Advertisement

How Cruise Control Systems Work
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email

Cruise control is an invaluable feature on American cars. Without cruise control, long road trips would be more tiring, for the driver at least, and those of us suffering from lead-foot syndrome would probably get a lot more speeding tickets.
Cruise control is far more common on American cars than European cars, because the roads in America are generally bigger and straighter, and destinations are farther apart. With traffic continually increasing, basic cruise control is becoming less useful, but instead of becoming obsolete, cruise control systems are adapting to this new reality -- soon, cars will be equipped with adaptive cruise control, which will allow your car to follow the car in front of it while continually adjusting speed to maintain a safe distance.
In this article, we'll learn how a conventional cruise control system works, and then we'll take a look at adaptive cruise control systems that are under development.
What Cruise Control Does
Cruise control acceleration and deceleration, controlling the cruise control, adaptive cruise control.

The cruise control system actually has a lot of functions other than controlling the speed of your car. For instance, the cruise control pictured below can accelerate or decelerate the car by 1 mph with the tap of a button. Hit the button five times to go 5 mph faster. There are also several important safety features -- the cruise control will disengage as soon as you hit the brake pedal, and it won't engage at speeds less than 25 mph (40 kph).
The system pictured below has five buttons: On, Off, Set/Accel, Resume and Coast. It also has a sixth control -- the brake pedal, and if your car has a manual transmission the clutch pedal is also hooked up to the cruise control.
- The on and off buttons don't actually do much. Hitting the on button does not do anything except tell the car that you might be hitting another button soon. The off button turns the cruise control off even if it is engaged. Some cruise controls don't have these buttons; instead, they turn off when the driver hits the brakes, and turn on when the driver hits the set button.
- The set/accel button tells the car to maintain the speed you are currently driving. If you hit the set button at 45 mph, the car will maintain your speed at 45 mph. Holding down the set/accel button will make the car accelerate; and on this car, tapping it once will make the car go 1 mph faster.
- If you recently disengaged the cruise control by hitting the brake pedal, hitting the resume button will command the car to accelerate back to the most recent speed setting.
- Holding down the coast button will cause the car to decelerate, just as if you took your foot completely off the gas. On this car, tapping the coast button once will cause the car to slow down by 1 mph.
- The brake pedal and clutch pedal each have a switch that disengages the cruise control as soon as the pedal is pressed, so you can shut off the cruise control with a light tap on the brake or clutch.

The cruise control system controls the speed of your car the same way you do -- by adjusting the throttle position . But cruise control actuates the throttle valve by a cable connected to an actuator , instead of by pressing a pedal. The throttle valve controls the power and speed of the engine by limiting how much air the engine takes in (see How Fuel Injection Systems Work for more details).
In the picture above, you can see two cables connected to a pivot that moves the throttle valve. One cable comes from the accelerator pedal, and one from the actuator. When the cruise control is engaged, the actuator moves the cable connected to the pivot, which adjusts the throttle; but it also pulls on the cable that is connected to the gas pedal -- this is why your pedal moves up and down when the cruise control is engaged.

Many cars use actuators powered by engine vacuum to open and close the throttle. These systems use a small, electronically-controlled valve to regulate the vacuum in a diaphragm. This works in a similar way to the brake booster , which provides power to your brake system.
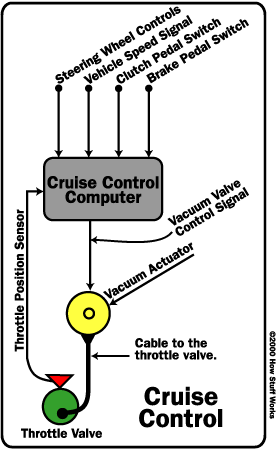
The brain of a cruise control system is a small computer that is normally found under the hood or behind the dashboard. It connects to the throttle control seen in the previous section, as well as several sensors. The diagram below shows the inputs and outputs of a typical cruise control system.
A good cruise control system accelerates aggressively to the desired speed without overshooting, and then maintains that speed with little deviation no matter how much weight is in the car, or how steep the hill you drive up. Controlling the speed of a car is a classic application of control system theory . The cruise control system controls the speed of the car by adjusting the throttle position, so it needs sensors to tell it the speed and throttle position. It also needs to monitor the controls so it can tell what the desired speed is and when to disengage.
The most important input is the speed signal; the cruise control system does a lot with this signal. First, let's start with one of the most basic control systems you could have -- a proportional control .
In a proportional control system, the cruise control adjusts the throttle proportional to the error, the error being the difference between the desired speed and the actual speed. So, if the cruise control is set at 60 mph and the car is going 50 mph, the throttle position will be open quite far. When the car is going 55 mph, the throttle position opening will be only half of what it was before. The result is that the closer the car gets to the desired speed, the slower it accelerates. Also, if you were on a steep enough hill, the car might not accelerate at all.
Most cruise control systems use a control scheme called proportional-integral-derivative control (a.k.a. PID control). Don't worry, you don't need to know any calculus to make it through this explanation -- just remember that:
- The integral of speed is distance.
- The derivative of speed is acceleration.
A PID control system uses these three factors -- proportional, integral and derivative, calculating each individually and adding them to get the throttle position.
We've already discussed the proportional factor. The integral factor is based on the time integral of the vehicle speed error . Translation: the difference between the distance your car actually traveled and the distance it would have traveled if it were going at the desired speed, calculated over a set period of time. This factor helps the car deal with hills, and also helps it settle into the correct speed and stay there. Let's say your car starts to go up a hill and slows down. The proportional control increases the throttle a little, but you may still slow down. After a little while, the integral control will start to increase the throttle, opening it more and more, because the longer the car maintains a speed slower than the desired speed, the larger the distance error gets.
Now let's add in the final factor, the derivative . Remember that the derivative of speed is acceleration. This factor helps the cruise control respond quickly to changes, such as hills. If the car starts to slow down, the cruise control can see this acceleration (slowing down and speeding up are both acceleration) before the speed can actually change much, and respond by increasing the throttle position.
Two companies are developing a more advanced cruise control that can automatically adjust a car's speed to maintain a safe following distance. This new technology, called adaptive cruise control , uses forward-looking radar , installed behind the grill of a vehicle, to detect the speed and distance of the vehicle ahead of it.
Adaptive cruise control is similar to conventional cruise control in that it maintains the vehicle's pre-set speed. However, unlike conventional cruise control, this new system can automatically adjust speed in order to maintain a proper distance between vehicles in the same lane. This is achieved through a radar headway sensor , digital signal processor and longitudinal controller . If the lead vehicle slows down, or if another object is detected, the system sends a signal to the engine or braking system to decelerate. Then, when the road is clear, the system will re-accelerate the vehicle back to the set speed.
The 77-GHz Autocruise radar system made by TRW has a forward-looking range of up to 492 feet (150 meters), and operates at vehicle speeds ranging from 18.6 miles per hour (30 kph) to 111 mph (180 kph). Delphi's 76-GHz system can also detect objects as far away as 492 feet, and operates at speeds as low as 20 mph (32 kph).
Adaptive cruise control is just a preview of the technology being developed by both companies. These systems are being enhanced to include collision warning capabilities that will warn drivers through visual and/or audio signals that a collision is imminent and that braking or evasive steering is needed.
For more information on cruise control, check out the links below.
Cruise Control FAQ
How does cruise control work, how does adaptive cruise control work, will adaptive cruise control stop the vehicle, when would you use cruise control, how useful is cruise control, lots more information, related articles.
- How Car Engines Work
- How Brakes Work
- How Manual Transmissions Work
- How Fuel Injection Systems Work
- How Radar Detectors Work
- Ignition System Quiz
More Great Links
- BMW: Cruise-control-equipped motorcycle
- Cruise Control Block Diagram
- Cruise Control Installers' Instructions
- Cruise Control Service Tips
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:
5 Reasons Why Your Cruise Control Stopped Working
- Updated: March 15, 2023

It would be difficult to find a vehicle on the road today without cruise control. This invaluable feature makes driving long distances easier but can also cause trouble when it malfunctions. Understanding the reasons your cruise control stopped working ensures that you can get the problem fixed quickly for a more enjoyable ride.
While this fault can cause issues with the cruise control system itself, there could also be an effect on the acceleration of your vehicle. That’s why you want to have it looked at as soon as you notice a problem. Let’s take a quick look at the reasons your cruise control may have stopped working.
Reasons Why Your Cruise Control Stopped Working
The most common reason a cruise control stops working is due to a blown fuse or a defective brake pedal switch . It can also be caused by issues with the throttle control system or the ABS. In older cruise control systems, it can be caused by a broken vacuum line.
Here is a more detailed list of the possible reasons your cruise control is not working:
1. Blown Fuse
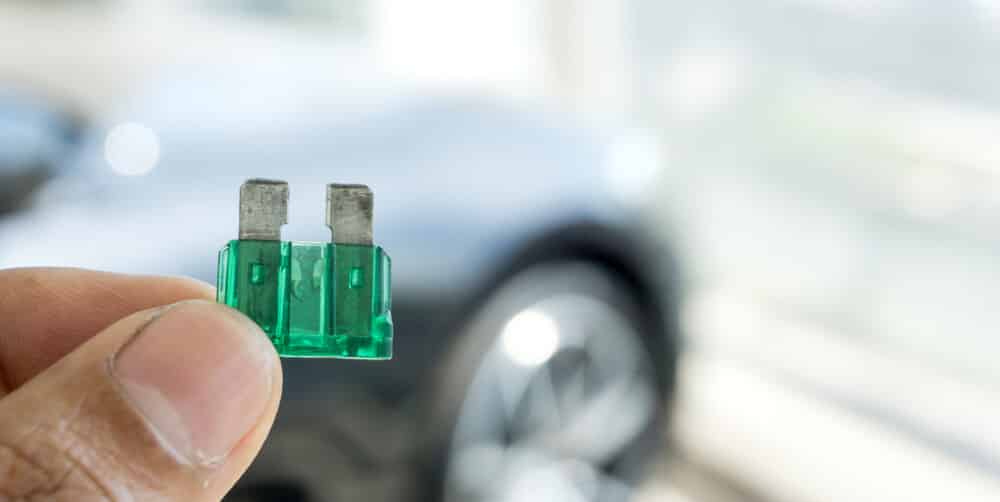

All electrical systems in the vehicle are controlled by fuses. Your cruise control system is attached to a fuse that can blow if there is a short circuit or fault. Without a good fuse, the cruise control system can’t work at all.
Thankfully, it’s not difficult to find and replace a blown fuse. Look in the owner’s manual to find the fuse that corresponds with the cruise control technology.
2. Defective Brake Pedal Switch
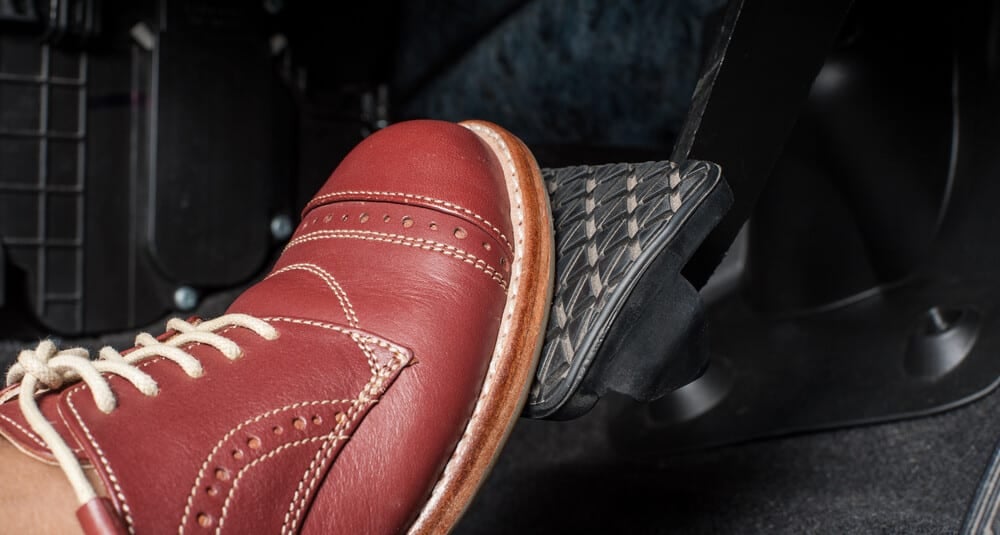

The brake pedal switch is responsible for turning the brake lights on and off based on the pedal position. Cruise control systems are designed to disengage whenever your brake pedal gets pressed.
Because the cruise control is wired into the brake pedal switch, any fault can cause it to stop working. When the brake pedal switch malfunctions, the car believes the brakes are engaged, causing the system to turn off automatically. Not only that, but your car’s brake light might also be stuck on, leaving confused drivers in your wake.
3. Malfunctioning Speed Sensor
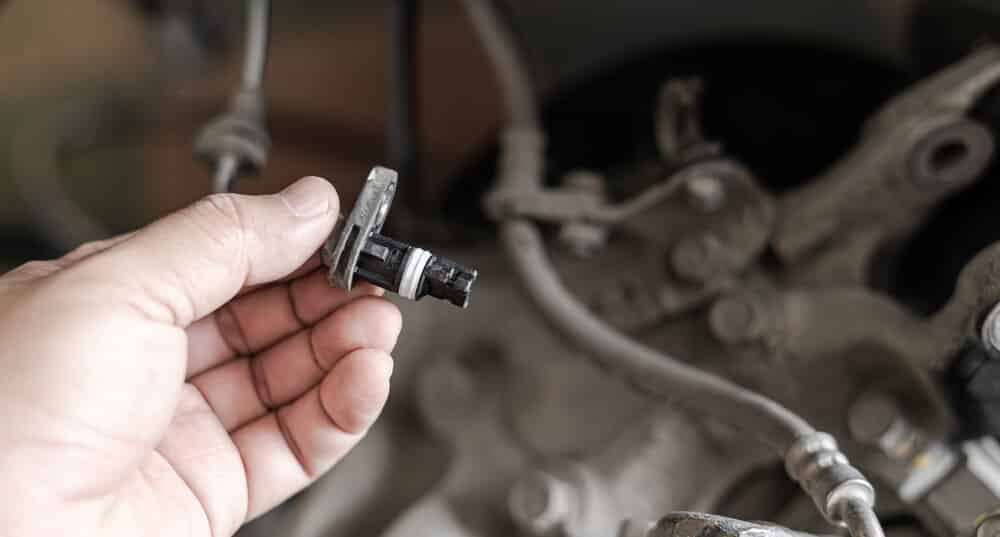

Speed sensors are located on every wheel or differential. The purpose of these sensors is to monitor the speed of the wheels to determine if traction control is needed.
The speed sensors are also part of the cruise control system. When a sensor fails, the cruise control can stop working and the speedometer might act strange as well.
If there is an issue with a speed sensor, it will often show with an ABS warning light or a check engine light on the dashboard.
RELATED: 3 Symptoms of a Bad ABS Wheel Speed Sensor
4. Electrical Issues

The cruise control system is electronic, with many components working together to make the system operate. If the cruise control fails to work, you want to check the wiring harness and associated connectors for a fault.
You also need to ensure that the voltage source is supplying enough power to the system. Even the smallest fault can cause defects with the cruise control. In many cases, there can be an issue with the cruise control lever or buttons causing the cruise control to not engage.
If your cruise control buttons are located on the steering wheel it could also be caused by a bad clock spring, which is located behind the steering wheel.
Check the system with an OBD2 scanner to look for any trouble codes related to the cruise control.
RELATED: 5 Symptoms of a Broken Clock Spring, Location & Replacement Cost
5. Damaged Vacuum Actuator, Hoses or Cable (Older cruise control)
If you drive an older vehicle with cruise control, you might have an issue with the vacuum actuator or the cable that connects to the throttle. If there has been damage done to the vacuum hoses or the actuator, the cruise control will stop working altogether.
Additionally, the cable linking the actuator to the throttle must be in good shape. If it has been broken, the cruise control will fail.
What is Cruise Control?
Cruise control is a feature that is used when you are traveling at a consistent speed. Cruise control was first introduced for automobiles in the 1950s. However, it took many years before it became a staple in the modern vehicle.
This electrical system allows you to set a predetermined speed and take your foot off of the gas pedal. If you are on a long drive, there is less fatigue because you don’t have to try to maintain your speed. Cruise control can also benefit fuel economy because the vehicle uses less fuel when traveling steadily.
In newer cars, you might be able to find adaptive cruise control , which is a smart technology. Adaptive cruise control allows you to travel at a predetermined speed, but it also helps to maintain a safe distance from the vehicles in front of you with the help of sensors. With conventional cruise control, you need to take over when the car in front of you slows down, but that’s not the case with adaptive cruise control.
There are also vehicles nowadays with not only cruise control, but fully self-driving vehicles . We will most likely see much more of this in the future.
Cruise Control Repair Cost
The cost to repair your cruise control system depends on what caused it to fail. If you need to replace a cruise control or brake switch, you might spend between $125 and $350, including parts and labor. However, the cost to change a fuse is only a few dollars and you can perform the replacement yourself in just a matter of seconds.
On the other hand, when something major fails, such as the actuator, you could be looking at a much higher repair bill. In some vehicles, the cost to replace a cruise control actuator can cost more than $700. These costs rise if you drive a luxury vehicle or one that is difficult to get parts for.
It might not seem immediately important for you to fix the broken cruise control, but this defective system can affect other performance aspects. You could start to notice issues with acceleration or have trouble with the speedometer. To play it safe, it’s always best to have the cruise control repaired as soon as you notice a problem.
Is there a fuse for the cruise control?
Yes. If the cruise control is installed from the factory, you should check your car’s owner’s manual for the fuse location. If it’s an aftermarket cruise control, you’ll need to follow the wires to find the fuse.
Does the brake switch affect the cruise control system?
Yes. The brake switch affects the cruise control system. The brake switch sends a signal to the cruise control system to let it know when the brakes are being applied for the engine to know when it should stop accelerating.
Will the cruise control work if the check engine light is on?
The cruise control function will be disabled when the check engine light is on in most car models, even if the cause of the check engine light is not the cruise control itself. This is mainly due to safety reasons.
Can a vacuum leak affect cruise control?
Older vehicles use vacuum to control the throttle for the cruise control, and in this case a vacuum leak can heavily affect the cruise control. However, modern cruise controls are fully electric and in most cases will not be affected by a vacuum leak if the check engine light is not illuminated.
Although many people may think that the cruise control system is unimportant and not worth spending money to repair, the problem can be caused by a faulty part that will affect the engine’s performance or durability. Therefore, it is best not to ignore the problem if your cruise control is not working without first diagnosing the car properly.
If your cruise control still isn’t working after trying all the tips in this article, it’s probably time to take it in for a professional opinion from a mechanic. It may be a more serious problem that requires replacement parts or repairs. In the meantime, drive safe and enjoy the open road!
Learn more:
- Brake Lights Not Working But Tail Lights Are? (How to Fix)
- Tail Lights Not Working But Brake Lights Are? (How to Fix)
- Brake Lights Stay On? (5 Causes & How to Fix it)
Categories: Electric , Troubleshooting
Related Posts

Latest Posts
- The Best & Worst Years Of Ford Explorer
- Best & Worst Years Of Toyota Corolla
- Best & Worst Years of Toyota RAV4
- When Should Your Child Switch To A Forward-Facing Car Seat?
- The Best & Worst Years Of Toyota Camry
- I Accidentally Put Premium Gas In My Car, What To Do?
- Why is my Cruise Control not Working? [14 reasons]
14 Reasons Why your Cruise Control may NOT Be Working
The reason for your cruise control not working could be as simple as a blown fuse to really complex electrical problems. Defective switches, sensors, and even “check engine” light, all could contribute to this problem.
If you like to travel and own a car fitted with cruise control, you know how comfortable it can be to maintain a constant speed! When a cruise control system gets damaged, it is just as annoying as it is dangerous.
Cruise control is connected to several components of the car, and when it fails it can mean that something could be wrong with the CC itself. It could also be a signal that something wrong is happening with any other component of the car.
Why is my cruise control not working?
In this article, I am going to show you the main reasons why your cruise control may not be working (from the simplest to the more complex ones):
Reason #1. Bad or blown fuse
The cruise control’s circuit (like many other electronic components of your car), is protected by a fuse that will blow to protect the system from short circuits and overloads. If your vehicle’s cruise control fuse is blown, the system will stop working.
You can replace the fuse with a new one of the correct amperage, according to your vehicle’s owner manual. If the new fuse doesn’t blow again, everything will be ok; if the fuse blows again, you have to keep searching for what is making that fuse blow.
Reason #2. Burnt brake lamp
Some cruise control systems are disabled when the brake lamp is blown. Check your brake lights. If you find a burnt brake light, just replace it and test the system again.
Reason #3. Defective brake light switch
A defective pedal switch can also make your cruise control stop working. Remember that all cruise control systems are automatically disengaged as soon as the brake pedal is pressed down.
If the cruise control didn’t stop working when a fault in the brake light or brake pedal switch is detected, it could be dangerous; that’s why the CC control unit constantly monitors the status of this switch.
Reason #4. Clutch pedal switch deactivation (for manual transmission vehicles)
Cruise control is deactivated when the clutch is pressed by the driver in manual transmission cars. The CC control unit monitors this switch as it does the brake light switch.
Reason #5. The vehicle speed sensor is not working
A vehicle’s cruise control needs to be able to determine the vehicle’s actual speed. This enables the system to determine how much throttle needs to be applied in order to keep a certain speed, among other things.
The speedometer speed sensor is not always the sensor used by cruise control. Some systems rely on the ABS speed sensors, others do an average and some have a dedicated speed sensor.
If the system can’t detect the vehicle’s speed or detects a problem with the speed sensor, it will stop working.
Reason #6. Faulty throttle body or accelerator pedal
In modern engines, the throttle body is driven electronically by the engine control unit (ECU), and the accelerator pedal works like a potentiometer. The processor managing the cruise control system will act as the accelerator pedal, sending more or less voltage to the throttle body to open or close the throttle body’s butterfly valve.
If there is a problem with your vehicle’s throttle body, your cruise control won’t work.
Reason #7. Check Engine light is “ON”
If your vehicle instrument panel has the “Check Engine Light” ON and the fault stored in the ECU’s memory is related to some component vital for the cruise control system, you will not be able to use your cruise control until you have fixed that problem.
Reason #8. Faulty steering wheel’s spiral cable/clock spring
The spiral cable connects all the switches from the steering wheel (in case your steering wheel has switches) to their respective modules. This includes the connection of the driver’s airbag.
These wires (also called clock springs) are prone to get cut. A faulty spiral cable may have an open circuit making it unable to reach the vehicle’s cruise control module (CCM).
Reason #9. Bad Cruise Control Switch
Your vehicle’s cruise control switches have internal contacts that wear out. If that happens, the switches won’t be able to contact the CCM.
Depending on which buttons are faulty, your whole cruise control can stop working or just some functions won’t work.
Reason #10. Electrical problems with different modules and wiring
Modern cruise control systems use electrical and electronic components, and they are connected to other modules and systems of the vehicle. Some of these systems are the ECU, ABS, and/or Stability Control Systems like ESP.
The CCM makes a check of these systems once the key is switched to ON, and if some of these components are not working in optimal conditions, the CCM won’t engage. If none of the above items seem to be the problem, the vehicle needs to be taken to a professional who can perform a full scan of all the components, check that all the voltages, wiring harnesses, and connectors are ok.
The professional is going to detect if there are any connection problems between modules and will be able to find the reason why the cruise control is not working.
Reason #11. Dirty or faulty camera or sensor (only for vehicles fitted with adaptive cruise controls)
Newer vehicles have adaptive cruise control systems. These devices not only keep a fixed speed by the driver; they also can detect other vehicles ahead and behind and are able to keep a safe fixed distance to avoid collisions.
Some of these new systems have laser sensors while others have cameras to calculate the right distance to follow considering the vehicle’s speed and acceleration. Any problem with the sensors will prevent adaptive cruise control from working.
Problems with older cruise control systems
Before electronic injection and electronic throttle bodies, some cars had the cruise control function. In fact, the first cruise controls were introduced in the early 1950s.
These electromechanical cruise controls are pretty simple. They have a vacuum actuator connected to the throttle linkage that opens and closes the throttle to maintain the vehicle’s speed.
In early injection cars, the throttle linkage was replaced by a cable. Some common faults of these old cruise control systems are:
- A faulty vacuum actuator. Vacuum actuators have a diaphragm inside that can break. Any vacuum leak will lead to failure.
- Faulty vacuum control solenoid. It can prevent the actuator from operating normally.
- Broken throttle cable. If the throttle cable or linkage is broken, it needs to be replaced.
I hope you enjoyed my guide to cruise control problems. Even though it doesn’t explain how to fix your cruise control, it gives you an idea of where to start looking if you are going to do it yourself.
Now you will have an idea about how the system works and what are the possible reasons why it’s failing (in case you have to take your vehicle to a shop to be repaired).
Attention! This article is for informational purposes ONLY and is NOT a replacement for professional advice! ALWAYS consult your local specialist for an appropriate solution to your problem. All statements, prices, contact information, recommendations, and reviews contained herein came from sources that we believe to be reliable, but the accuracy or completeness thereof is not guaranteed. Please contact the service provider for complete details and updates.
I always Know and admit that even though I went to school for ABR grad. In 1994 3.36gpa still have go go back to school for upgrades due to vehicle advancement but I still learned alot although I am dealing with an 05 f150 stx which has more recalls then a auto parts store where the employees don’t know a inerta. Switch from an ignition switch ,thanks for the information
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
- Blocking Diodes
- Diode Across Relay Coil
- Isolating Door Triggers
- Current (I) Calculators
- Power (P) Calculators
- Resistance (R) Calculators
- Voltage (E) Calculators
- Ohm's Law Pie Chart
- Diagrams Quick Reference
- SPDT and SPST Relays
- Converting Polarity
- Illuminated Entry & Light Flash
- Special Applications
- Starter Interrupts
- Relay Forum
- 4 & 5 Band Resistors
- Resistor Color Code Chart
- Resistor Color Code Calculator
- Pneumatic Tools
- Portable Power Tools
- Safety Equipment & Info
- Stationary Tools
- Test Equipment
- Tool Storage
- Miscellaneous Tools
- American Wire Gauge (AWG)
- Cable Size by Power & Distance
- Current Draw by Power
- Power & Ground Cable Specs
- Speaker Wire Size
- Car Audio Forum
- How to Choose a CD Receiver
- How to Choose an Amplifier
- How to Identify Stereo Wiring
- How to Upgrade the Big Three
- How to Wire through Door Molex
- View All...
- Mobile Video & Navigation
- Car Audio Manuals
- Car Audio Tech Tips
- Acoustical Output & Power
- High Pass/Low Pass Calculator
- Narrow Bandwith Calculator
- Zobel Calculator
- Low Pass Filters
- High Pass Filters
- Band Pass Filters
- Narrow Band Pass Filters
- Zobel Filter
- 1st Order Low Pass
- 1st Order High Pass
- 1st Order Band Pass
- 1st Order Narrow Band Pass
- 2nd Order Low Pass
- 2nd Order High Pass
- 2nd Order Band Pass
- 2nd Order Narrow Band Pass
- 3rd Order Low Pass
- 3rd Order High Pass
- 3rd Order Band Pass
- 3rd Order Narrow Band Pass
- 2 Ohm Charts
- 4 Ohm Charts
- 8 Ohm Charts
- Fraction to Decimal
- Parallel Calculator
- Port Length Calculator (round)
- Port Length Calculator (slot)
- Series Calculator
- Subwoofer Wiring Wizard
- Volume, Rectangular Enclosures
- Volume, Wedge Enclosures 1
- Volume, Wedge Enclosures 2
- Volume, Cylinder Enclosures
- 2nd Order, Infinite Baffle
- 2nd Order, Acoustic Suspension
- 4th Order, Bass Reflex/Bandpass
- 6th Order Enclosures
- 8th Order Enclosures
- Alarm Accessories
- Alarm Modules
- Alarm Sensors
- Add Auto Lock/Unlock
- Determining Switch Types
- Multiple Wire Systems
- Single Wire Systems
- Special Systems
- Negative Door Triggers
- Positive Door Triggers
- Basic Light Flash
- 2 Wire, Negative Output
- 2 Wire, Weak Negative Output
- 2 Wire, Positive Output
- Light Flash w/ Siren Output
- Normally Closed
- Normally Open
- Passive Starter Kill
- Car Alarm/RS Manuals
- Car Security Tech Tips
- Car Security & Convenience
- Car Security Hot Topics
- Car Security Pictorials
- Electrical Connections
- Mechanical Connections
- Servo Settings
- VSS and Tach Info
- Most Popular Topics
- Most Recent Topics
- Buy and Sell Equipment
- Car Audio Hot Topics
- Cellular & Communications
- Cruise Controls
- Fiberglass & Fabrication
- General Discussion
- Lights, Neon, LEDs, HIDs
- Marine Electronics
- Miscellaneous
- Mobile Video Hot Topics
- Motorcycle Electronics
- Music, Favorite Songs
- Rides & System Galleries
- Vehicle Information Requests
- Site Notices
- Forums - Q&A
- Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act
- Recommended Books/DVD's
- Et Cetera ► Back
- Advertising
- Click pointers (►) to expand menu.

I prefer to use the Micro Cruise, now manufactured by Rostra Precision Controls, Inc. , but there are others to choose from. Each has it's pro's and con's. The information below is most relevant to the installation of the Micro Cruise, but in general will apply to most cruise controls available on the market today.
Cruise Control Electrical Connections
Cruise control mechanical connections, cruise control servo settings & control switches, control arms / switches, cruise control clutch switches & signal generators, cruise control pick up coil & magnets, other cruise control connections.


[SOLVED] P0594 Code: Cruise Control Servo Circuit/Open – How To Fix It!
The automobile fault code P0594 indicates a problem with the servo motor.
Symptoms may include issues with the vehicle’s heating or cooling system.
The cause of this fault code could be a faulty servo motor, an open or shorted servo motor harness, or a poor electrical connection in the servo motor circuit. To fix this issue, it is recommended to visually inspect the wiring harness and connectors for any damage. Check for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded pins in the connectors.
The repair time for this issue is estimated to be around 1.0 hour. To interpret the fault code, it is important to refer to the possible causes and perform the necessary inspections and repairs.
Decode The Symptoms Of Fault Code P0594: Unveiling The Mystery!
Experiencing issues with your vehicle’s cooling system?
Check out the symptoms of fault code p0594 below.
- The symptoms of the automobile fault code P0594 may include: – Illuminated check engine light – Engine overheating – Poor engine performance – Reduced fuel efficiency – Engine stalling or rough idling – Inoperative cooling fan – Air conditioning not working properly – Increased emissions – Possible damage to engine components.
Unveiling The Culprits: What Causes Fault Code P0594?
The automobile fault code p0594 can be caused by a faulty servo motor, an open or shorted servo motor harness, or a poor electrical connection in the servo motor circuit.
- The fault code p0594 can be caused by a faulty servo motor, an open or shorted servo motor harness, or a poor electrical connection in the servo motor circuit.

Fixing Code P0594: Simple Steps To Resolve The Issue
To fix the automobile fault code p0594, start by visually inspecting the wiring harness, connectors, and components for any damage or corrosion.
- To fix the automobile fault code p0594, start by checking the possible causes mentioned above.
- Then, visually inspect the wiring harness and connectors related to the issue.
- Look for any damaged components and check for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded connector pins.
- This fix is estimated to take approximately 1.0 hour.
Cracking The Code: P0594 – Cost And Complexity Unveiled!
The factors influencing the diagnosis and fixing cost of the automobile fault code p0594 are the estimated repair time of 1.0 hour and the average hourly rate charged by auto repair shops, which ranges between $75 and $150.
Decode P0594: Unveiling The Possible Symptoms And Solutions
When you see the Engine Light ON or the Service Engine Soon Warning Light, it could be due to the fault code p0594. This code specifically relates to an issue with the cruise control system.
It indicates a problem with the cruise control servo control circuit, which is responsible for regulating the speed of your vehicle.
When this fault code appears, it means that there is a malfunction in the circuit that controls the cruise control system. This can result in the cruise control not working properly or not engaging at all. It may also cause the engine light to illuminate as a warning.
To fix this issue, you will need to diagnose the exact cause of the problem.
It could be a faulty cruise control switch, a damaged wiring harness, or a problem with the cruise control module. A professional mechanic will be able to use diagnostic tools to identify the specific issue and then repair or replace the faulty components.
It is important to address this problem promptly to ensure the safe and efficient operation of your vehicle’s cruise control system.
The fault code P0594 in an automobile can be caused by a faulty servo motor, an open or shorted servo motor harness, or a poor electrical connection in the servo motor circuit. To fix this issue, visually inspect the wiring harness and connectors for any damage. Check for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded pins in the connectors. Additionally, refer to the possible causes mentioned above for further troubleshooting.
To fix fault code p0594, start by visually inspecting the wiring harness and connectors. Look for any damaged components and check if there are any broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded pins in the connectors. This will help identify any issues with the servo motor harness, such as an open or shorted circuit or poor electrical connection. Make sure to check the possible causes mentioned above to ensure a thorough inspection.
To resolve fault code P0594, start by visually inspecting the wiring harness and connectors. Look for any signs of damage, such as broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded connector pins. Check the servo motor harness for any open or shorted circuits. Ensure there is a good electrical connection in the servo motor circuit. By checking for damaged components and connector pins, you can identify and resolve the issue causing the fault code.

If you’re experiencing issues with your vehicle and the fault code P0594 pops up, it could be due to a faulty servo motor or problems with the servo motor harness. To fix this, visually inspect the wiring harness and connectors for any damage or corrosion.
Make sure to check for broken or bent pins as well.
- What's My Car Worth?
- Buyer's Guide
What Is Adaptive Cruise Control?
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is a system designed to help road vehicles maintain a safe following distance and stay within the speed limit. This system adjusts a car's speed automatically so drivers don't have to.

Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is a system designed to help vehicles maintain a safe following distance and stay within the speed limit. This system adjusts a car's speed automatically so drivers don't have to.
Adaptive cruise control is one of 20 terms used to describe its functions so that you might see adaptive cruise control as the following in advertisements and vehicle descriptions:
- Active cruise control
- Dynamic cruise control
- Radar cruise control
- Automatic cruise control
- Intelligent cruise control
ACC functions by sensory technology installed within vehicles such as cameras, lasers, and radar equipment, which creates an idea of how close one car is to another, or other objects on the roadway. For this reason, ACC is the basis for future car intelligence.
These sensory technologies allow the car to detect and warn the driver about potential forward collisions. When this happens, red lights begin to flash, and the phrase 'brake now!' appears on the dashboard to help the driver slow down. There might also be an audible warning.
Advantages of Adaptive Cruise Control
Limitations of adaptive cruise control.
Although there are many advantages to adaptive cruise control, there are still limitations to consider. One of the main faults in this system is the fact that it is not entirely autonomous. The driver of the vehicle still needs to practice safe driving habits that will work in tandem with this technology to produce the best results. Similarly, adverse weather conditions like snow, rain, or fog might confuse the system's sensors, as well as environmental factors such as driving through tunnels.
What Is the Difference Between a Level 1 Autonomous Car and a Level 2 Autonomous Car?
According to SAE International, when a car only has autonomous cruise control , it is considered to be a level 1 autonomous car. In contrast, a vehicle with autonomous cruise control and an additional feature, such as lane control, gets classified as a level 2 autonomous car.
How Much Does an Adaptive Cruise Control System Cost?
According to ExtremeTech, The cost of an adaptive cruise control system will vary depending on how many features you want. If you're going to have an ACC with all available features, you should be willing to pay anywhere between $2000 and $2500. If you are looking for minimal cruise control that would benefit speeds of up to 20-25 miles per hour, these more basic ACCs can cost as low as $500. The good news is that as ACC becomes more common, it will most likely reduce in price.
History of Adaptive Cruise Control
U.S. News says Mitsubishi first introduced adaptive cruise control in Japan in 1992 . This was a lidar-based distance detection system that detected objects that were getting too close. It was labeled as 'Debonair' and it was programmed to provide a warning to the driver about oncoming objects. The main difference was that it was the driver's job to apply the brakes and reduce their speed.
However, two years later in 1995, the Mitsubishi Diamante featured an upgraded approach to the Debonair called 'Preview Distance Control.' Unlike the original technology, this laser-powered system could adjust a driver's speed by downshifting or controlling the throttle. The driver was still responsible for applying the brakes.
From the early 2000s onward, big names in the car industry, such as Ford, BMW, Mercedes, Cadillac, Volkswagen, Infinity, Hyundai, Toyota, and Audi, created their versions of adaptive cruise control in their vehicles. These individual features have evolved into a high-tech system with automatic braking and speed control.
Types of Adaptive Cruise Control
Radar-based systems.
According to eInfoChips, radar-based systems work by placing radar-based sensors on or around plastic fascias to detect your vehicle's surroundings. Each radar sensor works together to create a comprehensive picture of the vehicle's proximity to other cars or potentially hazardous objects. This type of sensor can look different depending on the design and model of the car.
Laser-Based Systems
As mentioned by Electronic Design , this type of ACC system operates out of a large black box typically placed in the grille of your vehicle. It uses laser technology to detect the proximity of objects to your car. It does not operate well during rainstorms and other weather conditions.
Binocular Computer Vision Systems (Optical)
According to ExtremeTech, this is a relatively new ACC system put into use in 2013. It uses small cameras that are placed on the back of a vehicle's rearview mirror to detect front-facing objects.
Assisting Systems
Assisting systems are radar-based add-ons that customers can buy together. These pre-crash systems can offer lane control, brake assistance, cruise control, proximity alerts to objects like corners, and steering power.
Multi-Sensor Systems
According to Fierce Electronics , adaptive cruise control systems sometimes integrate more than one type of sensor to aid in a vehicle's operation. Multi-sensor systems incorporate several different sensor types to provide a driver with advanced information. These sensors might include GPS data equipment or cameras to gather information about a vehicle's geographic environment and proximity to other cars.
Predictive Systems
As mentioned by Autoblog, prediction systems are a type of ACC that uses sensory data to predict the actions of neighboring vehicles. This means that your car might slow down to brace for another vehicle suddenly switching lanes and, in doing so, promotes passenger safety.
Adaptive cruise control is evolving each year. Car companies are continuously making adjustments to this technology and, in doing so, creating more common and affordable options that can be purchased with a new car or added to older car models, making driving safer for everyday people.
Information and research in this article verified by ASE-certified Master Technician Keith Canete of YourMechanic.com . For any feedback or correction requests please contact us at [email protected] .
https://www.einfochips.com/blog/why-automotive-companies-should-adopt-radar-based-adas-systems/
https://www.electronicdesign.com/markets/automotive/article/21797633/adaptive-cruise-control-laser-diodes-as-an-alternative-to-millimeterwave-radars
https://www.autoblog.com/2015/01/14/new-honda-smart-cruise-control-predicts-other-motorists-future/
https://www.fierceelectronics.com/components/three-sensor-types-drive-autonomous-vehicles
https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/157172-what-is-adaptive-cruise-control-and-how-does-it-work
https://mycardoeswhat.org/safety-features/adaptive-cruise-control/
https://cars.usnews.com/cars-trucks/what-is-adaptive-cruise-control
https://www.caranddriver.com/features/columns/
https://www.sae.org/
.css-190qir1:before{background-color:#000000;color:#fff;left:0;width:50%;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:48%;height:0.125rem;content:'';position:absolute;z-index:-10;} Research .css-188buow:after{background-color:#000000;color:#fff;right:0;width:50%;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:48%;height:0.125rem;content:'';position:absolute;z-index:-10;}

Tundra vs. Tacoma: Comparing Toyota Pickup Trucks

Honda HR-V vs. CR-V: Examining the Differences

Chevy Tahoe vs. Suburban: Here Are the Differences

What Are the Different EV Charging Levels?

Electric Car Battery Life

Electric Cars vs. Gas Cars: Pros and Cons

How to Clean Leather Car Seats

What to Buy: Subaru Crosstrek or Subaru Forester?

What to Buy: Jeep Cherokee or Jeep Grand Cherokee?

What to Buy: Hyundai Tucson or Hyundai Santa Fe?

2019 and 2020 Ford Edge Colors

- LRC circuit
- BoostConverter
- NEXT ►

Cruise Control: Simulink Modeling
Related tutorial links.
- Simulink Basics
- Modeling w/ Simulink
- Circuit Sim Activity
Related External Links
- Simulink Intro Video
- Simulink Modeling Video
- Modeling Challenges Video
Physical setup and system equations
Building the model, open-loop response.
The model of the cruise control system is relatively simple. If it is assumed that rolling resistance and air drag are proportional to the car's speed, then the problem is reduced to the simple mass and damper system shown below.

Using Newton's 2nd law, the governing equation for this system becomes:

where u is the force generated between the road/tire interface and can be controlled directly. For this example, let's assume that
This system will be modeled by summing the forces acting on the mass and integrating the acceleration to give the velocity. Open Simulink and open a new model window. First, we will model the integral of acceleration.

- Insert an Integrator block (from the Continuous library) and draw lines to and from its input and output terminals.
- Label the input line "vdot" and the output line "v" as shown below. To add such a label, double click in the empty space just above the line.

Since the acceleration (dv/dt) is equal to the sum of the forces divided by mass, we will divide the incoming signal by the mass.
- Insert a Gain block (from the Math Operations library) connected to the Integrator block input line and draw a line leading to the input of the Gain block.
- Edit the Gain block by double-clicking on it and change its value to "1/m".
- Change the label of the Gain block to "inertia" by clicking on the word "Gain" underneath the block.

Now, we will add in the forces which are represented in Equation (1). First, we will add in the damping force.
- Attach a Sum block (from the Math Operations library) to the line leading to the inertia Gain block.
- Change the signs of the Sum block to "+-".
- Insert a Gain block below the Inertia block, select it by single-clicking on it, and select Flip Block from the Rotate & Flip menu (or type Ctrl-I ) to flip it left-to-right.
- Set the block's value to "b" and rename this block to "damping".
- Tap a line (hold Ctrl while drawing) off the Integrator block's output and connect it to the input of the damping Gain block.
- Draw a line from the damping Gain block output to the negative input of the Sum Block.

The second force acting on the mass is the control input, u. We will apply a step input.
- Insert a Step block (from the Sources library) and connect it with a line to the positive input of the Sum Block.
- To view the output velocity, insert a Scope block (from the Sinks library) connected to the output of the Integrator.

- To provide an appropriate step input of 500 at time equals zero, double-click the Step block and set the Step Time to "0" and the Final Value to "u".

You can download a model file for the complete system by right-clicking here and selecting Save link as .
To simulate this system, first, an appropriate simulation time must be set.
- Select Parameters from the Simulation menu and enter "120" in the Stop Time field. 120 seconds is long enough to view the open-loop response.

The physical parameters must now be set. Run the following commands at the MATLAB prompt:
Run the simulation (hit Ctrl-T or select Run from the Simulation menu). When the simulation is finished you should see the following output.

Observing the above, we would like to improve the response of the cruise control system. The model created here will be employed for controller design and analysis within Simulink in the Cruise Control: Simulink Controller Design page.
Published with MATLAB® 9.2


CarParts.com will be back soon!
We apologize for the inconvenience. The CP Team is working on some upgrades to improve our service. Thank you for using CarParts.com!
You can call us at
1-866-529-0412
Reference ID: 18.6fc733e.1711757903.92fb562

- Forum Listing
- Marketplace
- Advanced Search
- 1st Generation Chevrolet Cruze
- Gen1 Powertrain
- Gen1 1.4L Turbo
P0597 'Cruise Control Circuit Open' Help!
- Add to quote
Newbie with a big dilemma. My Daughter's 2015 Cruze LT (1.4L Turbo) with 92,000 miles is throwing the P0597 code, but code reader says it's a cruise control issue. Water pump, thermostat (OEM), upper/lower radiator hoses replaced last fall. I checked the thermostat electrical connection, and all is well. Coolant is not leaking, and car seems to run fine. Coolant temp whiled parked and revving is between 194 & 199 degrees, per the code reader (Actron). Daughter needs to head to college Sunday (3 hour drive), so I only have 2 days to get this resolved. I would not expect a thermostat with less than 10,000 miles to fail, but it's possible. I have no problem replacing it, but the 'cruise control circuit open' message is throwing me for a loop. The code comes up pretty much immediately after erasing, and I did disconnect negative battery cable for about 10 minutes, but it did not help. Any advice would be greatly appreciated.
pcmett said: throwing the P0597 code, but code reader says it's a cruise control issue Click to expand...
pcmett said: Coolant temp whiled parked and revving is between 194 & 199 degrees, per the code reader (Actron). Click to expand...
pcmett said: but it's possible Click to expand...
pcmett said: disconnect negative battery cable for about 10 minutes Click to expand...
pcmett said: I have no problem replacing it Click to expand...
Thank you for the detailed reply. I'll look into new scan tool. Thermostat came from ebay Motors. Price was in line with OEM prices. Maybe I got a knock-off. Electrical connections are clean, but I'll try the CRC. Agreed about not up to normal operating temp. I've done more research. Going to find part # 131-180 this morning. I'll follow your recommendations, and reply with outcome. Thank you again!
All is good with the Cruze, except that someone backed into her and caused some front end damage. She's ok, and that's all that matters. Thank you very much for the help!!
- ?
- 737.6K posts
- 116.7K members
Top Contributors this Month
Detroit Diesel Engine Troubleshooting
Detroit Repair Manuals
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.7 Cruise Control Inoperative
Section 20.7 Cruise Control Inoperative
Before using this procedure, all basic mechanical checks and physical inspections should have been performed with no problem found.
Note: Some ECM/ECU software on newer engines will require that the ECM/ECU 'detects' activity on a brake, clutch and cruise active circuits. Following each ignition on cycle the ECM/ECU will require the brake, clutch and cruise activate (circuit goes open and close or message sent to the ECM/ECU) before cruise will be allowed to operate.
Section 20.7.1 Determine Type of Cruise Control System
Perform the following to determine the type of Cruise Control system:
- Check that this is a DDEC Cruise Control system.
- Turn ignition ON.
- Plug DDR into DDL connector.
- Select calibration configuration (Cruise Control).
- If Cruise Control is enabled, refer to "20.7.3 Check Pin Assignments" .
- If cruise is not enabled, refer to DDEC V Installation and Application Manual , 7SA821, for Cruise Control installation requirements.
Section 20.7.2 Check ECM/ECU Connectors
Perform the following to check the ECM/ECU connectors:
- Disconnect the vehicle harness connector at the ECM/ECU.
- If terminals and connectors are not damaged, reprogram the ECM/ECU. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
- If the terminals or connectors are damaged, repair them. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.3 Check Pin Assignments
Perform the following to check pin assignments:
- Plug in the DDR.
- Select calibration configuration (ECM/ECU Ins/Outs).
- An example listed in Table "Pin Assignments" shows pins, wires and functions. Refer to "20.7.4 Checking Out of Cruise Control Switch and Wiring" .
- If the functions are not assigned, reprogram the ECM/ECU. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.4 Checking Out of Cruise Control Switch and Wiring
To speed up the checking out of Cruise Control switches, quick check tables have been developed. These tests are to be run with the ignition ON, and the engine not running. A DDR must be plugged into the connector. All three quick check tables must be gone through to completely check out the Cruise Control wiring and switches.
For Example: Listed in Table "Cruise Control Quick Check Table I, Check Out Cruise Enable Switch and Wiring (Ignition ON Not Running)" , step 2, you would do the following:
- Ignition ON; engine not running; DDR plugged in.
- Turn the Cruise Enable Switch to ON.
- Select switch/light status on the DDR.
Section 20.7.5 Check for Short at the Cruise Enable Circuit
Perform the following steps to check for a short at the cruise enable circuit:
- Turn cruise engage switch to off.
- If the resistance measurement is less than or equal to 10,000 Ω, reconnect the vehicle harness. Turn the ignition on. Then run steps listed in Table "Cruise Control Quick Check Table II, Check Out Brake and Clutch Switch and Wiring (Ignition ON Not Running)" ; and listed in Table "Cruise Control Quick Check Table III, Check Out Set/Coast and Resume/Accel Switches and Wiring (Ignition ON Not Running)" . If any DDR display received is not okay, refer to the indicated step. If all steps listed in Table "Cruise Control Quick Check Table II, Check Out Brake and Clutch Switch and Wiring (Ignition ON Not Running)" and listed in Table "Cruise Control Quick Check Table III, Check Out Set/Coast and Resume/Accel Switches and Wiring (Ignition ON Not Running)" , pass, then the cruise engage wire is shorted to the ground. Repair the short, or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
- If the resistance measurement is greater than 10,000 Ω, refer to "20.7.2 Check ECM/ECU Connectors" .
Section 20.7.6 Check for Open at the Cruise Enable Circuit
Perform the following steps to check for an open at the cruise enable circuit:
- Turn cruise enable switch to ON.
- If the resistance measurement is greater than 5 Ω, or open, the cruise engage switch is bad, circuit V-59 is open or the cruise enable wire is open. Repair the open or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
- If the resistance measurement is less than or equal to 5 Ω, refer to "20.7.2 Check ECM/ECU Connectors" .
Section 20.7.7 Check for Open or Miswired Brake Switch
Perform the following steps to check for an open or miswired brake switch:
- Turn ignition OFF.
- Ensure the service brake is not engaged.
- If the resistance measurement is greater than 5 Ω, or open, the brake switch is miswired or faulty, circuit V-59 is open or the ground is bad. Repair the open, rewire or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.8 Check for Short at the Brake Switch or Circuit
Perform the following steps to check for a short at the brake switch or circuit:
- Engage the service brake.
- If the resistance measurement is less than or equal to 10,000 Ω, the brake switch is miswired or the service brake circuit is shorted to ground. Rewire, repair the short or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
- If the resistance measurement is greater than 10,000 Ω, or open, refer to "20.7.2 Check ECM/ECU Connectors" .
Section 20.7.9 Check for Open or Miswired Clutch Switch
Perform the following steps to check for an open or miswired clutch switch:
- Ensure the clutch is not engaged.
- If the resistance measurement is greater than 5 Ω, or open, the clutch switch is miswired or faulty, circuit V-59 is open, or there is a bad battery ground. Rewire, repair the short or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.10 Check for Short at the Clutch Service/Circuit
Perform the following steps to check for a short:
- Engage the clutch.
- If the resistance measurement is less than or equal to 10,000 Ω, the clutch switch is miswired or faulty, or the clutch circuit is shorted to ground. Rewire, repair the short or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.11 Check for Short at the Set/Coast Circuit
- If the resistance measurement is less than or equal to 10,000 Ω, the set/coast switch is shorted, or a short to ground exists in the set/coast circuit (V-47). Repair the short or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.12 Check for Open at the Set/Coast Circuit
Perform the following steps to check for an open:
- Find a means to press and hold the set/coast switch.
- If the resistance measurement is greater than 5 Ω, or open, the set/coast switch is open or miswired, circuit V-59 is open, or there is a bad battery ground. Rewire, repair the short or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.13 Check for Short at the Res/Accel Circuit
- If the resistance measurement is less than or equal to 10,000 Ω, the Res/Accel switch is shorted, or a short to ground exists in the Res/Accel circuit (V-8). Repair the short or replace the switch. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.14 Check for Open at the Res/Accel Circuit
- Find a means to press and hold the Res/Accel switch.
- If the resistance measurement is greater than 5 Ω, or open, the Res/Accel switch is open or miswired, circuit V-59 is open or the battery ground is bad. Repair the short, replace the switch, or rewire. Refer to "20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs" .
Section 20.7.15 Verify Problem Still Exists
Perform the following steps to verify the problem still exists:
- If you were referred to this step, you have completed the switch checkout process without detecting a fault.
- If Cruise Control operates correctly, the problem no longer exists. If any other problems exist, refer to "18.3 First Step for Diagnosing a Fault Within the DDEC System" .
- If Cruise Control does not operate correctly, check the Vehicle Speed Sensor. Refer to "56 Flash Code 54 - VSS Fault" .
Section 20.7.15.1 Verify Repairs
Perform the following steps to verify repairs:
- Reconnect all connectors.
- If Cruise Control operates correctly, troubleshooting is complete.
- If the Cruise Control does not operate correctly, all system diagnostics are complete. Review this section from the start to find the error. Refer to "20.7.1 Determine Type of Cruise Control System" .
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.17 Maintenance Alert System
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.18 Exhaust Gas Recirculation System Basic Checks for Series 60 Engines
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.16 Transmission Interface Fault
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.15 Optimized Idle Feature Does Not Function
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.13 Fire Truck Pressure Governor Fault
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.14 Troubleshooting Electronic Fire Commander
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.12 Miscellaneous Digital Output Fault
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.10 Engine Brake Inoperative
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.11 Miscellaneous Digital Input Fault
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.9 Fan Operational Concern (Variable Speed Type)
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.8 Fan Operational Concern (On/Off Type)
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.5 No Data to Diagnostic Data Reader
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.6 Diagnostic Request Switch Inoperative
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.4 Amber Warning Lamp and Red Stop Lamp Fault
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.2 Engine Cranks But Will Not Start
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.3 Erratic Performance and No Codes
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20 Intermittent Fault
- Series 60 DDEC V Troubleshooting – Section 20.1 Intermittent Code or a Symptom and No Codes
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
WassUp 1.9.4.5 timestamp: 2024-03-30 12:18:25AM UTC (07:18PM) If above timestamp is not current time, this page is cached.

- my account Sign in Register
Cruise Parts
There are no products listed under this category.
© 2024 The Cruise Control Store Powered by BigCommerce All rights reserved. | Sitemap

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The cruise control system controls the speed of your car the same way you do -- by adjusting the throttle position.But cruise control actuates the throttle valve by a cable connected to an actuator, instead of by pressing a pedal.The throttle valve controls the power and speed of the engine by limiting how much air the engine takes in (see How Fuel Injection Systems Work for more details).
It can also be caused by issues with the throttle control system or the ABS. In older cruise control systems, it can be caused by a broken vacuum line. Here is a more detailed list of the possible reasons your cruise control is not working: 1. Blown Fuse. All electrical systems in the vehicle are controlled by fuses.
The diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0571 indicates "Cruise Control/Brake Switch A Circuit Malfunction.". The powertrain control module (PCM) will log this code when it detects an issue with the operation of the brake light switch or, sometimes, the cruise control/brake switch "A" circuit. Common causes of the P0571 code are a defective ...
Reason #2. Burnt brake lamp. Some cruise control systems are disabled when the brake lamp is blown. Check your brake lights. If you find a burnt brake light, just replace it and test the system again. Reason #3. Defective brake light switch. A defective pedal switch can also make your cruise control stop working.
Use a vacuum pump to apply vacuum to the dump hose to approximately 15 inches, and then press on the brake pedal. The vacuum should be dumped and the gauge should read 0. If the vacuum is not ...
How does cruise control work? What is cruise control? This video explains how cruise control keeps a car running at a constant speed. It explains the mechani...
Consult your application guide or your dealer / distributor / manufacturer. This will provide a signal of 8000 ppm to the cruise control. Be sure to set the switches accordingly. If the unit is still plugged into the harness you will have to disconnect it first before the new settings will take effect.
The control module monitors the vehicle speed sensor (VSS) signal when setting and maintaining the cruise control speed. If the driver applies the brakes (or the clutch pedal if the vehicle has a manual transmission), the brake switch (or clutch switch) sends a signal to the control module, causing the module to disengage the cruise control.
Common cruise control icon on dashboards specified by ISO-7000-2047, ISO 2575:2010, and ISO 6727. Another icon exists for the more modern adaptive cruise control, but some cars also use the cruise control icon for the speed limiter function, which has no standard icon.. Cruise control (also known as speed control, cruise command, autocruise, or tempomat) is a system that automatically controls ...
Drive your vehicle to the test highway and accelerate to highway speeds. Step 4: Set your cruise control at 55 or 65 MPH. After the cruise control is set, slightly tap your brake pedal to verify the cruise control shuts off. Step 5: Reset the cruise control again and drive for 10 to 15 miles.
A control module manages your cruise control system. Code P0581 is triggered when the PCM detects a high electrical value within the "A" cruise control multi-function input circuit. The P0581 code is set when the PCM detects a fault in a specific circuit within the cruise control system. Note:The definition of code P0581 might be different ...
Cruise Control & Wiring DiagramAmazon Printed Bookshttps://www.createspace.com/3623931Amazon Kindle Editionhttp://www.amazon.com/Automotive-Electronic-Diagno...
P0571 is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) for "Cruise Control/Brake Switch A Circuit Malfunction". This can happen for multiple reasons and a mechanic needs to diagnose the specific cause for this code to be triggered in your situation. Our certified mobile mechanics can come to your home or office to perform the Check Engine Light diagnostic ...
Symptoms of a P0571 diagnostic code may include: Cruise control completely inoperative. Erratic cruise control operation. Certain functions not operating as they should (e.g. set,resume, accel., etc.) Cruise control turning on but not engaging. No brake lights if the brake light switch is faulty.
P0573 is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) for "Cruise Control/Brake Switch A Circuit High". This can happen for multiple reasons and a mechanic needs to diagnose the specific cause for this code to be triggered in your situation. Our certified mobile mechanics can come to your home or office to perform the Check Engine Light diagnostic for $154.99 .
To fix fault code p0594, start by visually inspecting the wiring harness and connectors. Look for any damaged components and check if there are any broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded pins in the connectors. This will help identify any issues with the servo motor harness, such as an open or shorted circuit or poor electrical connection.
The P0573 Cruise Control/Brake Switch A Circuit High and related codes (P0571 and P0572) are set when the ECM (engine control module) detects a malfunction within the cruise control/brake switch "A" circuit. In this case it means there is a detected high electrical condition within the circuit.
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is a system designed to help road vehicles maintain a safe following distance and stay within the speed limit. This system adjusts a car's speed automatically so ...
Open Simulink and open a new model window. First, we will model the integral of acceleration. (2) Insert an Integrator block (from the Continuous library) and draw lines to and from its input and output terminals. Label the input line "vdot" and the output line "v" as shown below. To add such a label, double click in the empty space just above ...
An activated cruise control system lets the vehicle maintain a preset speed until the driver steps on the gas pedal or brake pedal. In most cases, the system monitors the speed sensors and sends the information to the powertrain control module (PCM) for speed reference. If the PCM detects a problem with the cruise control system, on-board diagnostics will log a P0579 trouble code.
throwing the P0597 code, but code reader says it's a cruise control issue. Get yourself a better scanner. That code is definitely from an issue with the thermostat. pcmett said: Coolant temp whiled parked and revving is between 194 & 199 degrees, per the code reader (Actron). If you are trying to say the car is (or should be) at normal ...
Following each ignition on cycle the ECM/ECU will require the brake, clutch and cruise activate (circuit goes open and close or message sent to the ECM/ECU) before cruise will be allowed to operate. Section 20.7.1 Determine Type of Cruise Control System. Perform the following to determine the type of Cruise Control system:
Visit The Cruise Control Store for open and closed circuit switch adapters and more. phone: 800-343-1382. Toggle menu. my account. Sign in Register. Search; Search. Cart. Search. Home; Speed Limiter ... Installing Cruise Control in 2005-2009 Pontiac G6, Chevy Cobalt, and Pontiac G5;