than that, as part of the agreement he had with Spain, he was named the governor of Hispaniola. Later on, he was given an opportunity for a third voyage. For this, he left Sanlucar, Spain on May 30, 1498.
This time, he dared to go on a more southern route, heading towards Cape Verde and eventually reaching the river of Orinoco, as well as two places in the present South American mainland which he later named Tobago and Grenada. His arrival along the Orinoco River marked the second time that an explorer reached and stepped on the mainland; the first instance was done by the famous Viking Leif Ericson .
Christopher Columbus encountered a huge conflict in his life as an explorer when he passed by Hispaniola and heard about the discontent of the Spanish settlers, claiming that they had not found riches in this place. Columbus, however, said that the riches found in Hispaniola were that of people, as he believed that the natives could be acquired as slaves to be brought to the West.
Also, while staying in that place, he had some of his disobedient crewmen hanged, along with a few settlers. Because of this, he was accused of tyranny and abuse by 23 witnesses, and by his return, he and his brothers were chained and put to jail.
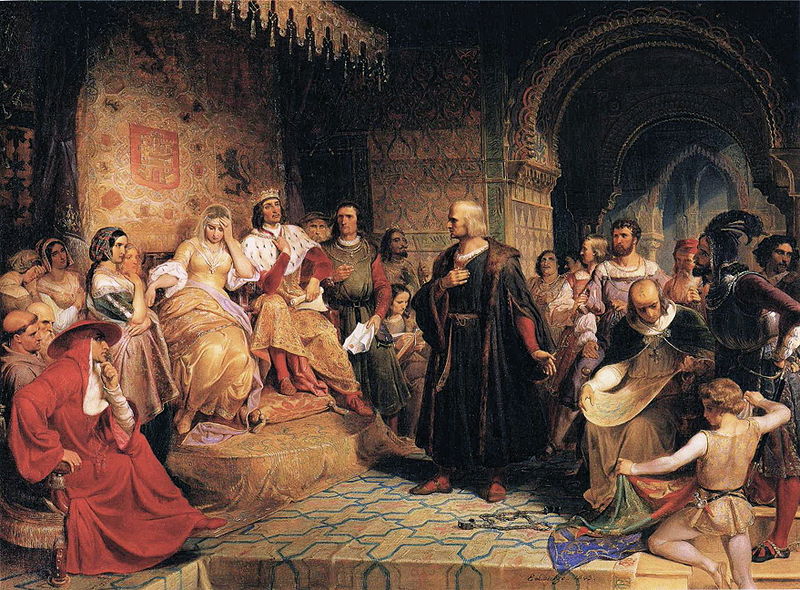

However, it was found out that he indeed used methods of torture to control the natives of Hispaniola. Due to that, he and his brothers remained in jail for six weeks until King Ferdinand had him released just in time for a fourth voyage. While he regained his freedom, he was not able to regain his position as governor. Instead, the Spanish Crown named Fray Nicolás de Ovando y Cáceres the governor of Hispaniola.
Fourth Voyage
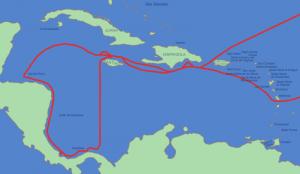
Christopher Columbus left Cadiz with his brothers along four ships, namely the Gallega, the Capitana, the Santiago de Palos, and the Vizcaina on May 11, 1502. His aim now was to find the Malaccan strait, which would serve as his access to the Indian Ocean. But he took care of other businesses first when he went to Arzila in the coast of Morocco to rescue soldiers held captive by Muslim warriors.
He then took a quick rest at Martinica, but during the time he continued his journey, a storm began to form. He planned to find shelter in Hispaniola, but was denied by the governor. His crew instead went to the island of Rio Jaina to let the storm calm down.
After the storm (and after dealing with the ship’s minor damages), he sailed to Jamaica and returned to the South American mainland where he landed at Guanaja. He then explored the South American coasts of Honduras, Costa Rica , and Nicaragua , eventually reaching Panama on October 16, 1502.
He stayed for two months exploring the mainland, but in the middle of things, they encountered a storm, much greater than the one in Rio Jaina . Columbus mentioned in his diary that it rained for nine straight days, and most of his crew was in despair, tired and with nothing to see except the turmoil of the seas.
Once the storm was gone, he sailed back to Panama and established a garrison in Rio Belen in January 1504. On his way there, he sighted the present Cayman Islands, and due to the number of sea turtles, named it Las Tortugas. He also headed back to Cuba , where he encountered another storm that forced him to just settle at St. Ann’s Bay in Jamaica for over a year.
Columbus’ crew was stuck there, before Diego Mendez and a few natives went to Hispaniola to ask for help by the use of canoes. But still, the governor refused to offer assistance. Out of desperation, Columbus asked for the help of the natives by predicting the next lunar eclipse for them, in exchange for providing them supplies and repairing their boats. Thanks to the astronomical table named Ephemeris, he was able to impress the natives and they in turn believed in him and helped him return home. He then left on June 29, arriving in Sanlucar on November 7, which marked the end of his great American voyages.
His Later Years
Columbus settled in Valladolid , a small town in central Spain, and it was said that he became a very religious man in his later years.
It was also said that with Diego, he published books containing the fruits of his expeditions. The first was the Book of Privileges, an account of the benefits and rewards he was entitled to from his deal with the Spanish Crown. The second, the Book of the Prophecies, was more religious in nature, where he used several scriptures from the Bible to claim that his achievements were part of God’s plan in the history of salvation.

Later on, he demanded through a series of legal demands and claims that the crown should give him a tenth of all the profits from all the lands that he had explored. Of course, the Spanish Crown rejected his demands; however, the lengthy legal process named pleitos colombinos ended in arbitration, subsequently giving Columbus the title of “Admiral of Indies” and the possession of Jamaica and Hispaniola , together with a payment of 1000 ducats.
On May 20, 1506, Columbus died of a heart attack due to arthritis (as claimed by researchers in 2003), in Valladolid . He was then buried in the La Cartuja monastery in Seville. At that time, he was known as one of the richest voyagers in Spain due to the massive amounts of gold that he was able to acquire in Hispaniola.
But then, it was not Columbus’ riches that made him significant as an Italian explorer. Rather, it was his painstaking hard work during all his four voyages that gave him the knowledge and the right to rule over the New World, thereby opening the gates for the formation of another colonial empire. It is in this aspect where Christopher Columbus’ greatness lies.

Newest Additions
- Malala Yousafzai
- Greta Thunberg
- Frederick Douglass
- Wangari Maathai
Copyright © 2020 · Totallyhistory.com · All Rights Reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Contact Us
We’re fighting to restore access to 500,000+ books in court this week. Join us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
A History of the Life and Voyages of Christopher Columbus
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
1,955 Views
4 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
For users with print-disabilities
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by Unknown on July 5, 2008
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
10 Famous Explorers Whose Discoveries Connected the World
From Christopher Columbus to Marco Polo, these celebrated—and controversial—explorers made groundbreaking journeys across the globe.

Some of these explorers, like Christopher Columbus , are both celebrated and vilified today. Others, like Ferdinand Magellan and Francisco Pizarro , were met with violent and untimely deaths. And some, like Marco Polo , failed to received recognition in their lifetime, only to have their discoveries confirmed centuries later.
Learn more about some of the history’s most famous explorers and what they are remembered for today.
Time Period: Late 13 th century Destination: Asia

Marco Polo was a Venetian explorer known for the book The Travels of Marco Polo , which describes his voyage to and experiences in Asia. Polo traveled extensively with his family, journeying from Europe to Asia from 1271 to 1295, remaining in China for 17 of those years. As the years wore on, Polo rose through the ranks, serving as governor of a Chinese city. Later, Kublai Khan appointed him as an official of the Privy Council. At one point, he was the tax inspector in the city of Yanzhou.
Around 1292, he left China, acting as consort along the way to a Mongol princess who was being sent to Persia. In the centuries since his death, Polo has received the recognition that failed to come his way during his lifetime. So much of what he claimed to have seen has been verified by researchers, academics, and other explorers. Even if his accounts came from other travelers he met along the way, Polo’s story has inspired countless other adventurers to set off and see the world.
Christopher Columbus
Time Period: Turn of the 16 th century Destination: Caribbean and South America
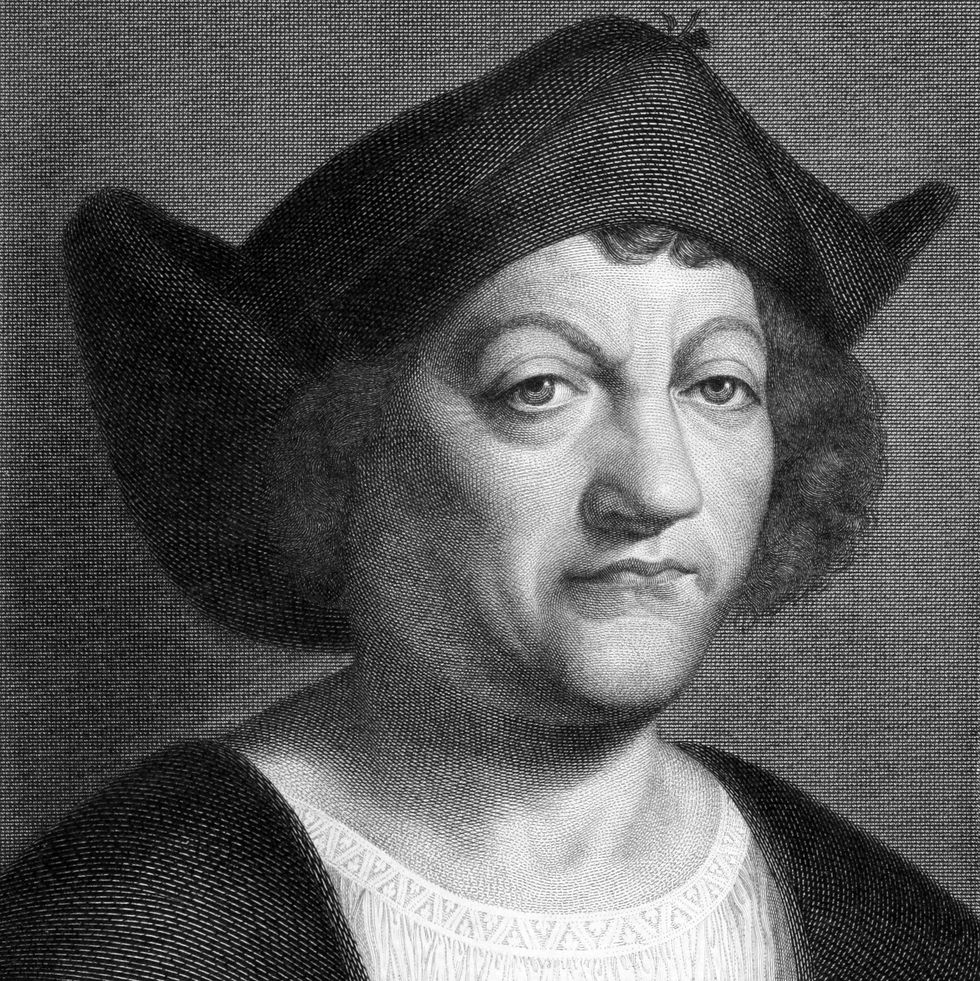

Christopher Columbus was an Italian explorer and navigator. Columbus first went to sea as a teenager, participating in several trading voyages in the Mediterranean and Aegean seas. One such voyage, to the island of Khios, in modern-day Greece, brought him the closest he would ever come to Asia.
In 1492, he sailed across the Atlantic Ocean from Spain in the Santa Maria , with the Pinta and the Niña ships alongside, hoping to find a new route to India. Between that year and 1504, he made a total of four voyages to the Caribbean and South America and has been credited—and blamed —for opening up the Americas to European colonization. Columbus died in May 1506, probably from severe arthritis following an infection, still believing he had discovered a shorter route to Asia.
More about Christopher Columbus
Amerigo Vespucci
Time period: turn of the 16 th century destination: south america.

America was named after Amerigo Vespucci , a Florentine navigator and explorer who played a prominent role in exploring the New World.
On May 10, 1497, Vespucci embarked on his first voyage, departing from Cadiz with a fleet of Spanish ships. In May 1499, sailing under the Spanish flag, Vespucci embarked on his next expedition, as a navigator under the command of Alonzo de Ojeda. Crossing the equator, they traveled to the coast of what is now Guyana, where it’s believed that Vespucci left Ojeda and went on to explore the coast of Brazil. During this journey, Vespucci is said to have discovered the Amazon River and Cape St. Augustine.
On his third and most successful voyage, he discovered present-day Rio de Janeiro and Rio de la Plata. Believing he had discovered a new continent, he called South America the New World. In 1507, America was named after him . He died of malaria in Seville, Spain, in February 1512.
More about Amerigo Vespucci
Time Period: Late 15 th century Destination: Canada

John Cabot was a Venetian explorer and navigator known for his 1497 voyage to North America, where he made a British claim to land in Canada, mistaking it for Asia . The precise location of Cabot’s landing is subject to controversy. Some historians believe that Cabot landed at Cape Breton Island or mainland Nova Scotia. Others believe he might have landed at Newfoundland, Labrador, or even Maine.
In February 1498, Cabot was given permission to make a new voyage to North America. The May, he departed from Bristol, England, with five ships and a crew of 300 men. En route, one ship became disabled and sailed to Ireland, while the other four ships continued on. On the journey, Cabot disappeared, and his final days remain a mystery. It’s believed Cabot died sometime in 1499 or 1500, but his fate remains a mystery.
More about John Cabot
Ferdinand Magellan
Time Period: Early 16 th century Destination: Global circumnavigation
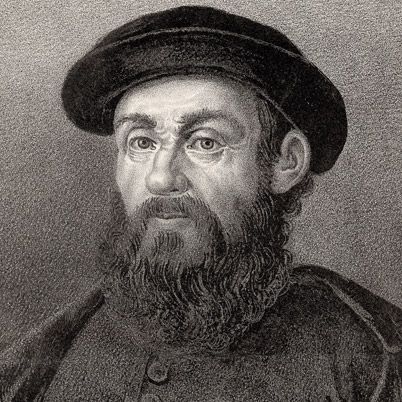

While in the service of Spain, Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan led the first European voyage of discovery to circumnavigate the globe. As a boy, Magellan studied mapmaking and navigation. In 1505, when Magellan was in his mid-20s, he joined a Portuguese fleet that was sailing to East Africa. By 1509, he found himself at the Battle of Diu, in which the Portuguese destroyed Egyptian ships in the Arabian Sea. Two years later, he explored Malacca, located in present-day Malaysia, and participated in the conquest of Malacca’s port.
In 1519, with the support of Holy Roman Emperor Charles V (also known as Spain’s King Charles I), Magellan set out to find a better route to the Spice Islands. In March 1521, Magellan’s fleet reached Homonhom Island on the edge of the Philippines with less than 150 of the 270 men who started the expedition. Magellan traded with the island’s king Rajah Humabon, and their bond quickly formed. The Spanish crew soon became involved in a war between Humabon and another rival leader, and Magellan was killed in battle in April 1521.
More about Ferdinand Magellan
Hernán Cortés
Time period: 16 th century destination: central america.

Hernán Cortés was a Spanish conquistador who explored Central America, overthrew Montezuma and his vast Aztec empire, and won Mexico for the crown of Spain. He first set sail to the New World at the age of 19. Cortés later joined an expedition to Cuba.
In 1518, he set off to explore Mexico. Cortés became allies with some of the Indigenous peoples he encountered there, but with others, he used deadly force to conquer Mexico . He fought Tlaxacan and Cholula warriors and then set his sights on taking over the Aztec empire. In their bloody battles for domination over the Aztecs, Cortés and his men are estimated to have killed as many as 100,000 Indigenous peoples. In his role as the Spanish king, Emperor Charles V appointed him the governor of New Spain in 1522.
More about Hernán Cortés
Sir Francis Drake
Time period: late 16 th century destination: global circumnavigation.

English admiral Sir Francis Drake was the second person to circumnavigated the globe and was the most renowned seaman of the Elizabethan era. In 1577, Drake was chosen as the leader of an expedition intended to pass around South America, through the Strait of Magellan, and explore the coast that lay beyond. Drake successfully completed the journey and was knighted by Queen Elizabeth I upon his triumphant return in 1580.
In 1588, Drake saw action in the English defeat of the Spanish Armada , though he died in 1596 from dysentery after undertaking an unsuccessful raiding mission.
More about Francis Drake
Sir Walter Raleigh
Time Period: Late 16 th century Destination: United States

Sir Walter Raleigh was an English explorer, soldier, and writer. At age 17, he fought with the French Huguenots and later studied at Oxford. He became a favorite of Queen Elizabeth I after serving in her army in Ireland. He was knighted in 1585 and, within two years, became captain of the Queen’s Guard.
An early supporter of colonizing North America, Raleigh sought to establish a colony, but the queen initially forbade him to leave her service. Between 1585 to 1588, he invested in a number of expeditions across the Atlantic, attempting to establish a colony near Roanoke, on the coast of what is now North Carolina, and name it “Virginia” in honor of the virgin queen, Elizabeth. Accused of treason by King James I, Raleigh was imprisoned and eventually put to death.
More about Walter Raleigh
Time Period: Late 18 th century Destination: New Zealand and Australia

James Cook was a naval captain, navigator, and explorer. After serving as an apprentice, Cook eventually joined the British Navy and, at age 29, was promoted to ship’s master. During the Seven Years War that began in 1756, he commanded a captured ship for the Royal Navy. Then, in 1768, he took command of the first scientific expedition to the Pacific.
In 1770, on his ship the HMB Endeavour , Cook charted New Zealand and the Great Barrier Reef of Australia. This area has since been credited as one of the world’s most dangerous areas to navigate . He later disproved the existence of Terra Australis, a fabled southern continent. Cook’s voyages helped guide generations of explorers and provided the first accurate map of the Pacific.
More about James Cook
Francisco Pizarro
Time period: early 16 th century destination: central and south america.

In 1513, Spanish explorer and conquistador Francisco Pizarro joined Vasco Núñez de Balboa in his march to the “South Sea,” across the Isthmus of Panama. During their journey, Balboa and Pizarro discovered what is now known as the Pacific Ocean, though Balboa allegedly spied it first and was therefore credited with the ocean’s first European discovery.
In 1528, Pizarro went back to Spain and managed to procure a commission from Emperor Charles V. Pizarro was to conquer the southern territory and establish a new Spanish province there. In 1532, accompanied by his brothers, Pizarro overthrew the Inca leader Atahualpa and conquered Peru. Three years later, he founded the new capital city of Lima. Over time, tensions increasingly built up between the conquistadors who had originally conquered Peru and those who arrived later to stake some claim in the new Spanish province. This conflict eventually led to Pizarro’s assassination in 1541.
More about Francisco Pizarro
Watch Next .css-16toot1:after{background-color:#262626;color:#fff;margin-left:1.8rem;margin-top:1.25rem;width:1.5rem;height:0.063rem;content:'';display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;}

European Explorers

Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo

Leif Eriksson

Vasco da Gama

Bartolomeu Dias

Giovanni da Verrazzano

Jacques Marquette

René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle


Walz 'Erased Our Culture,' Says Italian-American Guy Who Thinks Pavarotti Wrote 'Nessun Dorma'
As an italian-american, i am personally insulted..

I had absolutely no idea that anyone had resurrected the Italian-American Civil Rights League (IACRL).
In case you’re not familiar, it’s an organization that, swear to God, in 1970, was founded by Joseph Colombo Sr., the boss of the Colombo crime family, after his kid was arrested for melting down coins. Its supposed mission was to defend Italian-Americans against insulting and defamatory stereotypes — like, for instance, that we are all in the mob or that we’re ignorant (the whole “they’re all anarchists!” thing had died out a few decades earlier). Its actual purpose was to deny the existence of the mob and get people to stop talking about the mob so that Joseph Colombo Sr. and others could do more mob crimes. Their most notable accomplishment was getting the Justice Department to stop using the words “mafia” and “cosa nostra” and getting those words taken out of The Godfather , which surely prevented everyone from knowing it was about the mafia.
They were also in cahoots with the Jewish Defense League, a violent Southern Poverty Law Center-designated hate group.
For some reason, it’s made a comeback, and the only reason I know this is because some guy who claims to be on its board is out here losing his shit because Tim Walz didn’t stop activists from tearing down a statue of Christopher Columbus.
Loving this post? Not a free or paid subscriber yet? Let’s fix that!
Mike Crispi, who is best known as the guy on whose Rumble show George Santos compared himself to Rosa Parks, clearly thinks he’s found a real winner of an issue with which to attack America’s Dad, Tim Walz.
“Tim Walz is an enemy of the Italian American Community,” Mike Crispi wrote, quite disingenuously, on social media. “He has a long history of being in favor of erasing our culture. He strongly has supported the removal of Christopher Columbus statues. We will call it for what it is: racism.”
No. That is definitely not what that is. First of all, Italian-Americans are not a race. Second, no one is mad at Christopher Columbus for being Italian (he wasn’t, he was Genoese, no one was Italian back then, and he sailed under the Spanish flag), they are mad at him for the whole “genocidal maniac” thing. Big, big difference.

I Am An Italian-American And I Think Columbus Day Is Garbage
Personally, I think it’s rude to assume that the rest of us want to be associated with someone so famous for enslaving and massacring people, someone who was such a genocidal maniac, the Spanish queen locked him up (temporarily, before restoring his wealth and funding his next voyage). That’s at least as embarrassing as people thinking we’re all connected, without any of the interpersonal convenience of people assuming there’s a chance you could have them taken care of if you wanted. (I KID.)
Attached to the post, he quoted himself in a sad little press release:
Italian American Civil Rights League Board Member Mike Crispi today denounced Minnesota Governor Tim Walz for allowing roving mobs of left-wing criminals to destroy the State statue of Christopher Columbus. "Tim Walz did nothing to stop radical vandals from targeting the most prominent symbol of Italian-American culture in a flagrant hate crime," Crispi said. "He knew they were coming and he did nothing to protect the statue." […] Crispi went on to say private emails among Walz staff revealed the reason why. In order to placate indigenous activists and other anti-Italian-American sympathizers, Walz and his cronies colluded to keep the statue down," Crispi said. "They hate the Western tradition that made America great and they will do anything to undermine it and destroy our country from within."
There is a whole lot that is gross about calling indigenous activists or anyone else who opposes celebrating Columbus “anti-Italian-American.” Especially since, again, many Italian-Americans feel the same way.
Crispi, meanwhile, is the absolute last person who should ever accuse anyone of disrespecting Italian culture. I only had to scroll a little bit down the IACRL Twitter feed to see a tweet in which he wrote “Trump concluding the convention with classic Italian music from Pavarotti was PERFECT! IACRL approved!” and shared a video of the MAGA tenor singing Nessun Dorma .
Donate Just Once!
This can mean only one of two things — he thinks that guy is Luciano Pavarotti, who has been rather dead since 2007, or he thinks that Nessun Dorma, a very famous aria from Puccini’s Turandot , is a Pavarotti original.
Now that’s disrespectful to Italian culture.

Italian Tenor Serenades Florence With Lovely Aria About Wanting To Marry A Very Murder-y Princess
I will note, however, that it is a fairly poetic choice, given that it’s a song sung by a man who is waiting to find out if a woman will kill him.
Thank you for reading Wonkette. This post is public so feel free to share it with everyone you love (or hate).
Ready for more?

COMMENTS
The explorer Christopher Columbus made four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean from Spain: in 1492, 1493, 1498 and 1502. His most famous was his first voyage, commanding the ships the Nina, the ...
Between 1492 and 1504, the Italian navigator and explorer Christopher Columbus [a] led four transatlantic maritime expeditions in the name of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain to the Caribbean and to Central and South America. These voyages led to the widespread knowledge of the New World.This breakthrough inaugurated the period known as the Age of Discovery, which saw the colonization of the ...
Christopher Columbus, the intrepid Italian explorer, embarked on a historic voyage across the Atlantic in 1492 and opened up new horizons for European exploration and colonization.
Christopher Columbus[ b] ( / kəˈlʌmbəs /; [ 2] between 25 August and 31 October 1451 - 20 May 1506) was an Italian [ 3][ c] explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed four Spanish-based voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs, opening the way for the widespread European exploration and colonization of the Americas. His expeditions were ...
Columbus' journeys, by contrast, opened the way for later European expeditions, but he himself never claimed to have discovered America. The story of his "discovery of America" was established and first celebrated in A History of the Life and Voyages of Christopher Columbus by the American author Washington Irving (l. 1783-1859 CE) published in 1828 CE and this narrative (largely fictional ...
Italian explorer Christopher Columbus discovered the "New World" of the Americas on a 1492 expedition. Learn about his landing spot, route, ships, and more.
Christopher Columbus - Explorer, Voyages, New World: The ships for the first voyage—the Niña, Pinta, and Santa María—were fitted out at Palos, on the Tinto River in Spain. Consortia put together by a royal treasury official and composed mainly of Genoese and Florentine bankers in Sevilla (Seville) provided at least 1,140,000 maravedis to outfit the expedition, and Columbus supplied more ...
Christopher Columbus leaving Palos, Spain Christopher Columbus aboard the "Santa Maria" leaving Palos, Spain on his first voyage across the Atlantic Ocean. The Mariners' Museum 1933.0746.000001 Introduction We know that In 1492, Columbus sailed the ocean blue. But what did he actually discover?
In October 1501 Columbus went to Sevilla to make ready his fourth and final expedition. Christopher Columbus - Exploration, Caribbean, Americas: The gold, parrots, spices, and human captives Columbus displayed for his sovereigns at Barcelona convinced all of the need for a rapid second voyage. Columbus was now at the height of his popularity ...
Christopher is best known for his maiden voyage across the Atlantic in 1492. Learn about the three trips Columbus made to the New World in the decade following his first journey.
The Book of Privileges is a collection of agreements between Columbus and the crowns of Spain prepared in Seville in 1502 before his 4th and final voyage to America. The compilation of documents includes the 1497 confirmation of the rights to titles and profits granted to the Admiral by the 1492 Contract of Santa Fé and augmented in 1493 and ...
Learn about the life and voyages of Christopher Columbus, the famous explorer who changed the course of history, in this original video.
Between 1485 and 1488 Columbus began his relations with Doña Beatriz Enriquez de Arana, or Harana, of a good family of the city of Cordova, from which sprang his much beloved son Fernando, next to Christopher and his brother Bartholomew the most gifted of the Colombos.
Two of Christopher Columbus' ships were so small that men had no refuge to sleep and poor food storage led to wormy meals.
How was the first voyage of Columbus to the New World undertaken, and what was its legacy? Having convinced the King and Queen of Spain to finance his voyage, Christopher Columbus departed mainland Spain on August 3, 1492. He quickly made port in the Canary Islands for a final restocking and left there on September 6.
An animation of Christopher Columbus life and voyages. This video will answer various questions:What are the 4 voyages of Columbus?Where did Christopher Colu...
A History of the Life and Voyages of Christopher Columbus is a fictional biographical account of Christopher Columbus written by Washington Irving in 1828. It was published in four volumes in Britain and in three volumes in the United States.
Christopher Columbus - Exploration, Caribbean, Legacy: The winter and spring of 1501-02 were exceedingly busy. The four chosen ships were bought, fitted, and crewed, and some 20 of Columbus's extant letters and memoranda were written then, many in exculpation of Bobadilla's charges, others pressing even harder the nearness of the Earthly Paradise and the need to reconquer Jerusalem ...
by Irving, Washington, 1783-1859 Publication date 1828 Topics Columbus, Christopher Publisher London : John Murray Collection cdl; americana Contributor University of California Libraries Language English Volume 1 Item Size 915089735 4 v. 22 1/2 cm BAL 10123: first London edition; vol. I-IV, setting A; vol. IV, p. 393, state 2
Christopher Columbus The name "Christopher Columbus" is a household name, especially among people who are familiar with the history of the Americas. He is popular because he was the explorer who tried to prove that the world was round by sailing across the seas and trying to reach other, unexplored regions on the globe, eventually making a mistake that would mark the beginning of a ...
by Washington Irving Publication date 1828 Topics columbus, voyages, roldan, admiral, las, christopher, island, cacique, spaniards, adelantado, las casas, white men, hist del, south side, boca del, set sail, public domain, young indian, southern side, pedro alonzo Publisher G. & C. Carvill Collection americana Book from the collections of ...
A timeline of major events in the life of Italian-born navigator and explorer Christopher Columbus, whose four transatlantic voyages (1492-93, 1493-96, 1498-1500, and 1502-04) opened the way for European exploration, exploitation, and colonization of the Americas.
Some people mistakenly think that Christopher Columbus was the first person to suggest that the world was round, leading to his travels to America.
From Christopher Columbus to Marco Polo, these celebrated—and controversial—explorers made groundbreaking journeys across the globe.
The voyages of Christopher Columbus, the Knights of Columbus namesake namesake, were an important moment in history. He has been recently recast as a villain
Italian American Civil Rights League Board Member Mike Crispi today denounced Minnesota Governor Tim Walz for allowing roving mobs of left-wing criminals to destroy the State statue of Christopher Columbus.