The differences between outbound and inbound tour operator agents

By Blake Ng — 25 Mar 2018
distribution inbound tour operator inbound travel outbound tour operator outbound travel
Updated January 2023 – Are you a tour operator trying to find which option is best for you? Or alternatively, are you a tourism professional trying to set up your distribution system? Trying to make your mark and stand out in a highly competitive industry? Let’s start at the beginning to help you understand the types of travel agents available to partner with.
The role of a tour operator is to brainstorm ideas and conduct research to design holiday packages for travelers. In essence, they curate and compile various travel elements into a package that people will find appealing — creating a tailored and individual experience based on the interests and needs of various travelers. Holiday packages usually combine accommodation, cuisine, sightseeing, and transport.

Inbound vs. outbound travel

An inbound tourist is someone who visits a country but is not a resident of it. In outbound tourism, residents of a country visit another country. Does this sound like two sides of the same coin? That’s because it is.
Let’s look at an example:
Kevin, an Australian citizen, is traveling to Argentina for a holiday.
Kevin is an inbound tourist to Argentina. In contrast, Kevin is an outbound tourist from Australia.
Depending on where Kevin chooses to organize his holiday packages will depend on if he makes use of inbound tourism or outbound tourism.
An inbound tour operator will sell to people soon to be arriving in their countries, whereas an outbound tour operator will sell to people before they arrive at their destination.
Inbound tour operator agents
An inbound tour operator, also known as a destination management company, is a locally-based business or individual that provides holiday planning. This includes itinerary planning and arrangement of payment for their overseas clients.
Inbound tour operators deal with both individuals and groups of international travelers. They make arrangements that are specifically catered to international guests, ensuring their clients have a comfortable and enjoyable stay.
An inbound operator can work with the convenience of being able to operate at the same location in which they are organizing the holiday packages. Compared to outbound tour operators, an inbound operator would better understand the local area and its culture. This is especially true when receiving any inquiries or questions about tour information from a potential client. Additionally, an inbound tour operator is usually encouraged to develop strategic partnerships with other local companies and tour and activity operators . Building these relationships is a lot easier due to geographical location.
Inbound tour operators are locally based

The purpose of inbound tour operators is to promote the entire destination to potential visitors from their local viewpoint. The operational advantage of being locally based is having easy access to work with other companies to promote the location as a whole to interested overseas travelers. Additionally, inbound tour operators can offer a more personalized service to their customers by having direct contact with them in their chosen destinations.
Inbound tour operators often work with other travel agents and distribution partners
Tour packages are often created and promoted by inbound tour operators in partnership with other travel agent s and travel distribution channels . Inbound tour operators work under the assumption that travelers are often motivated by package deals and promotions, and take advantage of this when marketing their destination. This means it’s beneficial for inbound tour operators to create packages that include local tourism businesses such as hotels, transportation, and tours and activities. Following that, these same packages are promoted to segments of the target market that are most likely to visit the region in the near future.
Choose an inbound tour operator if:
Working with an inbound tour operator is a good idea if you want to increase your visibility in a chosen destination. This will be increasingly beneficial if your target market shows interest in package deals.
Outbound tour operator agents

A typical outbound tour operator works with international tourists. In contrast to inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators take travelers overseas from their home country. They offer a variety of tour packages that enable tourists across borders to travel abroad easily.
Outbound tour operators contribute significantly to the destination country’s economic growth. The majority of outbound tour operators choose to focus on a specific destination. This may be a destination that is currently popular or a destination in which they have special expertise and distribution partners.
Most outbound tour operators cater to international travelers.
Outbound tour operators offer travelers the convenience of visiting another country of their choice through tour packages. When travelers book a tour with an outbound tour operator, they can get everything they need under one roof — simplifying the travel experience.
A particular region of the world is often their specialty
Outbound tour operators have the benefit of being experts in the destinations they serve. European destinations are a very popular choice with outbound tour operators; however other destinations, such as Southeast Asia and the Middle East, are growing in popularity. A successful outbound tour operator will often be very tuned-in to trends, one step ahead of the crowds, so they know which destinations to specialize in next.
Choose an outbound tour operator if:
If your business strategy includes targeting international travelers, partnering with an outbound tour operator is likely to be a good fit. Additionally, an outbound tour operator will be a good fit if you understand overseas offerings and have the ability to promote them to domestic customers.
Advantages and Disadvantages

Just like running any form of travel company, there will always be some advantages and disadvantages. before working with either an inbound or outbound tour operator, here are a few pros and cons you should consider.
Inbound tour operators
As an inbound tour operator, you’ll have the advantage of convenience. This is due to being able to operate in the same location or home country as the tours you offer. This is extremely beneficial when receiving any inquiries or questions about the tours as you’d have a greater understanding of the local area and its culture compared to outbound tour operators. Furthermore, as an inbound tour operator, developing strategic partnerships and forming great relationships with other local companies and tour and activity operators will be a lot easier and is usually encouraged.
Another major advantage an inbound tour operator has is that most of the interactions with their customers will be direct. Meaning, it will allow them to offer a more personalized experience based on their customer’s needs.
Outbound tour operators
Just like the inbound operators, outbound tour operators deal with customers from their own countries. This makes designing and creating tour packages a whole lot simpler as they can customize the tours based on the customer’s interests. However, a disadvantage outbound tour operators have is not being based on the travel destination itself. This could create problems and can be more difficult to resolve any issues that may arise.
Fortunately, outbound tour operators have the flexibility to update their products and packages based on the latest travel trends and demands. As we all know, the travel industry is highly competitive and constantly evolving. Offering outbound tours gives you the freedom to adapt to changes in the travel and tourism market swiftly.
Which one should you choose?
The key difference between inbound and outbound tour operators comes down to whether they provide tours in their home country or abroad. You should consider both types of tour operator agents when developing your distribution strategy. Partnering with these two agents will maximize your reach to both international and domestic travelers.
Now, it’s time to think about ways to make your distribution and marketing channels more effective. You can identify your key partners via your research or by connecting with a tour wholesaler . By establishing partnerships with a large tour operator network , you can advance your business — both inbound and outbound. Read our previous blog if you are looking for tips and tricks for partnering with travel agencies or download our online distribution ebook today.
In general, both types of tour operator agents play an important role in the overall success of your distribution strategy. By partnering with both of these agents, you’ll be able to maximize your reach to both international and domestic travelers.
When bookings start to come through, you’d want to ensure that you’re providing your customers with a simple booking journey. By utilizing an online booking software , you’re not only simplifying the customer’s booking journey, you’re streamlining your processes as well. This is due to advanced features that automate your processes that allow your customers to make a booking on the spot. These features include a real-time availability viewer, that allows your customers to book based on your exact availabilities. Payment gateway integrations that provide your customers with the convenience of secure online payments. And Automatic communication, which sends your customers confirmation and updates regarding their bookings.
To top this all off, you can easily manage your partnership with both outbound and inbound tour operators via an online tour operator marketplace like Rezdy Channel Manager . Rezdy’s marketplace broadens your reach to over 25,000 active resellers in the industry.
Using Rezdy Channel Manager is as simple as:
- Naming your price
- Setting your rates
- Letting resellers sell and promote your products
On top of that, you don’t have to worry about collecting payments and paying commissions as Rezdy automatically organizes payments for both parties. This reduces the need to chase your agents for payments.
Ready to capture more inbound and outbound bookings with Rezdy? Start a FREE 21-day trial or book a free demo today.
If you enjoyed this article, then make sure to sign up for our newsletter where you’ll receive the latest marketing tools and tour operator tips designed with businesses like yours in mind.
Start free trial
Enjoy 21 days to take a look around and see if we are a good fit for your business.
No obligations, no catches, no limits, nada
Distribution

eBook: Guide to growing your tourism business through distribution & channel management tools

How to navigate API connections with resellers

Case Study: Wendella Tours & Cruises

What is a tour operator and how does it work?
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
The tour operator is an integral component of tourism , yet many people are unclear about what a tour operator actually is or what they do.
In this article I will explain what a tour operator is and why tour operators are important. I will also talk about what the difference between a tour operator and a travel agent is, as well as the different types of tour operators.
What is a tour operator?
Definitions of tour operator, importance of tour operators, the difference between a tour operator and a travel agent, what does a tour operator do, products and services sold by tour operators, inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators, domestic tour operators, ground tour operators, the association of independent tour operators, the tour operator: to conclude.
Tour operators are inextricably linked to the package holiday model. The tour operator is the person or organisation who creates the package. A travel agency is then used to sell the package holiday.
In the chain of distribution , the tour operator is represented by the term ‘wholesaler’. This is because the tour operator is responsible for purchasing products of services in bulk and then redistributing them as a packaged product to consumers.
To put it simply, a tour operator is the person or organisation who takes the individual elements of a holiday (e.g. transfer, hotel, transport) and packages these together.
The types of package vary. Most commonly, tour operators are associated with mass tourism and the traditional package holiday market. However, tour operators do also play an important role in the production of niche tourism products and services too.
If you’re looking for a formal definition of a tour operator with a reputable source, you may want to reference Polyther, who in 1993, defined the tour operator as;
‘[an organisation or person] who has the responsibility of putting the tour ingredients together, marketing it, making reservations and handling actual operation’.
Similarly, Holloway (1992) states that;
tour operations undertake a distinct function in the tourism industry, they purchase separate e lements of tourism products/services and combine them into a package tour which they sell directly or indirectly to the tourists .
The Organisation for Economic and Cultural Development (OECD) define a tour operator as follows;
‘Tour operators are businesses that combine two or more travel services (e.g., transport, accommodation, meals, entertainment, sightseeing) and sell them through travel agencies or directly to final consumers as a single product (called a package tour) for a global price. The components of a package tour might be pre-established or can result from an “a la carte” procedure, in which the visitor decides the combination of services he/she wishes to acquire.’
Tour operators are an important part of the tourism industry .
Tour operators make the logistics of organising a holiday much easier for the consumer. This makes people more likely to travel, more often.
Tour operators have a lot of power. If they choose to sell holidays in a particular location, for example, then that location will receive many of the associated positive and negative economic impacts of tourism .
Tour operators are often vertically or horizontally integrated with other organisations, such as travel agents and airlines. This allows for easier management and distribution of products.
Tour operators typically build holidays en masse. This means that economies of scale play a key role in driving down prices- the more you produce the cheaper the product becomes! This is obviously beneficial to the consumer and helps travel agents to have a competitive advantage when selling holidays.
Many people are not aware that a travel agent and a tour operator are actually two totally different organisations and they are not aware of the difference between a tour operator and a travel agent.
In fact, it is quite easy to understand this difference!
A tour operator is the organisation which puts the different elements of a holiday together. And the travel agent is the organisation who sells it to the consumer.
Whilst this differentiation is pretty easy to comprehend, it is easy to understand why people get tour operators and travel agents confused. This is largely because many organisations will operate under the same company. For example, TUI has a tour operator and a travel agent (and an airline too). As a result, many people do not realise that in actual fact, there are two separate organisations doing two separate jobs.

Ultimately, a tour operator is responsible for putting the different elements of a holiday together into a commodified package.
To do this, there are a number of different roles and responsibilities that tour operator staff will have. This includes:
- Data analysis- which destinations will sell best, how many holidays should they sell etc
- Assessing suitability of accommodation, transfer and transport options
- Liaising with stakeholders e.g. coach operators, airlines, hoteliers and resort representatives
- Negotiating contracts
- Confirming reservations with airlines/hotels
- Managing and responding to customer feedback
- Undertaking market research
- Production of marketing material
- Providing pricing information
- Handling bookings, invoicing and issuing of tickets
- Working with travel consultants from different travel agencies to put holiday packages together
Tour operators have a number of products and services that they sell, depending on their specific business model, business intentions and target market. A tour operator will typically package together two of more elements to form a packaged product, which is then sold at an inclusive price.
Examples include:
- Package holidays
- Accommodation
- Information on destinations
- Representative service in resorts
Types of tour operator
Tour operators come in all shapes and sizes. Some are large, multinational organisations and other are small, independent business.
Different types of tour operators develop products for different types of tourism . This can include the mass market, niche tourism market, special interest tourism, the luxury market, tailor-made products and dynamic packages .

There are four different types of tour operators, which I will explain below.
- Inbound Tour Operators
- Outbound Tour Operators
- Domestic Tour Operators
- Ground Operators

An inbound tour operator is one who facilitates inbound tourism .
The aim of an inbound tour operator is to bring tourists in to a particular country or countries.
Inbound tour operators will often collaborate with local travel agencies and transport operators to facilitate travel arrangements for their customers.
Inbound tour operator example: A group of German tourists conduct a tour of China, encompassing a visit to Shanghai , Hangzhou and the Yellow Mountains . The tour operator who organises their travel is Chinese-based company China Highlights . This company is based locally in China and they offer local, Chinese tours.
An outbound tour operator is one who facilitates outbound tourism .
The aim of an outbound tour operator is to send tourists out of a particular country or countries.
Outbound tour operators will often collaborate with foreign travel agencies and transport operators to facilitate travel arrangements for their customers.
Outbound tour operator example : A family of four from Liverpool, UK want to book an all-inclusive summer sun holiday in Alicante. They book through TUI , the largest tour operator in Britain, who specialises in outbound travel. They are based in the UK, but they work with foreign partners to facilitate holidays overseas.
A domestic tour operator is one who facilitates domestic tourism .
The aim of a domestic tour operator is to organise travel within a particular country or countries.
Domestic tour operators will often collaborate with domestic travel agencies and transport operators to facilitate travel arrangements for their customers. Domestic tour operators will often also serve the inbound tourism market.
Domestic tour operator example : A group of twenty-something boys from Chicago want to travel to Florida for the spring break holiday. They want to do a tour of the local attractions in the area and have some time to relax on the beach . They organise their travel through the tour company, Trek America . Staff at this company are experts in domestic travel within the USA.
A ground tour operator is an organisation who dopes the ground work as grass roots level.
Many tour operators do not have connections in all places around the world, therefore they build a network of connections to help them run their business.
Essentially, some of the work is passed on to a third party, known as a ground operator. This work may include negotiating local contracts, liaising with local suppliers and providing market data, amongst other things.
This is especially common for small tour operators.
You may also hear ground tour operators referred to as handling operators or handling agents.
Ground tour operator example : A backpacker wants to ‘give something back’ and book a volunteer tourism holiday in Kerala. She wanted to use a known and trusted tour operator to book her trip so she booked it with Intrepid Travel . Intrepid Travel create and sell adventure holidays all over the world, and it is impossible for them to have contacts and every staff in every corner of the globe. Therefore they work with local ground operators, who do the work on the ground. In this instance, the ground organisation is Iris Travel – a tour operator based in Kerela, India.
The Association of Independent Tour Operators , abbreviated as AITO, is a travel industry trade group (like ABTA or ATOL) based in Britain. They launched in 1976.
The AITO represents around 120 independent tour operators across 200 countries.
These tour operators provide access to a huge range of activities including city breaks, safaris, luxury holidays and much more. The AITO is based in Twickenham, south-west London.
The AITO does a variety of things. Most importantly, you can be reassured that your holiday is well-protected thanks to the Association of Independent Tour Operators.
They assess every member financially as well as by their own business practice code before granting membership; this means that you are guaranteed clear and accurate descriptions of holidays as well as tour standards that are consistently monitored.
Tour operators are an important part of the tourism industry, and with AITO, you have added security when booking your travels through a tour operator. Hopefully after reading this article you are now confident with what a tour operator is, how these organisations work and the different types of tour operators operating the market.
If you liked this article, why not take a look at these too?
- Types of travel agents | Understanding tourism
- What is e-tourism and how is it changing travel?
- 10 jobs in travel and tourism that will be BIG in 2022 and beyond
- What does the World Travel and Tourism Council do?
Liked this article? Click to share!
Tour Operators
Tour operator is an organization, firm, or company who buys individual travel components, separately from their suppliers and combines them into a package tour, which is sold with their own price tag to the public directly or through middlemen, is called a Tour Operator .
More precise tour operators are primarily responsible for delivering and performing the services specified in a given package tour. They can provide these services themselves as some have their own cars and coaches, hotels, and other travel-related services or can obtain these from the other suppliers. That is why they are called manufacturers of tourism products .
Tour operators are sometimes called wholesalers but this is partially true because a wholesaler buys goods and services in bulk at his own account to prepare a tour package and then retails it through the travel agencies or directly to clients. However, a tour operator who has his own one or more tourists products components, (SOTC, TCI, Thomas Cook, Indo Asia KUONI formulates a new tourist product for example ‘ inclusive tours .’
Tour operators generally offer a variety of package tours to cater to the needs of different kinds of travelers.
Definitions of Tour Operator
Poyther (1993) defines, “tour operator is one who has the responsibility of putting the tour ingredients together, marketing it, making reservations and handling actual operation.”
Holloway (1992) stated that tour operations undertake a distinct function in the tourism industry, they purchase separate elements of tourism products/services and combine them into a package tour which they sell directly or indirectly to the tourists.
Today, tour operators have become highly competitive. They endeavor to achieve a high volume of turnover, and maximum International and domestic market share by effectively operating. Moreover, the success of many developed and developing nations as tourists destinations depend heavily on a tour operator’s ability to attract tourists, development and promotion of tourism plant, diversification of tourism product and their social responsibilities to develop a remote and backward area.
Types of Tour Operators
Tour operators are basically categorized into four types . These are categories on the basis of their nature of the business and its operations.
Inbound Tour Operators
Outbound tour operators, domestic tour operators.
- Ground Operators
These are also known as incoming tour operators . Technically, the operators who receive guests, clients/tourists, and handle arrangements in the host country are c alled inbound tour operators . For example, a group of American Tourists is coming through TCI Ltd. to India and the company makes arrangements and handles the group in India then TCI is called an inbound tour operator.
Incidentally, the inbound traffic to the country for the last two decades has been decreasing. Essentially the tour operators need to adopt innovative marketing strategies and should introduce a special interest tour to cater the special needs of Japanese, Americans, French and British people.
Tour operator who promote tours for foreign destinations, maybe business tour or leisure tour is called outbound tour operators . For example a group of American tourists going to a trip of India and Thomas Cook handle arrangement in America like as ticket reservation, hotel booking etc. then Thomas Cook is called Outbound Tour operators in the context of America.
Domestic tour operators are those who assemble, combine tourist components into inclusive tours and sell it to the domestic travelers. In general, these tour operators provide travel services within the tourist’s native country.
The domestic tour operators operate within the boundary of the home country and offer package tour to the travelers viz. Domestic inclusive tours or independent tours.
Ground Operators/Destination Management Companies
These are commonly known as handling agencies and their main function is to organize tour arrangements for incoming tourists on the behalf of overseas operators. Let us take the case of India as a destination that – has a varied culture.
When a tour operator himself promotes beach holidays, wildlife holidays, adventure tours, heritage tours at the different places, the difficulty arises. It is the ground operator then who by handling the incoming travelers in the same season but at different places ensures that the entire operation is according to the package tours or agreements.
Sometime when a handling agency is at a prominent tourist place i.e., Delhi and it has to make arrangements to Goa, then it contracts (If it has no office of its own) with a local operator (known as excursion agent) to handle the arrangement on his behalf.
Why Ground Operators?
Obviously, the tour operation companies do not have close contact with suppliers, governments, destinations and so on. It leaves no choice with the companies but to appoint handling agencies at the destinations. The main reasons are:
- Introduction of new products or plant to promote an exotic destination.
- Lack of Government regulations.
- Lack of personal contract.
- Language problem.
- The company cannot establish its own branch.
Recognizing the very fact that the reputation, performance, and profitability of tour company in its own market largely depends on the efficiency and effectiveness of ground operators, it has because necessary for the company to consider various factors before the selection of a handling agency, they are:
- Size of business
- Professional staff
- Length of business
- Area of operation/Product line
- Market share
Functions of Ground Tour Operators
Over the years of functions and activities of the destination, companies have changed drastically to cope with the changing environment of the tourism industry. In fact, today’s destination companies have become more professional and are bound to provide personalized travel services to the tourists. The following functions are performed by ground tours operators:
- Land arrangement
- Contract and Negotiate with other vendors
- Handling of Arrival and departure procedure
- Planning and organizing local package tour
- Escorting the tourists
- Providing market information
- Costing and pricing package tour
Practically, if we see the working of the travel agencies and tour operators in the industry we find that most of the organizations are performing different types of activities like the retail travel agency , wholesale travel agency, and tour operators.
The travel agency business is no longer an amateurism. Over the last two decades, the pattern and structure of travel agencies have changed to meet tough challenges in the international market. Today, small-scale agencies are finding the travel industry increasingly complex.
Thus, the small and medium scale travel agencies are disappearing or merging or falling instead of rising. On the other hand, a new concept has also emerged i.e. tour operation business . The tour operation business is new but a maturing business at the global level.
Functions of Tour Operator
A tour operator is an organization, firm, or person who is responsible for the actual arrangement of transport and accommodation facilities on any tour or vacations. They are also responsible for operating and providing vacation through contracting, booking, and packaging together of the various components of the tour such as hotel, transportation, meals, guides, optional tours, and sometimes flights.
A tour operator is like a service provider, providing the most convenient option for tourists to stay, visit, as well as leave from the city. A tour operator owns a high volume of travel services across carriers, services, and accommodation. Some most important functions of the tour operators are following as:
Planning a Tour
The most important functions of the tour operators are planning a tour. Tour operators plan a tour and make tour itinerary which contains the identification of the origin, destination and all the stopping point in a traveler’s tours. A prospective tour operator also gives advice to intending tourists in various types of tour programmes, which they may choose for their leisure or commercial travel.
Making Tour Package
Tour operator buys individual travel components, separately from there suppliers and combines them into a package tour. Tour operators make tour package by assembling various travel components into a final product that is called tour package which is sold to tourist with own price tag. Making tour packages is also an important function of Tour Operator.
Arranging a Tour
Tour operators make tour package and also arrange a tour according to tourist demands. Tour operators arrange the tour package and various tourists activities to provide the best experience to tourists/traveler.
Travel Information
Whatever the size of tour operators, it has provided necessary travel information to the tourists. This task is utterly difficult and very complicated. A tour operator must give up-to-date, accurate and timely information regarding destinations, modes of travel, accommodation, sightseeing, immigration, health and security rules about various permits required to travel in a particular area etc.
Reservation
It is a very important function of all type tour operators and travel agencies. Tour operator makes all the reservation by making linkages with accommodation sector, transport sector and other entertainment organizations to reserve rooms, and seats in cultural programmes and transportation.
Travel Management
Tour operators manage tour from beginning to the end of the tour. A tour operator has the responsibility to look after the finer details of a vacation or tour such as hotel, accommodation, meals, conveyance etc. Tour operators provide travel guide, escorting services and arrange all travel related needs and wants.
Evaluate the Option Available
Tour operators evaluate all available options to provide a unique or unforgettable travel experience to tourists during their journey. Tour operators evaluate the various options available for a tour package and provide best of them to tourists.
Tour Operators makes tour packages and promote them into various tourists markets at domestic as well international level. Tour operators promote a travel destination to attract a large group of tourists at domestic as well as international level. In the promotion of tourist destination, tour operators play a key role. Travel agencies or tour operators are called as image builder of a country.
Sales and Marketing
Tour operators do sales and marketing of tourist products. Tour operators buy individual travel components, separately and combine them into a tour package, which is sold with their own price tag to the public directly. Tour operators do marketing of tourist destinations and tourism product to attracts the attention of the tourists/travelers.
Taking Care of Glitch
Tours operators are also called handling agencies which handles tour package and take care of all the glitches and problems arises during a tour package. Tour operators fix the glitches and provide the best available alternative to tourists during their journey.
Importance of Tour Operators
Tours operators play a key role in the tourism sector. Tour operators create tourist products, promote them a finally sold them to tourists.
Tour operators provide the best and competitive price to the tourist. Tour operators negotiate with suppliers of tourism products such as hotels, airlines and provide the best possible price to the tourist. Tour operators buy tourist products in bulk and get huge discounts from suppliers. So that they provide tourist products at a cheap price.
Tour operators organized a tour in the best way. They personalize and make sure each and every component of the tour is well-taken care. Tour operators provide the best travel experience during a tour. Tour operators save tourists time and money.
Tour operators provide immediate support systems at the host country as well as a foreign land. When tourists travel to a foreign land and things get uncertain, maybe its a health or loss of documents and need to return back or change of travel plan. A qualified tour operator takes care of all these unseen events with efficiency.
Tour operator caters to the needs of tourists on the based on their taste of travel. Tour operator provides all the best available option according to tourist needs and demands
Difference between Travel Agent and Tour Operator
There is a lot of confusion about the difference between tour operators and travel agents what exactly makes them different. The main difference between a Travel agent and Tour operator are following as:
- A travel agent is a person who has full knowledge of tourist product – destinations, modes of travel, climate, accommodation, and other areas of the service sector. He acts on the behalf of the product providers/principals and in return get a commission.
- Tour operator is an organization, firm, or company that buys individual travel components, separately from their suppliers and combines them into a package tour, which is sold with their own price tag to the public directly or through middlemen.
- Tour operators are like wholesalers and travel agents are the retailers.
- A tour operator makes the package holidays up and the travel agents sell them on.
- Tour operator taking up the bulk of the responsibilities and his fee is obviously much greater than a travel agent.
- A tour operator has the responsibility to look after the finer details of a vacation or tour such as hotel, accommodation, meals, conveyance, etc.
The wholesale travel agencies may offer or operate the package tours or may specialize in developing tours for inbound as well as outbound travelers. They are often referred to as tour operators, but there is a difference between Wholesale Travel Agencies and Tour operators .

Before you go, check this out!
We have lots more on the site to show you. You've only seen one page. Check out this post which is one of the most popular of all time.
The Ultimate Guide All About Outbound Tourism
All About Outbound Tourism, also known as international tourism, is an ever-growing sector that has been gaining popularity in the past few decades. With the increase in globalization, people have become more interested in exploring new cultures, cuisines, and destinations around the world.
In this highly competitive travel industry, it’s important to understand the ins and outs of outbound tourism to stay ahead of the game. Whether you’re a travel enthusiast, a travel agent , or a seasoned professional in the industry, this ultimate guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of outbound tourism.
We will discuss everything you need to know about outbound tourism, including the current trends, the top destinations, the benefits and challenges of outbound tourism, and the best practices for the industry. We will be delving into the different types of outbound tourists, such as business, adventure, and leisure travelers, and their unique requirements.

All About Outbound Tourism In Details

Traveling overseas to experience new cultures is becoming increasingly popular among leisure travelers. This section covers everything you need to know All About Outbound Tourism its definition, reasons why it’s preferred over domestic travel, top destinations favored by outbound tourists like Spain and France, and planning tips.
It’s worth noting that international tourism supports economies around the world with a positive impact on GDP, as per WTO and United Nations reports.
Historical Overview Of Outbound Tourism
Outbound tourism, or traveling to a foreign country for leisure or business purposes, has a long and fascinating history. While ancient civilizations such as the Greeks and Romans engaged in travel for trade and diplomacy, it wasn’t until the 19th century that leisure travel began to take off.
The advent of steamships and railways made it easier and more affordable for people to travel abroad, leading to the rise of mass tourism. In the early 20th century, advancements in aviation technology further revolutionized outbound tourism.
Air travel has become faster and more comfortable, making it possible for people to visit far-off destinations in hours rather than days or weeks. Outbound tourism is a major industry today, with millions of people traveling abroad each year for vacation, education, business, and other purposes.
As technology continues to evolve and the world becomes increasingly connected, it will be interesting to see how outbound tourism continues to change and adapt over time.
Factors Affecting Outbound Tourism
There are several factors that can affect outbound tourism, including economic conditions, political stability, cultural differences, and technological advancements. Economic conditions play a significant role in outbound tourism, as individuals are more likely to travel when they have disposable income and job security.
Political stability is also an important factor, as individuals are less likely to travel to countries with high levels of political unrest or instability. Cultural differences can also impact outbound tourism as individuals may be hesitant to visit countries with vastly different customs and traditions than their own.
Technological advancements have also made travel more accessible and affordable, allowing more individuals to participate in outbound tourism. By considering these factors when planning for outbound tourism, individuals can make informed decisions and have a safe and enjoyable travel experience.
Planning An Outbound Trip

Planning an outbound trip can be an exciting and daunting task. To ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience, it is important to consider a few key factors before embarking on your journey. First, decide on your destination and research any necessary visas or travel requirements.
Next, budget your trip, including transportation, accommodation, and activities. Creating an itinerary to make the most of your time abroad may also be helpful. When booking flights and accommodations, compare prices and read reviews from previous travelers.
Finally, don’t forget to purchase travel insurance to protect yourself in case of any unexpected events. With careful planning and preparation, you can have a successful outbound trip filled with new experiences and unforgettable memories.
Choosing A Destination
Choosing the right destination is crucial while planning an outbound trip for leisure or vacationing abroad. Cost-effectiveness, accessibility by air or road transport, and safety concerns must be considered when selecting a place.
Researching the local culture and customs can ensure that travelers are respectful to natives and avoid offending them at any cost. Weather patterns and climatic conditions in the desired location are equally important before making any reservations. Opt for a spot that caters to your interests, such as historical sites or adventure activities.
Transportation Options For Outbound Travel

Travelers going on an outbound trip have multiple transportation options to choose from. For longer distances, air travel is the most popular and convenient choice. Land transport like buses, trains, and cars can be chosen if you’re traveling shorter distances or in groups.
Sea transport options such as cruises and ferries offer a unique experience with onboard amenities while exploring different destinations. Budgets and personal preferences help determine which mode of transportation to select.
Accommodation Options For Outbound Travel
When selecting accommodation options for outbound tourism, you must take into account your budget and travel style. Hotels are renowned for their variety of services and facilities; however, they tend to be more costly than other choices.
Hostels are an economical option that fosters socializing amongst travelers while sacrificing privacy. Vacation rentals provide homelike vibes, with kitchens and living rooms requiring prior scheduling. Homestays offer an authentic experience of the local culture but necessitate adaptability.
Activities And Attractions For Outbound Travel

When traveling outside your home country for leisure or business purposes, there are many activities and attractions you can experience as part of outbound tourism. From sightseeing to adventure sports and cultural experiences to food tours, there is truly something for everyone.
Popular outbound tourist attractions include museums, historical sites, national parks, and beaches. As always, conducting thorough research before departure ensures a meaningful travel experience. Outbound tourism has a positive impact on global economies through international trade growth and inbound tourism increases.
Cultural Considerations For Outbound Travel
When planning an outbound trip, it is essential to consider cultural differences in your destination. Understanding different customs and traditions can help you avoid potential misunderstandings while traveling abroad. Dressing appropriately and respecting religious practices are also important factors to consider.
Awareness of these cultural considerations will help make your outbound travel experience even more enjoyable. Outbound tourism significantly contributes to the GDP of many countries, including Spain, France, America, Germany, Australia, Italy, Japan, and Thailand.
Health And Safety Precautions For Outbound Travel

To avoid potential health and safety risks while traveling outbound, it’s vital to research potential risks and take necessary precautions.
This can include obtaining vaccinations or medications before the trip, packing appropriate clothing and gear based on local weather conditions, researching any safety concerns or political instability in the destination such as in the United States or Spain, being aware of cultural norms like respecting religious practices and restrictions on photography or other activities such as leisurely visits to France’s wine country.
Outbound travelers should also keep in mind the positive impact of outbound tourism on GDPs, like in Germany or Australia, as well as international trade per the WTO. By following these guidelines for safe travel during outbound tourism, you can enjoy your travels worry-free.
Economic Impact Of Outbound Tourism
Outbound tourism can have a significant economic impact on both the home country and the destination country. Individuals who travel abroad typically spend money on transportation, accommodations, food, and entertainment. This spending can generate revenue for local businesses and help stimulate the destination country’s economy.
Additionally, outbound tourism can create job opportunities in the travel industry and related sectors such as hospitality and transportation. On the flip side, outbound tourism may also have an impact on the home country’s economy. While individuals are spending money abroad, they may not be contributing to their home country’s economy.
However, some argue that outbound tourism can also benefit the home country by promoting cultural exchange and increasing international cooperation. Overall, outbound tourism has both positive and negative economic impacts that should be carefully considered when analyzing its effects on society.
The Benefits Of Outbound Tourism

Outbound tourism, or traveling outside of one’s home country, can have numerous benefits for individuals and society as a whole. For individuals, outbound tourism can provide new experiences, cultural immersion, and personal growth. It can also be a way to escape from the stresses of everyday life and recharge.
From a societal perspective, outbound tourism can bring economic benefits to both the home country and the destination country. It can create job opportunities in the travel industry and support local businesses.
Outbound tourism can also foster cultural exchange and promote understanding between different countries and cultures. Overall, many benefits to outbound tourism make it a worthwhile endeavor for both individuals and society.
The Impact Of Outbound Tourism On The Economy
Outbound travel continues to be a major contributor to economies around the world. It plays a crucial role in job creation and increased revenue across regions like Europe and Asia. In fact, many countries like Spain and France rely heavily on inbound tourists for their GDP growth.
Governments should continue implementing policies like visa facilitation or marketing campaigns that support this growing market. While it’s true that there are negative impacts like environmental degradation or cultural homogenization associated with it, we need to strike a balance between promoting outbound tourism for economic benefits and ensuring sustainable practices.
Planning an outbound trip can be a daunting task, but with the right information and preparation, it can be a wonderful experience. From choosing a destination to picking the right transportation and accommodation options, there are many factors to consider for a successful trip .
Understanding outbound tourism’s historical overview and cultural considerations can help you navigate different customs and traditions. It’s also important to take health and safety precautions to avoid potential risks while traveling. All About Outbound Tourism not only benefits individuals but has a significant impact on the economy as well.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is outbound tourism.
Outbound tourism means traveling from one’s home country to another destination for leisure or business. It has become more popular due to advancements in transportation and communication. This type of tourism benefits both the home country and the destination economically. Sightseeing, shopping, and trying new cuisines are among the favorite activities of outbound tourists.
What Are Examples Of Outbound Travel?
Outbound travel involves leaving one’s home country for another, be it for leisure, education, business, or other purposes. Examples include vacations, conferences, visiting loved ones, volunteering, and adventure tourism. Thorough research and planning are essential for a successful and safe trip.
What Is The Role Of An Outbound Tour Operator?
An outbound tour operator is responsible for arranging travel plans for people traveling outside of their home country. They collaborate with airlines, hotels, and transportation providers to create all-inclusive travel packages, handle visa applications and logistics, and aim to provide a stress-free and pleasurable experience for their clients while discovering new places.
What Are The 4 Main Types Of Tourism?
Tourism can be divided into four main categories: cultural, adventure, eco, and leisure. Cultural tourism involves visiting historical sites and landmarks to learn about a region’s culture. Adventure tourism involves thrilling activities like skiing or bungee jumping. Eco-tourism promotes sustainable practices and supports conservation efforts. Leisure tourism is a more relaxed form of travel for rest and relaxation.
What Are Some Popular Destinations For Outbound Tourism?
The choice of an outbound tourism destination depends on the traveler’s preferences and budget. Popular options include Europe, Southeast Asia, Australia, and the US, as well as beach destinations such as Mexico, Thailand, and the Maldives. Adventure travel to places like New Zealand, Iceland, and Canada is also becoming more popular.
Michael C. Herrera
I’m a travel blogger with a focus on safety. I’ve been to all seven continents, and I love sharing my tips for staying safe while traveling. I also have a lot of experience with travel hacking and finding the best deals on airfare and hotels. My blog features reviews of restaurants, hotels, and attractions around the world.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Flixbus Luggage - What You Need To Know
When travelling by bus, you must consider the amount and type of luggage you'll bring. That's where FlixBus luggage comes in. FlixBus is a popular bus company that operates in Europe and the United...
Lucas Luggage Replacement Wheels: A Simple Guide
Lucas luggage replacement wheels are an essential component for any frequent traveler. These wheels are designed to replace worn-out or damaged ones on your existing Lucas luggage. Providing an...
How do Tour Operators Work?
To unlock the tourism industry's business and leisure travel potential, you must understand how tour operators work.
From package holidays to bespoke tours, tour operators make memorable holidays. Whether you're a domestic operator focusing on your country's destinations or an outbound operator designing trips abroad, this guide is for you.
The Role of Tour and Activity Providers
At the heart of the travel industry, tour operators like you, whether inbound or outbound, design travel packages that simplify things for tourists. This involves meticulous planning of land arrangements, accommodation, tours, and transport.
As a tour company, you may specialize in specific types of trips, such as leisure travel or business trips, creating packages that cater to your target market's preferences.
What are the different types of tour operators?
- Domestic Tour Operators : Focusing on the domestic tourism market, these operators provide travel packages within their home country.
- Outbound Tour Operators : These companies design holiday packages for travelers visiting other countries, often incorporating international destinations into their itineraries.
- Inbound Tour Operators : Inbound operators cater to tourists coming into their host country, providing local insights and experiences.
- Ground Tour Operators : Often known as ground operators, these firms handle local arrangements in the destination country, often working in collaboration with other tour operators.
How do tour operators work with accommodation and transport providers?

Tour operators play a pivotal role in crafting the perfect travel experience, and a big part of this involves working closely with accommodation and transport providers. Here's a glimpse at how this collaboration typically works:
Building Relationships with Accommodation Providers
- Negotiating Rates : Tour operators negotiate contracts with hotels and resorts to secure competitive rates. This often involves bulk booking or agreeing on fixed rates for a certain period.
- Customizing Guest Experiences : They work with these providers to tailor lodging experiences that align with the overall theme of the tour, whether it's luxury, adventure, or cultural immersion.
- Ensuring Quality and Standards : Regular inspections and feedback mechanisms are put in place to ensure that the accommodation meets the expectations and standards required for their clients.
Partnering with Transport Providers
- Seamless Logistics : Tour operators coordinate with various transport providers, including airlines, bus companies, and car rental services, to manage the logistics of getting travelers from one point to another.
- Group Deals and Scheduling : They often negotiate deals for group travel and ensure that transportation schedules align seamlessly with the overall tour itinerary.
- Quality and Safety Checks : Ensuring travelers' comfort and safety is paramount, so tour operators regularly check the quality of vehicles and the reliability of transport services.
Creating Cohesive Travel Packages
By integrating accommodation and transport seamlessly, tour operators create cohesive and hassle-free travel packages. This integration is crucial in providing a smooth and enjoyable experience for travelers, where every aspect of their journey is well-coordinated and managed.
Adapting to Client Needs
Tour operators remain flexible and responsive to their clients' needs, often customizing aspects of accommodation and transport to cater to specific preferences or requirements.
To summarize, negotiating strategically, ensuring quality, and meticulous planning are crucial to the relationship between tour operators, accommodation providers, and transport providers. In order to deliver great travel experiences that aren't just fun, they must be safe, comfortable, and just right to match discerning travelers' expectations.
How do tour operators work with travel agents and OTAs?

Tour operators team up with travel agents and OTAs? It's like having the best of both worlds in the travel industry.
Here's the lowdown: travel agents are like sales gurus. They've got the skills to match your cool tour packages with travelers looking for their next adventure. It's all about personal touches and making travelers feel special.
Now, let's talk about OTAs – think big names like Expedia and Booking.com . These guys are your ticket to the global stage. They're not just about showing off your tours; they're about connecting you with travelers from all over, 24/7. Plus, with their smart marketing tools and the power of customer reviews (which, let's face it, are gold in our world), you're setting yourself up for some serious visibility and street cred.
Combining travel agents' personal selling charm with OTAs' global reach is how tour packages stand out in this competitive market.
Talking about creating packages, how can you work with accommodation and transportation providers?
How to create inclusive tour packages?

As a tour provider, crafting appealing and inclusive tour packages, also known as package holidays or package tours, is key to attracting travelers.
These packages bundle services like flights, accommodations, and transportation for a hassle-free experience. Here’s how you can create comprehensive offers:
- Understand Your Travelers : Know who you’re designing for. Are they families, solo travelers, or adventure seekers? Tailoring your packages to fit their preferences is crucial.
- Forge Strong Relationships with Suppliers : Collaborate closely with accommodation and transportation providers. Strong partnerships can lead to better rates and unique offerings, making your packages more attractive.
- Quality Over Quantity : When choosing hotels and transportation options, prioritize quality. A well-selected hotel or comfortable transport experience can elevate your entire package.
- Flexibility is Key : Offer flexibility in your packages. Options for room upgrades, transport preferences, or even alternative activities can make your package more appealing to a diverse range of travelers.
- Highlight Unique Experiences : Include special experiences travelers can’t find elsewhere. Unique local tours or exclusive access to attractions can make your package stand out.
- Transparent Pricing : Ensure transparency in pricing. Hidden costs discourage travelers. Clear, upfront pricing builds trust and satisfaction.
- Feedback Loop : Regularly gather feedback from your customers and adjust your packages accordingly. Continuous improvement based on customer insights can significantly enhance your offerings.
By focusing on these areas, you can create inclusive tour packages that meet but exceed the expectations of your travelers, ensuring memorable and hassle-free trips.
How do tour operators pay suppliers?
For tour operators, establishing and maintaining a solid financial relationship with suppliers — including accommodation and transportation providers — is crucial for a smooth and successful business and tour operation itself. Here's a look at how these payments are typically managed:
Advance Payments and Deposits
Tour operators often make advance payments or deposits to secure services well ahead of tour dates. This is especially common with hotels and special activities that require early booking.
Credit Facilities and Post-Payment Agreements
In some cases, tour operators may have credit arrangements with suppliers, allowing them to pay after the service is delivered. This requires a high level of trust and a proven track record of reliable payments.
Bulk Payment Contracts
For regular or frequent services, operators might negotiate bulk payment contracts. Under these agreements, they pay a lump sum for a specified number of services or bookings over a period, often at a discounted rate.
Net Rate Agreements
Suppliers may offer net rates to tour operators, which are discounted prices exclusive of commissions. The domestic tour operators then mark up these rates when selling to customers, and the difference forms their profit margin.
Direct Billing for Services
In some collaborations, suppliers might directly bill the tour operator for services rendered, usually after completion.
Electronic Payments and Wire Transfers
With the digitalization of financial transactions, most payments are now made electronically. This ensures quick, secure, and traceable transactions.
Managing Currencies and Exchange Rates
For international tours, operators must adeptly manage payments in different currencies, considering exchange rates and transaction fees.
Contingency Funds for Unforeseen Expenses
Operators often set aside contingency funds to cover unexpected costs or last-minute bookings, ensuring that the tour runs smoothly without financial hiccups.
Why is the booking process so important for selling tours?

The booking process is crucial in the tour industry for several key reasons:
- First Impression Matters : This initial interaction sets the tone for customer experience and expectations.
- Ease Equals Sales : A simple, user-friendly booking system encourages more purchases.
- Trust Building : A smooth process builds trust, showing customers that they’re dealing with a professional operator.
- Upselling Opportunities : During the booking, there’s a chance to offer additional services or upgrades, enhancing the experience and increasing revenue.
- Data for Personalization : The information collected can be used to tailor future offerings and improve service.
- Effective Communication : This stage is vital for conveying key tour information and ensuring customer understanding.
- Reputation Impact : A positive experience can lead to recommendations and positive reviews, while a negative one can harm the operator's reputation.
- Resource Management : Understanding booking trends helps manage tours and resources.
In short, the booking process isn't just about securing sales; it's about shaping the entire customer journey, from first impressions to post-tour feedback.
Tips for Operators
Invest in a good, easy-to-use, and cost-effective booking software solution. Granted, it may incur some fees on your part, but think of the heavy lifting it does for you.
It does more than take reservations and bookings. It saves you tons of time with manual tracking, guest follow-up, and ticket management. It also eases the customer journey from point one to post-tour feedback.
Booking software solutions like TicketingHub save you stress and ease your guests. It charges 3% only for successful bookings.
Trusted by Egypt Sound and Light Shows, The Immersive Gamebox, Secret Food Tours, Sipsmith Distillery , and a hundred folds more - this software solution is jam-packed with time-saving features in an easy-interfaced navigation.
Whatever software solution you pick, aim for the solution that saves you time from needless complexities in design and usability - all while helping you stay profitable and leaving your guests satisfied right from the booking page.
Conclusion: Making Great Tours Happen
In wrapping up, it's clear that being a tour operator is about connecting the dots to create amazing travel experiences. Whether you're showing off the best spots in your own country or taking people on adventures abroad, the key is in the details – from picking great hotels to organizing smooth rides.
Your partnerships with local travel agencies, agents and OTAs are super important too. They help you reach more people and make sure your tours stand out. And when making tour packages, remember to listen to what travelers want and keep things flexible and interesting.
Don't forget, managing your money well, especially when paying for services, keeps everything running smoothly. And the booking process? That's your chance to make a great first impression and keep things hassle-free for your customers.
So, there you have it – mix in a bit of planning, a dash of good relationships, and a sprinkle of creativity, and you're on your way to creating trips that travelers will love. Happy touring!
FAQ Section
How important are tour operators.
Tour operators play a pivotal role in the tourism industry. They create and organize tour packages, catering to both business and leisure travelers. These packages simplify travel arrangements, offering hassle-free travel.
Tour operators are the key architects of memorable trips, ensuring travelers can explore various destinations easily.
What is the life of a tour operator?
Tour operators plan meticulously and collaborate with various stakeholders. They work closely with outbound and inbound tour operators, accommodation and transport providers, and even travel agents and online travel agencies (OTAs).
Their goal is to create appealing package holidays, manage travel arrangements, and provide tourism products that meet their target market's preferences.
What are the strengths of tour operators?
Tour operators have several strengths, including the ability to create inclusive tour packages that simplify travel for tourists. They can specialize in various categories, such as business or leisure travel. They can also collaborate with distribution partners like travel agents and OTAs to reach a wider audience.
Tour operators leverage market data to sell directly to their target market, offering tourism products that cater to different preferences.
What's the difference between a tour operator and a travel agent?
Tour operators and travel agents serve different roles in the travel industry. Tour operators design and create tour packages, manage travel logistics, and provide tourism products.
Travel agents, on the other hand, act as intermediaries between travelers and tour operators or suppliers. They assist customers in choosing and booking the right travel options, including tours created by tour operators, but they don't create the tours themselves.
Get the latest news and stay in touch with the industry secrets.
By clicking "Subscribe", you agree to our Privacy Policy and the data we do collect.

What to Look For in the Best Online Booking Software?

Online Travel Booking Tool: How Magic Link is Solving the Rebooking Problem
.webp)
FareHarbor vs Rezdy vs TicketingHub: Honest Tour Booking Software Comparison Guide

Why Online Reputation Management Is Important for Tour Operators
Keep Reading

Navigating Success: Essential Business Tips for Tour Business Owners
We've compiled a comprehensive guide of essential business tips tailored specifically for tour business owners.
Discover how tour operators create seamless travel experiences through great partnerships, flexible packages, and easy booking processes.
Wait you forgot to try your Luck
Enter your email and get details on how you can win Prizes/ Shopping Vouchers

- Business Courses How to start a travel agency 4Ps of Tourism Marketing Interpersonal Skills Training Mastering in AIRBNB Travel Consultant Course Travel Photography Travel Agent Essentials Tourism Marketing Course International Tourism Course View All
- Destinations Alpines of Graubunden Lakshadweep Oman Andaman Manali Hampi Hawaii Hungary Saudi Arabia Ooty View All
- Hotels Centara Ras Fushi Resort Maldives Centara Grand Maldives Courtyard By Marriott Bangkok JW Marriott Bangkok FIVE Zurich Hyatt Ziva Los Cabos Hyatt Ziva Puerto Vallarta Sinner Paris Kandima Maldives View All
- Experiences ARTECHOUSE Kennedy Space Center An out of this world adventure SUMMIT One Vanderbilt Phillip Island Nature Park Trans Studio Bali Theme Park Zoos Victoria Vana Nava The Wheel at ICON Park View All Free Vouchers

- Register with us
- Webinar Registration
- Destinations
- Experiences
- Business Courses
- TBO Portal Training
- Strategic Alliance
Existing Agents Login Here

Reset Password
Different types of tour operators that you should know about.
Tour operators are an integral part of the travel industry. They play a crucial role in creating and selling travel packages to different destinations worldwide. A tour operator is a company that puts together travel packages, which usually include transportation, accommodation, and activities, and sells them to consumers. This blog will discuss the different types of tour operators and their roles in the travel industry. Knowing the types will help one to choose the better fit.
Types of tour operators
As per the requirement, there are different types of tour operators in the travel industry. Some of these include inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators, domestic, specialist among others. Let us explore them one by one.
1. Inbound Tour Operators
Inbound tour operators organize and sell travel packages for visitors coming into the country. They are responsible for creating itineraries and ensuring that visitors have a memorable experience during their stay. They typically work with local suppliers, such as hotels, transportation companies, and tour guides, to assemble their packages.
2. Outbound Tour Operators
Outbound tour operators are companies that organize and sell travel packages for consumers who are traveling out of their home country. They are responsible for creating itineraries and ensuring that travelers have everything they need for their trip. They work with local suppliers in the destination country to ensure everything is in place when their clients arrive.
3. Domestic Tour Operators
Domestic tour operators organize and sell travel packages within their home country. They specialize in creating tours that showcase the best that their country has to offer. They work with local suppliers, such as hotels, transportation companies, and attractions, to create their packages.
4. Specialist Tour Operators
Specialist tour operators focus on specific niches within the travel industry. They may specialize in adventure, education, luxury, or any other type of travel that appeals to a particular group of travelers. They typically have a deep knowledge of their niche and can create unique and memorable client experiences.
5. Travel Agency and Tour Operators
Travel agencies and tour operators are often used interchangeably, but there is a noticeable difference between the two. Travel agencies typically sell flights, hotels, and transportation, while tour operators create and sell complete travel packages that include activities and accommodation.
6. Luxury Tour Operators
Luxury tour operators create and sell high-end travel packages to discerning travelers. They typically offer personalized service, exclusive access to attractions and activities, and top-of-the-line accommodations. Luxury tour operators cater to travelers who are looking for a one-of-a-kind experience.
7. International Tour Operators
International tour operators are companies that create and sell travel packages to destinations around the world. They work with local suppliers in each destination to develop itineraries that showcase the best of what the goal has to offer.
8. Coach Tour Operators
Coach tour operators are companies that organize and sell tours that are conducted on a coach or bus. These tours typically cover a large area or several countries. They offer a convenient and affordable way to see multiple destinations in one trip.
9. Receptive Tour Operators
Receptive tour operators work with other tour operators to create travel packages for a specific destination. They are responsible for coordinating the local suppliers and ensuring that everything runs smoothly during the trip.
10. Adventure Tour Operators
Adventure tour operators specialize in creating and selling travel packages that offer outdoor activities and adventures. These tours may include hiking, rafting, or wildlife safaris and are designed for travelers looking for an adrenaline rush.
11. Educational Tour Operators
Educational tour operators create and sell travel packages that focus on educational experiences. These tours may include visits to historical sites, museums, or cultural events and are designed to give travelers a deeper understanding of the destination.
Why tour operators are crucial?
Tour operators play a vital role in the travel industry as they create and sell travel packages that offer unique and memorable experiences for travelers. By understanding the different types of tour operators, travelers can choose the right tour operator for their specific needs and preferences.
It's also worth noting that many travel agencies also offer tour operator services, so it's important to do your research and choose a reputable company with experience in the destinations and types of travel that interest you.
Whether planning a domestic trip or an international adventure, working with a tour operator can save time and hassle while providing unique and memorable travel experiences. In addition, many tour operators are now offering more sustainable travel options, such as eco-tourism and responsible travel. These tours aim to minimize the impact of tourism on the environment and local communities while providing travelers with unique and authentic travel experiences.
Another trend in the tour operator industry is using technology to enhance the travel experience. For example, some tour operators now use virtual reality to provide travelers with a preview of their destination or to offer immersive experiences during the trip. Tour operators will likely continue to adapt and innovate as the travel industry continues to evolve to meet travelers' changing needs and preferences. Suggested Read: How to Become a Travel Agent
In summary, tour operators play a vital role in the travel industry, offering travelers a wide range of options and experiences. By understanding the different types of tour operators and their functions, travelers can make more informed choices when planning their trips. With the increasing focus on sustainability, responsible travel, and technological innovation, the tour operator industry is poised to continue growing and evolving in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. what are the criteria for classifying tour operators, q2. who do tour operators collaborate with, q3. what industry does a tour operator work in, q4. what is the role of an inbound tour operator, q5. what sets luxury tour operators apart.
- Things to do in Phillip Island: For an Incredible trip to Melbourne, Victoria
- Top 15 Things to Do in Victoria: Exploring Melbourne and Beyond
- Top 6 Places to Visit in Muscat: Top Attractions & Hidden Gems
- 10 Things to Do in Saudi Arabia Beyond a Spiritual Experience
- 8 Adventures in Oman: You shouldn’t be missing
- 8 Tourist Places to Visit in Lakshadweep: India’s Island Paradise
- 8 Best Things to do in Oman for a Holiday to Remember
- Full Proof Guide to 13 Top New Attractions in Dubai
- Top Things to Do at Katara Cultural Village, Doha, Qatar
- Exploring the Breathtaking Beaches of Tanzania: A Coastal Paradise
- Discovering Willy’s Rock: Boracay's Hidden Gem
- 10 Top Places to Visit in Oman, Tourist Places & Tourist Attractions
- Camping in Riyadh: A Recreational Escapade in the Desert
- Exploring the Serene Beauty of Big Buddha Temple Pattaya
- Top 8 Cafes and Restaurants in Yas Island: Casual Dining Options

Tour Operator Terminology
On this page we’ll try to clearly define the terms you need to know to run a tour business, and interact in our Tourpreneur Facebook Group .
General Tour Industry Terms
- Tour This is a catch-all term that implies a type of travel experience that takes place over time, generally visiting multiple sights. It could last 1 hour or 30 days, and be done as a walk, or in vehicle. It could be a solo traveler or a group of 50 people. Other words might be used to describe the same thing: tour, experience, journey, excursion , etc. It usually implies something organized, either by the traveler themselves, or a tour operator, who designs and delivers a tour for a traveler or group of travelers.
- Guest/Customer/Client/Passenger/Participant/Traveler Thanks to Disney, guest is what we generally use to refer to our customers. Why the difference? “Customer” implies a financial relationship, whereas guest relates more to a personal connection and a sense of welcome and hospitality. But it’s the same as customer, passenger (PAX), traveler, etc., and different companies will prefer different terminology.
- Guide / Tour Guide / Tourist Guide “tour guide” is used more often in Anglophone countries, especially in the U.S., whereas “Tourist Guide” is used in Europe and elsewhere globally.
- Tour Leader/Tour Director/Tour Manager/Tour Escort/Trip Leader This role goes by many different names. It refers to a guide who works over multiple days, usually traveling with a group of guests to multiple cities or regions. In addition to delivering commentary about the locations visited, a tour leader also handles the tour logistics, including working with the motor coach driver, staying on schedule, checking into hotels, meals and activities on time.
- Interpreter A guide working often at National Parks or heritage sights; interpretation theory is a 100-year old body of theoretical work focused on strategies for helping individuals make their audience connect with and care for the site that’s being interpreted.
- Docent The name sometimes used for a guide usually in a museum or cultural heritage sight.
- Day Tour A type of experience that begins and ends in the same day. Usually used to distinguish an experience from a multi-day tour.
- Multi-Day Tour Any type of experience that lasts for more than one day. Often includes hotels, meals, short activities, and a form of transportation.
- Package Tour A kind of experience (usually multi-day) in which several different components are bundled together: it may or may not include airfare, hotels, guided experiences, meals, etc.
- Group Tour You’ll see these terms used differently to a kind of experience in which separate individuals or smaller groups come together to share an experience. Group tours can be public or private .
- Public Tour As the name implies, this is a tour that’s open to the general public to sign up. The tour therefore consists of a variety of people who don’t already know each other. A public tour is usually offered at a set time and day.
- Private Tour A tour that is sold specifically to an already-organized group of travelers who don’t wish to experience the tour with others. A private tour might be a couple, a small group of friends, or a large church group. Private tours might be at a set time, or organized according to group’s specific needs.
- Custom Tour A custom tour is usually also a private tour. Custom refers to the operator crafting an experience customized to the specific demands of a client. A tour operator might be engaged by a client to design a unique experience, for one person or a large group.
- Pre-Formed/Affinity Group These are commonly used terms in the multi-day tour space to refer to a group tour not made up of individual solo travelers & couples, but instead of an alread-formed large group of travelers. An “affinity group” shares a common trait—they belong to a church, a retirement community, or a family reunion traveling together, for example. A pre-formed group might also be created by a “Group Leader” who sells a tour for a tour operator , often in exchange for a free trip or a commission.
- Escorted Tour Used most often in the multi-day tour space, an escorted tour means you’re traveling with an escort (old fashioned term), more commonly referred to today as a tour manager, tour director, tour leader, or trip leader. The TM’s job is to handle the logistics of keeping the group together, checked into hotels, arranging meals, etc. They work for the tour operator.
- Guided Tour In short, an organized excursion led by an individual or individuals. “Tour Guide” is the generalized term, but a guide could be a museum “docent” or an adventure guide, tour leader, etc.
- Self-Guided Tour This has two different meanings, one related to technology, one related to nature. When talking about mobile phone apps, a self-guided tour is one usually done in-destination using audio recordings and GPS data to guide an individual along a tour route, sharing recorded stories. In the world of adventure tours, a self-guided tour happens when an individual hires a tour operator to provide guidance in the form of itineraries, maps, possibly technology, all to facilitate an extended journey involving walking, hiking, biking, etc.
- FAM Tour A “familiarization” tour, focused on helping one set of professionals (travel agents, for example) learn about a destination, or about vendors in an area. A group of tour guides might take a FAM tour to a new attraction that opened in town, to become familiar with it. A group of travel agents might sign up for a FAM to a destination that they’ll then sell to clients.
- FIT Tour Very confusing term. It’s evolved over time. It once meant “foreign independent travel” but now is more often thought of as “flexible independent travel.” The goal is to distinguish this kind of independent traveler from someone who buys into a packaged group tour. FIT is more associated with a client who engages with a travel agent or operator to design something that suits their specific customized needs.
- Activity An activity is usually different than a tour in that it is less about guided sightseeing and more about doing something, well, activity based. Examples might be watersports, biking, hiking, etc.
- Attraction Think amusement parks, museums, and the Eiffel Tower. What do they all have in common? They require tickets, they’re single place-based experiences, and rather than do them in groups, thousands of people pour in at once, with no specific booked time requirements (unless doing so for crowd control or pandemic related reasons).
- “Tours & Activities Industry” This is just one of many ways to talk about our industry. You’ll also hear Tours, Attractions & Activities,
- DMO/CVB/Tourism Board A Tourism Board or Destination Marketing Organization (DMO) or Convention & Visitors Bureau (CVB) are all essentially the same thing. — an organization (public, private, or a mix) whose goal it is to promote a destination, be it a city, region or country. Examples include NYC & Company and Visit Scotland .
- MICE Pronounced like the animal, stands for Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Events. From a tour perspective, this is where an operator might work with a CVB (see above) to organize tours for business customers hosting or attending a conference in a location. Incentive tours are reward experiences that a company offers a group of employees.
- B2B Tour operators who work with other operators
Types of Tour Operators
- Tour Operator A business that organizes and sells tours. They sell to a customer, and possibly work with vendors (hotels, restaurants, vehicle companies, etc.) to create an organized tour experience. In short, operators do the grunt work.
- Travel Agent/Agency In general, an agency works with travelers, and books travel components to relieve the traveler’s burden of figuring it out on their own. An agency might book a tour operator’s tour as part of the services they provide the travel, in exchange for a commission from the operator.
- [insert word here] Operator Tour Operator is a general term, but that’s not the only kind of operator out there. You might also be an adventure operator, watersports operator, ATV rental operator, you name it. But in all cases, you’re not an agency booking someone else’s service, you’re providing the service yourself.
- Day (or Multi-Day) Tour Operator Both are subsets of “tour operators” in general. It might be used in the Tourpreneur community when we’re referring to the specific challenges of a specific kind of operator, since the products and challenges of each type of tour can be very different.
- Inbound / Receptive Operator / DMC (destination management company) These are all versions of the same thing, with terminology that is sometimes preferred over the other words for various reasons. This kind of tour operator creates experiences in a certain location (often a specific city or a region or country), working B2B with tour operators or corporate entities needing local knowledge and connections. Receptive operator is an older term meaning they “receive” clients who are coming in (or inbound) from somewhere else.
- Outbound Operator This version of tour operator (usually multi-day) designs experiences that take guests elsewhere. An outbound operator might be based somewhere (Australia, for example) but focus on creating trips that send their Australian customers outbound to other countries.
Sales, Marketing & Software Terms
- SEO Search Engine Optimization—the art of optimizing your website and online presence to bring your content to the top of search engine results (principally Google).
- PPC Means “Pay-per-click” and references the kind of digital advertising done by companies like Google: you create an advertisement to appear in search engine results, for example, and you pay for that ad a specific market rate each time someone clicks on your link.
- OTA Online Travel Agency—this is a catch-all term for a wide variety of online marketplaces servicing the travel industry, selling everything from rental cars to flights to hotels to tours. An OTA in the general industry might refer to big players like Expedia or Booking.com; in the tour industry, it refers to companies like Viator (the largest tour OTA) and GetYourGuide. There is a long tail of “niche OTAs” that serve specific types of tours and activities (like watersports) or a specific region.
- Online Marketplace / Platform This is a more general term for the kind of website platform (like Viator) that sells a wide variety of tours online. Think Guide Marketplaces like ToursByLocals or Withlocals, companies that curate large amounts of guides, but aren’t traditional OTAs like viator.
- Restech/Booking Software You’ll hear “restech” (alternately reztech, rez-tech, etc…) as a fast way to refer to the software industry centered around creating helping tour operators accept online bookings, and keep those bookings organized. The largest companies in this space work mainly with day tour operators.
- Tour Operator Software Different than booking software/restech, TO software offers an extended suite of features meant to help operators across their whole business, from operators to itinerary proposals to budgeting and pricing. This software may include a booking/payment component, but is a much more fully integrated and holistic (and expensive) solution.
- SaaS Short for “Software as a Service” — this is how the tech industry refers usually subscription-based websites or software that help you do something. Examples of SaaS include booking software and CRMs.
- Supplier In the language of selling tours to customers on a platform, tour operators are suppliers; you supply tours that are then re-sold by the platform.
- Connectivity This is the dark art of how you, the operator (supplier) connect to sales channels.
- Distributor/Reseller These are sales channels that sell tickets to your tours on behalf of you. They could be everything from an online marketplace like Viator and GetYourGuide, to a personal travel agent or hotel concierge..
- Channel Manager This is software that helps you manager all your different sales channels in one place.

Types of Tour Operators
Introduction.
We know that the travel market is vast, and it can be confusing trying to navigate the different types of tour operators and their offerings.
Whether you are a tour operator trying to choose which market to specialise in or a traveller looking for assistance with your next trip, we’ve got you covered!
In this blog post we will walk you through the main types of tour operators and explain how each one can help their customers to plan and book their dream trips.
What is the role of a Tour Operator?
Tour operators help travellers to design, plan, book and enjoy their trips, assisting with the entire customer journey from beginning to end.
They often combine components from several different companies such as airlines and accommodation providers as well as extras such as activities, transfers and entertainment, transforming them into tours which are sold to the public as a package .
The tour operators themselves are also responsible for the marketing of their travel packages, a topic that we covered in ‘ the tour operators’ guide to creating an exciting marketing strategy ’, and should be available for direct communication with the customer throughout the entire process.
Wondering what the differences are between each tour operator?
Well, we’re here to help.
While there are several different types of tour operator, the main ones include:
- Inbound Tour Operator
- Outbound Tour Operator
- Domestic Tour Operator
- Ground Operator
- Receptive Tour Operator
These companies can also focus on the mass market or can specialise on a niche group, such as eco-tourism, adventure sports or food tours.

Inbound Tour Operators
As we explained in ‘ Outbound vs Inbound Tour Operators ’, inbound tour operators are locally-based companies that work by bringing visitors into a specific country or destination , often partnering with other businesses such as accommodation and transport providers in order to offer customers package deals.
Inbound tour operators are also sometimes referred to as destination management companies, aiming to promote their destination as a whole to incoming travellers and assist them with all aspects of their trip. This also requires a knowledge of overseas markets and the needs and interests of different types of customers in order for them to promote their tours effectively.
Outbound Tour Operators
While inbound tour operators bring tourists into a country, outbound tour operators market to travellers in their own country and offer tours in international destinations .
When creating tour packages, outbound tour operators usually focus on specific countries, destinations or regions of the world, and also partner with businesses in the host country to provide customers with convenient and comprehensive packages.
A good example of an outbound tour operator is TUI , one of the world’s largest travel companies that works mainly by selling tours to overseas destinations and who is also one of our customers.
Domestic Tour Operators
As the name suggests, domestic tour operators put together packages for domestic travellers – those who are travelling within their native country . This type of business aims to promote travel within their own country, and offers packages in popular destinations.
Haven Holidays is a domestic tour operator that focuses on the British market by offering breaks in its self-catering holiday parks in an array of coastal destinations around the UK. These types of tour operators frequently offer family-friendly activities and diverse entertainment options for those who want to enjoy weekend breaks or summer holidays within their own country.

Ground Operators
Like domestic tour operators, ground operators also work within their own country . However, ground operators usually work on behalf of inbound or outbound tour operators and are the ones that provide the actual travel service in a destination, helping to organise and assist tourists.
This type of tour operator is especially useful for tours in far-flung destinations where it can be difficult to plan itineraries without local knowledge, expertise and contacts. Ground operators are likely to be on hand in the destination itself to organise transfers, negotiate special rates with accommodation providers or find the best local tour guides.
Receptive Tour Operators
Receptive Tour Operators provide tourism products , whether in the form of packages or single components, to other tour operators or travel agents . They do not sell directly to the public and usually follow a structure similar to a wholesaler.
RTOs are experts in their market , and help their customers to find the best accommodation providers, services and activities in their chosen destination. This type of tour operator makes money by adding a percentage rate to the final price that their customer is selling the travel product for.
For example, a receptive tour operator may work with an outbound tour operator by providing them with travel packages for a specific destination. The outbound tour operator then sells this tour package to its customers and adds an extra fee to the cost, which goes directly to the receptive tour operator.
Technology for Tour Operators
Here at Nezasa , we provide tour operators with a cutting-edge product that allows them to plan, book and customise their customers’ trips with ease. The use of a software solution like ours is an excellent way to simplify aspects of your business, allowing you to focus on the customer themselves.
Our TripBuilder software is a unique, seamless and integrated solution, designed to help you efficiently create hyper-personalised and flexible itineraries for your customers.
To find out more about our innovative products, make sure to sign up for our next webinar here .

- Skift Research
- Airline Weekly
- Skift Meetings
- Daily Lodging Report

Multi-Day Tour Operators 2021: Reshaping Supply Chains and Distribution
Executive summary, definition and core products, the tour operator value chain, digital marketing to become primary sales channel, rise of online booking platforms, the ongoing shake-up of supply chain roles, the new era of modernization and professionalization, covid-19 is driving new types of tours, the pandemic also accelerated many existing trip trends, collaboration and transparency across the industry, bankruptcies are coming, what will the new multi-day tour landscape look like as covid fades, related reports, report overview.
Perhaps no sector has been as badly hit by the pandemic as tour operators, given their intrinsic connection to cross-border travel as well as human interaction. Based on our research and discussions with over a dozen executives we see an industry on the precipice of major changes.
This report will focus on the global multi-day tour operator sector with a heavy emphasis on itinerary-based guided tours. We will also briefly touch upon packaged tour sales. Multi-day tours are one of the last truly offline spaces of the travel industry. But that isolation cannot last. This report will cover the structure of this complex and fragmented industry. We see an ecommerce revolution occurring in the next five years that will reshape the way the industry supplies and distributes its products.
We will also discuss the impact of COVID-19 on the industry and how we see the types of tours offered, and the operators themselves, evolving as a result.
What You'll Learn From This Report
- How the complex supply chain of the multi-day tour industry works and the different kinds of businesses and tours that exist within it.
- How digitalization is disrupting the industry and where the biggest new opportunities exists
- How tour operators have responded to the pandemic
- What we think the new multi-day tour landscape will look like as COVID-19 fades
Executives Interviewed
- Matt Berna, Managing Director, North America for Intrepid Travel
- Murray Decker, Chief Executive Officer of Tour Amigo
- Gavin Delaney, CEO and Co-Founder of TravelStride
- Tom Hale, Founder and President of Backroads
- Travis Pittman, CEO and Co-Founder of TourRadar
- Catherine Prather, President of the National Tour Association
- Massimo Prioreschi, CEO of MT Sobek
- James Thornton, Chief Executive Officer of Intrepid Travel
- Gavin Tollman, President of The Travel Corporation
- Enrique Velasco Jr., Chief Commercial Officer of Coltur Peru
- With special thanks to Jared Alster and Tom Buckley, Co-Founders of Dune7 for their background contributions to this report
From our vantage point today it’s easy to take for granted that people across the world would use their leisure time to travel. But tourism — traveling for the pure enjoyment of it rather than for trade or religion — is a relatively recent development in the grand scheme of things. Most date the birth of modern mass tourism to Thomas Cook’s first package tour in 1841.
But naturally a lot has changed since then. Today’s tour operators need to be constantly evolving to keep up with the changing face of modern travel, as Thomas Cook itself discovered the hard way — and that was before a global pandemic hit!
This report will focus on the global multi-day tour operator sector with a heavy emphasis on itinerary-based guided tours. We will also briefly touch upon packaged tour sales. Though smaller than the hotel or airline industry, anyone seeking to understand leisure travel overlooks tour operators at their own risk. Pre-COVID, 12% of U.S. leisure travelers booked a package tour and in the United Kingdom, 47% of household travel spending was on packages. In Southeast Asia, 60%+ of trips were packaged or semi-guided tours.
Perhaps no sector has been as badly hit by the COVID-19 pandemic as tour operators, given their intrinsic connection to cross-border travel and human interaction. Many operators are still seeing revenues down 80%+ even as other sectors like hotels and airlines are moving to a recovery. The pandemic changed the kind of tours that people want, driving them to seek the outdoors, small groups, and domestic trips.
Based on our research and discussions with over a dozen executives, we see an industry on the precipice of major changes. It is one of the last truly offline spaces of the travel industry, but that isolation cannot last. There is a need for new modern tools and digital distribution, which presents a massive opportunity for new tech startups in the space. We see an ecommerce revolution occurring in the next five years, similar to what short-term rentals experienced following the success of Airbnb. This disruption will be compounded by the profound damage inflicted by the pandemic
In a sense, we already have a bit of a roadmap based on the past trajectory of other travel businesses that moved offline to online. We expect to see the emergence of a few major online booking sites and a new class of intermediary tech vendors to handle online bookings, channel distribution, and inventory management. Eventually this will lead to conflicts over direct distribution, repeat guests, and rate parity.
We also believe that the pandemic will spur a winnowing of the ‘middle class’ of tour operators. A wave of bankruptcies and mergers is likely to come leading to consolidation in a handful of large players on one side and on the other side a long-tail of specialist operators that can niche down into their own unique offerings.
The Tour Operator Landscape
The multi-day tour industry is a big tent that incorporates a wide range of operators, suppliers, and distributors. Plus, at times it seems like every company in the space is running a slightly different business model.
Our first step towards untangling this web of interconnected tour companies is to put a basic definition in place.
Tour Operator : A tour operator is any company that sells two or more trip components together. At its most simple this could be a flight, hotel, or cruise sold together as a package. More complex tour operators bring together transportation and accommodation with local meals, activities, and guides.
There are three core products sold by tour operators: packaged travel, itinerary-based tours, and small ship & adventure cruises.
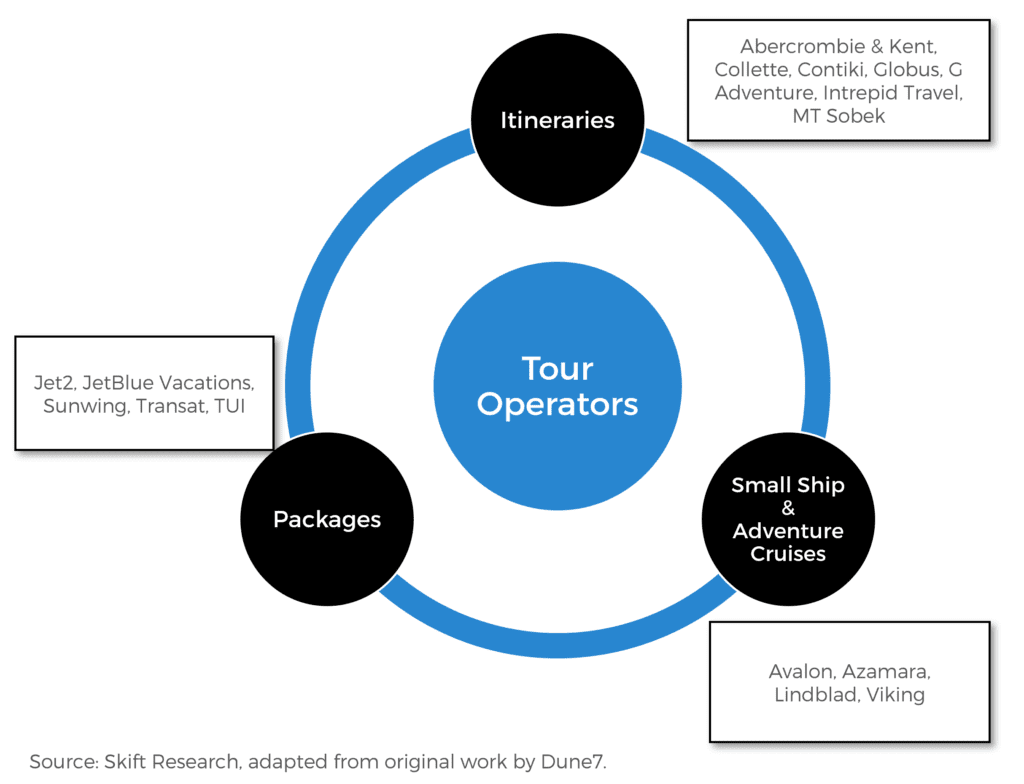
Small Ship, Adventure, and River Cruising
Small expedition ships and river cruises are often included as within the tour operator space. The same travel agents that sell land-based multi-tours frequently also offer specialized cruises. Major booking sites like TourRadar have a prominent and well-stocked river cruise section.
This space was traditionally dominated by specialists, like Azamara, Lindblad Expeditions, orViking River Cruises and they are some of the fastest growing businesses in the entire cruising sector. Arguably these smaller companies have as much, if not more, in common with a land-based tour operator than they do with the mega-ships of Carnival or Royal Caribbean. And to that point, we are now starting to see traditionally land-locked operators go to sea, with, for instance, Intrepid Travel now offers polar cruises and TUI owns several cruise ships.
Small ships do meet our definition of a tour operator as they bring together transportation, accommodation, activities and food into one package. Though in fact, if you stop and think about it, so does the entire cruise industry, regardless of ship size. In order to prevent this report becoming too big we will set aside all cruising — big and small — as its own topic to be covered in future research. The rest of this report will be focused on land-based multi-day tours.
Packaged Travel
Packaged travel offers the distilled essence of our original tour operator definition. These trips bring together two or more components of travel supply, usually a flight and a hotel, and offer the combination together as a single new product to the consumer. The main selling propositions for this kind of product is typically value for money, convenience, or unique supply. Packages are also very commonly sold as an upsell for travel suppliers.
Given that there is no itinerary design included, this type of product is most popular among those looking to ‘fly and flop.’ These guests are typically looking to spend their leisure time off in a hot location with a cold beverage. And they want to access that vacation as easily and cheaply as possible.
One of the main reasons why package tours can offer better pricing to a traveler than assembling the separate components of the trip themselves is because, from the point of view of a travel supplier, packagers operate as an opaque selling channel.
Take hotels as an example: in a package the customer is quoted a single price for the entire bundle – flight + hotel + car – so the traveler can’t pinpoint how much they are paying per room night. This means that hotels can offer discounted rates without violating rate parity and undercutting first-party pricing. Tour operators tend to move high volumes so hotels are incentivized to offer bulk pricing for their business. Bed banks and global distribution systems often act as intermediaries providing wholesale supply to tour packagers.
Convenience is another main driver of packaged tour sales. There is a large segment of consumers, especially in Europe, that don’t want the stress and confusion of booking all of their own travel arrangements. While those of us that have the most severe cases of the ‘travel bug’ may have turned booking travel into a hobby (perhaps many of you reading this), we can admit that this is possibly not the most fun part of a trip for an average vacationer.
Another reason why a traveler might pick a packaged tour operator is because they can offer exclusive supply. Perhaps there is a resort that the operator owns and therefore the only way to visit it is by booking via a package. One of the best examples of this is TUI owns or operates over 400 hotels to ensure it can control the guest experience and provide access to rooms in supply-constrained markets like Cape Verde. It also owns nearly a dozen cruise ships and several charter airlines. Jet2 also follows a similar model with its own in-house airline that complements its vacation packages as it can offer uniquely convenient airlift for its guests only.
Dynamic Packaging
One of the most exciting developments in the packaged tour space is dynamic packaging. This is a relatively new development in the packaged tour space driven by the growth of tech connectivity in the industry. The concept is that, rather than operators or agents manually pulling rates and building bundles by hand, algorithms automatically create package deals live during the guests’ shopping experience.
The next step for this market is the development of open platforms that plug into suppliers’ booking engines and allow dynamic packaging ‘as a service.’ For example Hotelbeds offers dynamic packaging via an API that could allow for this. Third-party platforms for bundling opens up a whole new world of plug-and-play upselling capabilities for travel suppliers that might not have traditionally considered a packaged tour product, although it also brings with it the potential for rate parity issues.
Airlines have long used packaged tours as an upsell to drive revenue and margin on the flight products they were already selling. These bundled upsells often accounted for a small slice of revenue. JetBlue in a 2018 investor day disclosed that its attach rate for JetBlue Vacation was just 1.5% of transactions. However these small percentages can add up to big dollars, like at LatAm which sold $22 million worth of tour packages in 2020, still less than 1% of group revenues. But the package revenue shares can go quite high, even at a traditional mainline carrier. Japan Airlines Group (JAL) — certainly not a discount packager like Jet2 — sold $485 million of packaged tours in 2021, accounting for ~10% of group revenue, according to IdeaWorks .
Most airlines, if they sell tours at all, operate closer to Jetblue with the business driving a low single-digit share of group revenues. But JAL and other exceptions prove just how high the numbers could potentially get. Many airlines see today’s low package numbers as a mere starting point from which to build significant ancillary revenue streams to complement their unbundled retail strategies. Dynamic packaging has made this far more feasible and now airlines of all types from AirAsia, Allegiant, and EasyJet to Emirates and American Airlines are selling tour packages.
In the past, standing up a packaged tour offering at an airline would require a lot of time-consuming negotiations with hotel and car rental suppliers and even after all of that work, supply might still be limited. Airlines are in the core business of selling flights and not negotiating hotel wholesale rate contracts. With dynamic packaging airlines have the ability to tap into B2B platforms that can build bundles around their routes with relatively low lift. Bedbanks, like Hotelbeds , GDSs, like Amadeus , and tech vendors, like Switchfly all now offer dynamic packaging tools. This means that in today’s fast evolving landscape, airlines can add new routes and immediately be selling dynamic packages around that destination on launch.
The development of dynamic packaging further blurs the line between a tour operator, like a TUI, and an online agent, like Expedia. If JetBlue (supplier), TUI (operator), and Expedia (OTA) can all sell the same flight plus hotel package, what is fundamentally the difference between these three companies?
We believe that online travel agencies like Expedia and Booking will be some of the biggest beneficiaries of the move towards dynamic packaging and the above blurring of industry lines. In a dynamic world, having the most possible permutations of trip choices is a key differentiator. And the OTAs sit in a sweet spot where they have strong pre-existing direct customer relationships while also having millions of hotel, flight, and car listings across the globe already live in their databases. When guests shop for a flight, the OTA can then offer them the upsell to add on a hotel room or car booking, all for one packaged rate. The discounted package price is calculated automatically on the fly based on the unique combination of travel choices selected by the shopper. The discount can come from specific wholesale rates pushed by the suppliers to the OTA or the booking site might just choose to algorithmically reduce its commission margin to encourage an upsell to a higher ticket purchase. They can also resell their inventory and technology as white-label dynamic packaging tools to other agents, hotels, and airlines. Both Booking Holdings and Expedia as well as smaller OTA players like lastminute.com have all been running experiments around the best way to sell tour packages. Expect to see more developments in this space.
Itinerary-Based Tours
Itinerary-based tours are, arguably, the heart of the tour operator industry. These tours go beyond simply bundling component travel products, adding on top of that core package a layer of local expertise and itinerary design. These tour operators will be the focus of the rest of this report.
Price is not often the main selling point here. Rather, the convenience of not having to plan, the assistance of a guide, or the uniqueness of an itinerary is the main selling point. There is quite a lot of variety within products offered in this space.
There are three main variables that we can use to define the main types of itinerary-based tour products:
- Fixed-Date Departures vs. Custom: Fixed date tours are offered with a pre-scheduled departure date and a set itinerary. Travelers buy these pre-built itineraries off the shelf. In contrast, custom tours are built to suit each individual guest with a unique schedule and departure date.
- Guided vs. Self-Guided: Though the classic image of a tour includes a guide leading a group, this does not always have to be the case. Self-guided tours are growing in popularity. In this case, the traveler buys a travel package that can include local connections, activities, meals, and suggested sights, but no in-person guide to contextualize the destination.
- Group vs. Individual: This has more to do with the buying behavior of the guest than the actual itinerary on offer. In group travel, the entire tour is booked up by a single organization, perhaps a school group, work retreat, or a large family. On the other hand, individuals traveling book a single slot as part of a larger overall planned departure that combines many other individuals or a small group of travelers that don’t know each other.
We can mix and match these different variables, offering for instance a guided group fixed date tour or an individual self-guided custom tour.
In addition to the main products on offer, there are two primary layers of operators in the itinerary-based space. One is based on the source market that the travelers buying the tour are departing from, and the other based on the destination market that the tour is taking place in.
- Outbound Tour Operators: These tour operators service international travelers. They typically focus on a single origin market but often service multiple overseas destinations. Outbounds specialize in the market that travelers purchasing a tour are departing from and can provide native language marketing, sales, and customer support. They also have the cultural context to understand what kind of itineraries may appeal in their home market. Outbound businesses may operate their own in-destination trips or outsource the local logistics to a destination management company. An example would be a UK based tour company that offers British travelers a variety of trips across Asia and continental Europe.
- Destination Management Companies: Also known as inbound tour operators or receiving tour operators. These operators receive inbound international travelers. They typically focus on a single destination market but often service travelers from multiple overseas origins. By specializing in a single destination, they have the local know-how and logistics to ‘make the trains run on time.’ They can sometimes use their local connections to source unique experiences. DMCs usually contract with an outbound tour operator but increasingly may sell direct to the overseas consumer. An example would be a local Peruvian tour operator that specializes in running Machu Picchu treks for guests coming from many different outbound operators and nations.
The line between outbound and inbound operators has always been blurry and it is only getting hazier. The core distinction we will be making when referring to outbound operators vs. DMCs is the difference between retail-specialists focused on the source market and logistic-specialists focused on the destination.
These terms originate from the cross-border market but, especially as local tourism boomed during the pandemic, have a place in domestic markets as well. While they may not technically be ‘outbound’ operators when within the same country, there can still often be a separation between the retail tour operators and their domestic DMC partners or subsidiaries (though one could even argue New York City might as well be an outbound foreign market from the perspective of a Utah river guide).
Illustrative Example of the difference and connections between Outbound Tour Operators and Destination Management Companies.
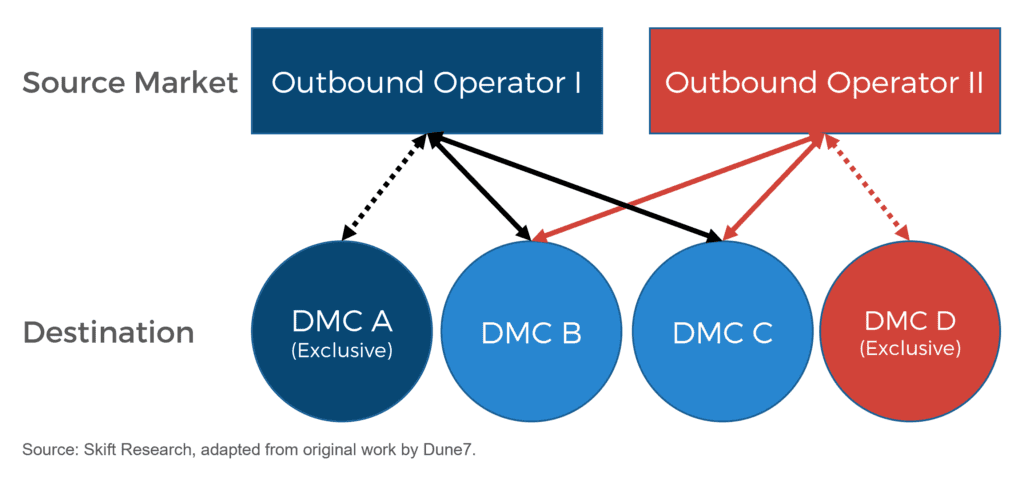
With the baseline definitions and products understood, let’s examine the lifecycle of how a tour is created and comes to market in the land-based tour operator space.
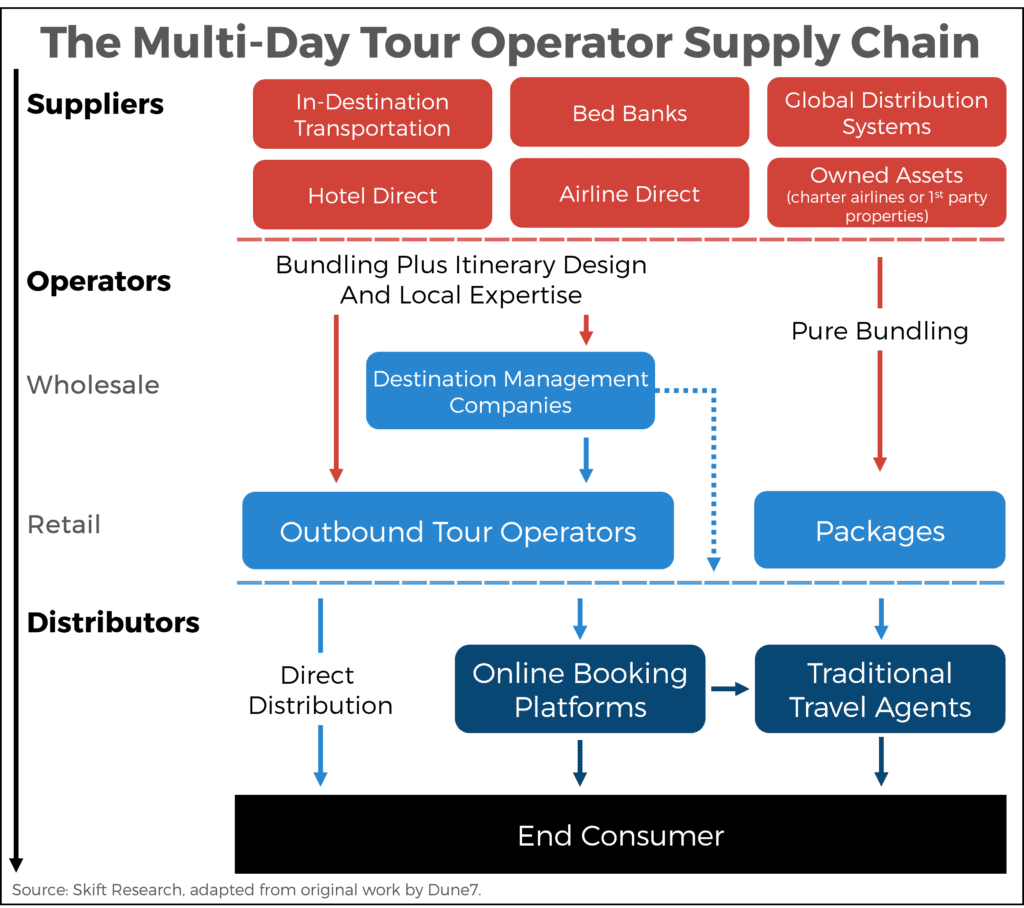
Our model of the tour operator chain has three layers of value add. It starts with the supply of core travel products like hotels, flights, trains, and cars. These ‘raw materials’ of the tour might come from direct contracting with an airline or via a reseller like a bed bank. Some fully integrated tour operators even own their own charter airline or resort properties.
The next layer is the tour operator itself. “The tour operator is the manufacturer,” says Catherine Prather, President of the National Tour Association. Unlike a hotel or airline that is fundamentally anchored to a physical asset, tour operators sell a value-added travel service not tied to a single tangible product. By that we mean that tour companies ‘assemble’ unique trips by taking building blocks from other travel suppliers and adding an additional layer of intangible value-add. That value-add might be local expertise, cheap bundled pricing, or peace of mind. This transforms the raw materials into a more valuable new product which they can resell into the marketplace.
We distinguish here between tour packagers that are doing pure bundling and itinerary-based tours where an additional layer of in-destination curation and expertise is used in the ‘manufacturing’ process. A company like TUI is still a multi-day tour operator at this tier. It ‘manufactures’ its own tour products and retails them through first-party channels and also re-sells through agents and other distribution channels. But the tour products it offers are mainly a bundling of different supply components. In contrast, a G Adventures both bundles the supply components and adds an additional design component by planning daily activities and arranging for local guides.
There is also the opportunity in this layer for wholesalers and retailers. Specialist DMCs often design local tours that can be resold to larger retail travel agencies that can tap into their local market of outbound travelers.
The final layer is that of distribution. There are three primary channels. First is the direct channel driven by in-house sales and marketing efforts. Then there are the two major intermediaries in the space, online booking sites, which operate on both commission and advertising models, and travel agents. It should be noted that tours are one of the last great bastions of traditional travel agents (along with business travel). A very significant volume of tour products is distributed by the large travel consortia and even, in some countries, by brick-and-mortar retailers. This is because tours are one of the most complex travel products, a result of the above ‘manufacturing’ process, making a human intermediary much more valuable.
A hotel room might have a handful of core attributes (star rating, price, location, room type) and several more secondary ones (Wi-Fi, pool, view, floor height). But even the most basic tour can have dozens or more key attributes (departure date, size of group, length of trip, itinerary variations, level of physical activity, type of accommodation, age of participants, etc.). This creates difficulty to code for tours in the back end, as well as for consumers to shop and compare multi-day tours. This has made it doubly hard for online booking sites to take off in the space; however, these challenges are slowly but surely being overcome and digital platforms are growing in prominence as distributors of tours.
We understand that we have tried to simplify a very complex space and so there may be many nits to pick with this diagram. But we think that these core mental models of three main tour products (packages, itineraries, and cruises) sold via layers of value (supply, operation, and distribution) is a useful way to help decipher the tangle of different operators in this industry.
A lot of the confusion in the space seems to stem from the many different permutations of how vertically integrated an organization chooses to be and what permutation of products they choose to sell. But by building this mental model of the industry we can better see past the superficial differences of each specific company. A lot of the variation we see across tour companies is often reflective of different choices about what parts of the value chain to vertically integrate and what products to sell. But within each specific part of the value chain in isolation, business models are often more similar than they may first appear.
For example, tour operators that run their own in-destination programs vs. ones that outsource to a DMC are not two fundamentally different types of tour companies but are instead making different decisions about how vertically integrated they want their organizations to be. Or a travel agent that sells tour packages is best thought of as vertical integration between the ‘manufacturing’ stage of packaging process and a distribution channel, rather than as a wholly separate kind of company from a tour operator with a large first-party salesforce.
Technology Shakes Up The Multi-Day Tour Industry
It is clear from our research that a wave of technological change is washing over tour operators as we write. Tours are one of the last major travel industry categories still heavily built off analog tools and manual processes. Catalogs and phone calls are frequently a part of the tour sales cycle.
Research from the Adventure Travel Trade Association (ATTA) suggests that just 8% of bookings came via online travel agents. And that more than two-thirds of bookings came from some form of offline channel. Though this was just a small sample and only representative of a niche type of tour operator, it speaks to just how small online distribution platforms are in this space.
Travel has attracted significant investor attention — nearly $30 billion of funding over the last five years — much of it focused on the digital transformation of the industry. Online platforms, which started in just airlines and hotels, have pushed into nearly every travel market. Nowadays practically every sub-sector from short-term rentals and business travel to day tours and packaged tours has either a major public company or a “unicorn” private startup valued at more than $1B, oftentimes both. All that is except for multi-day tours.
Tours and in-destination activities have actually been one of the fastest growing categories of travel investment, raising nearly $900 million in 2019, but almost all of these dollars seem to focus on single-day, rather than multi-day tours. Three of the largest startups in multi-days tours — Evaneos, Tourland, and TourRadar, have collectively raised under $300 million in capital while activity OTA Klook has raised $720 million by itself.

Part of this is the challenge of marketing complex tours online as well as resistance from incumbents content with the old ways of doing business. But changing expectations among employees, supplies, and customers, accelerated by COVID-19, are driving digital innovation to the fore in the sector.
This digital ‘splash’ will have ripple effects up and down the entire tour value chain, affecting everything from the smallest on-the-ground guide to the largest corporation. Gavin Tollman, President of The Travel Corporation, one of the largest tour operators in the world, believes that, “digital has really been one of the greatest evolutionary changes during [the pandemic] for us.” And being the last major travel sector to digitize does have a silver lining: by drawing on lessons from other sectors, we have a pretty good road map for how the industry may be transformed.
As with hotels and airlines, digital marketing will only continue to grow in importance to the industry. Naturally, this means that search engine marketing budgets will have to grow.
This is especially true in the U.S. market. Matt Berna, Managing Director, North America for Intrepid Travel, explained that, “[in America] We spend the lion’s share, easily 80% of our budget, on direct digital marketing strategies.” Although Berna caveats that in other markets, like Australia, travel agents and retail storefronts remain key marketing tools, that a large tour operator like Intrepid is so heavily invested in digital marketing should be a sign of the times.
But the rise of digital marketing goes beyond performance marketing. For instance, Search engine optimization is arguably just as important and when done right is not cheap either. “We’ve done a lot with SEO,” says Berna, “building a lot of new content, writing content, building out our pages and website.”
Digital marketing also involves building brand recognition at the top of a sales funnel moving online, with brand advertising shifting to platforms like YouTube and ‘word of mouth’ being spread on social media. In fact, Gavin Delaney, CEO and cofounder of online tour site Travelstride told us that 90%+ of customers start their tour research online.
Speaking to the power of social media, Tollman told us, “if you said to me, what has been one of our greatest success stories in the last year? It has been the use of social channels to tell our stories in a robust way that people can look and see. When the world was shut down and we were still operating trips, how powerful it was to show people that they could still go and show them what we were actually doing.”
Directly linked to the growth in digital marketing techniques is the rise of online booking platforms for multi-day tours. That’s primarily startup websites like TourRadar, Tourlane, Evaneos, and TravelStride. Today, these come in two flavors: commission-based agents (e.g. TourRadar) and advertising-based listing sites (e.g. TravelStride). There are still few true metasearch sites that search other online booking sites due to complexities of itineraries in the space.
Complex itineraries make it difficult to convert online intent to online bookings and Travelstride’s Delaney says that two-thirds of the industry still ends up being booked over the phone or via another direct channel through an operator or agent. “One thing to keep in mind,” he explains, is that “a hotel and a flight, they have five key data points… a departure date, an arrival date, a return flight, a price, a seat type, right?” And while alternative accommodations may expand that to 10 data points, Delaney points out that, “In a multi-day tour, typically, we have 125 data elements… does day three include breakfast? What are you doing in the afternoon of day four? What’s the average physical level? How much walking is there? Is this appropriate for an age group? … [Multi-day tours are] a step function, more complex in terms of how you organize that information to make it useful for travelers to search and feel confident enough to book.”
Adding to the difficulty of driving online sales is that these are expensive bookings, the average transaction at TourRadar is $2,500. But Travis Pittman, CEO and cofounder of the online booking site says that it regularly takes “bookings up to $10,000, $20,000.” In contrast the average transaction on Airbnb is ~$400.
Despite these challenges, online booking sites are making strong headway. We note that large online travel transactions are becoming increasingly common. To continue the previous example, despite its low overall average transaction size, Airbnb’s fastest growing category is long-term stays of 28+ days which can easily run up to $2,000 – $3,000 ticket sizes, all sold online.
And as aggregators of both tour supply and online demand, multi-day tour OTAs are uniquely positioned to win in a digital marketing heavy environment. We believe that the industry will inevitably close the gap between the 90% of travelers that start their searches online versus the third of travelers that end up completing this process by booking online.
For starters, consumers are increasingly coming to trust these online platforms. To that end TourRadar’s Pittman highlighted that, “a key part of TourRadar has always been reviews… that’s how we began really, and that’s stayed throughout.” Those reviews do more than just establish credibility with guests, they also help from a search engine optimization standpoint.
Reviews paired with the wide range of tour supply on the platform, means that an online booking site will probably be a highly ranked organic result for high intent tour searches. This also drives a “billboard effect” where online users that are “passing by” while searching for travel inspiration repeatedly come across the same few multi-day tour aggregator and review sites.
The guest starts by searching for a tour in Peru but also considers one in Columbia, and ultimately shifts focus to a Costa Rican trip. The destination specific brands will change each time, but TourRadar, TravelStride, and others will keep popping up. This familiarity drives trust in the platforms and makes users more likely to eventually book via an online intermediary, even if not for the destination they were originally searching for.
These platforms also have an advantage in online distribution by means of the wide range of supply that they aggregate. This comprehensive supply lets them drive repeat customers who want to explore a variety of different tours and destinations. An Argentinian tour specialist will struggle to drive guest loyalty because as Delaney points out, “even if you have the best possible trip, most people won’t go back to Argentina twice in a lifetime.”
It’s more than that, customers can be quite picky about even simple things like departure dates. Says Delaney, “the vast majority [of tour customers], even when they have a great time with that tour operator, … It’s just like, oh, I really liked Intrepid, but their itinerary dates don’t quite match up and G Adventures has a very similar one but their dates … match up with what I want better.” This mercenary behavior plays into the hands of online booking sites and other aggregators like travel agents who have cross-brand supply and allow for comparison shopping across dates and prices for similar itineraries.
This means that all else equal, the same exact customer probably has a higher lifetime value to an online booking site than they do to a regional tour operator. Pittman emphasized that, “CRM [customer relationship management] and bringing customers back is an extremely important part of this journey.” Accordingly, TourRadar and similar sites can ‘afford’ to outbid regional tour operators in performance marketing because even though they may end up paying more in dollar terms, they could still well be earning the same or an even better ROI on their ad dollars than what the regional specialist was targeting.
The final piece of the puzzle comes from the focus and size of an online travel agency. As we have seen with flight and accommodation OTAs, these booking sites eventually grow to have larger marketing budgets than most individual tour operators can hope to muster. This, paired with the above ROI efficiencies, let online booking sites win more online performance marketing search auctions, more consistently than other operators, driving traffic.
All of this means that if, as we believe, the amount of multi-day tours being booked online grows, then the relative importance of these OTAs is also likely to grow.
In our previous section on the tour operator value chain, we discussed the difference between local wholesale tour operators and outbound retail tour operators. In the past these two businesses had a mutually beneficial relationship. Running dozens of local operations was impractical for the retailer while for a local operator, in Morocco say, it would have been unthinkable to directly market tours abroad in multiple countries.
But the accessibility of online marketing and digital distributors has upended this relationship. It has opened a whole new world of opportunities that were never before possible while also bringing with it a whole new slew of challenges. “We’re seeing DMCs also work with us now,” says TourRadar’s Pittman. “… They’re [DMCs] seeing the opportunity to go direct to market. So they’re not just reliant on these bigger operators to get to [market]”.
That local DMC in Morocco can now list its tours on an online booking site and collect bookings from across the globe. Though it will have to pay a commission – likely 15% to 25% – a DMC can now cut out the intermediary and bring those retail margins in-house. All of this without a direct booking engine! If the Moroccan DMC chooses to invest in an English-language webpage and a modest AdWords budget it could be in the direct tour business across the U.S., Canada, UK, and Australia almost overnight.
“What’s happening is that the producer and the consumer are getting closer and closer and closer,” says Enrique Velasco Jr., Chief Commercial Officer of Coltur Peru, a local DMC. “They [the producer and consumer] can start speaking to each other. Whereas before, they were thousands of miles apart, there was no communication between them.”
Wholesalers are now competing directly against their retail partners. And to make matters more confusing, many of these retail tour operators also distribute through travel agents and OTAs. That means that the same exact tour could well be marketed to the consumer in four different places (direct via wholesaler, direct via retailer, indirect via OTA, and indirect via travel agent).
Adding in another layer of complexity, Pittman told Skift that TourRadar plans to launch a new platform for redistribution by the end of the year that will, “basically allow any third party to distribute the inventory that we have… the GDS of multi-day [tours].” The ability to push the same tours through as many distribution channels as possible will never have been easier.
On the one hand, this breadth of channels means more shots on goal and more chances for the right guest to find the right tour. As TTC’s Tollman puts it, “Consumers are going to buy travel where they want to buy travel. And we will ensure that we are in those places for them.”
But on the other hand, imagine a physical store putting the same exact products right next to each other on the shelf, just with slightly modified packaging. Each variation with different pricing and margins. That would never fly in the real world, the consumer would optimize for lowest price and the manufacturer for best margin until only one product remained.
The main reason it works with tours is because of confusion in the space and unsophisticated customers that prevent true comparison shopping. Travel agent clients today are unlikely to be comparison shopping with online travel agents or direct channels. And guests are often afraid to book complex and expensive itineraries online or with a party they don’t have a pre-existing relationship with.
Compounding this, many tour operators – both wholesale and retail – are heavily reliant on third-party sales. Though they see the potential of direct, it is currently too small a part of their business to be self-sufficient and they are afraid that too sharp a pivot towards direct will alienate distributors and result in a net overall decline in sales.
But we would argue that fear and opacity are not a strong foundation to build a business on. The clear trend in online shopping is towards more transparency across products and prices and for the rising generation of customers to be more comfortable with making large ticket purchases online. Plus, over time, tour operators will become more confident in the size and stability of their direct channels and more willing to confront distributors over commissions.
We think that the blurring of industry lines will drive several reactions. It will cause distributors to delineate their value add more clearly, with travel agents for instance retrenching into high-touch luxury service with many add-ons and complex arrangements. Wholesalers will be able to compete on price as direct-to-consumer wholesale clubs like Costco do today. And retailers will be driven to vertically integrate so that they can offer more destinations, in turn driving repeat guests, and potentially also create more exclusive supply arrangements so that they cannot be undercut or resold by other players.
James Thornton of Intrepid told us that, “I think we’ll increasingly be more vertically integrated as an organization. In 80% of the cases it’s our DMCs operating the products that we sell [and] you’ll see us potentially move into other aspects of verticals. It might be more accommodation, it might be having exclusivity of certain routes or departures. You might see us have more small ships, for example.”
Let’s face it, most founders of a tour operator didn’t jump into the business out of their love for programming. They did it for the love of travel! But with the world going the digital direction we describe above, the need to modernize and professionalize many tour operators, especially smaller ones, is becoming increasingly urgent.
Many operators still keep the details of their tours logged on excel or even pen and paper. And we know of operators and travel agents that need to make multiple phone calls to confirm a booking. According to Tourism Research Australia, 88% of bookings are still made manually through email booking requests and offline methods. A survey by ATTA found that just 50% of operators they surveyed have an online reservation system that takes credit cards. This won’t fly in the coming era of tour operators.
In order to drive effective direct to consumer capabilities, tour operators will need to develop a full technology stack. This includes responsive websites with SEO in mind, booking engines to capture sales, customer relationship management software to track guest inquiries and bookings and MarTech tools for performance advertising, retargeting, and email marketing, among other techniques.
James Thornton told Skift that Intrepid Travel wants to have “more focus on customer experience on the website. [We are] trying to improve the overall digital experience both at the point where people come into the brand and transact with us, but then also when they come on the trip more of the documentation being served up in a digital format, the feedback loops being in a digital format. And that just helps us as an organization be able to react more real-time than previously we would.”
Shockingly to us, Intrepid Travel only installed its first CRM system just three years ago. This is a standard sales and marketing tool for major corporations and Intrepid’s late adoption of this software speaks broadly to the industry’s need to modernize its tech stacks.
We should note that Intrepid still managed to attract 460,000 customers a year and a 25% repeat rate without CRM software. Pretty good. But it could be better, and looked at from a glass half full perspective there is a huge amount of untapped potential ahead for Intrepid to grow into as it modernizes its sales operations.
Even though Massimo Prioreschi, CEO of MT Sobek, a boutique mountaineering and outdoor adventure company, runs a smaller business than Thornton, he too has been investing in new technology. “In the last 18 months we’ve revamped our reservation system, phone system, CRM, and guest portal” he says. “This time of fallow, where there weren’t guests traveling”, Prioreschi explains, “[was an] opportunity to upgrade our technology. And so I think in five years, our guests will feel this ease of dealing with us.”
Above these core investments, a particularly exciting tech development we heard about came from The Travel Corporation, which “started using robots for all yield management,” according to its President Tollman. “We have dynamic pricing on all of our trips,” he explained. “And what that has done for us is … if costs are added to [a tour], we can adjust them dynamically as we move. So we are not stuck with flat pricing, which is one of the most high-risk features of the old way that tour operators used to work.”
This kind of revenue management is industry standard in the airline and seeing growing adoption across hotels. Based on this cross-industry trend, while TTC may be an early adopter, we expect more tour operators to adopt similar pricing tech.
And all of this is just on the direct-to-consumer side.
The technology for business-to-business (B2B) distribution is evolving as well. “Historically it was PDF and Excel files,” Berna explains. “[Peak DMC would] get a quote and then they’d send it to an Intrepid salesperson, who would make it look good and send it to the client.” That approach won’t fly anymore. Berna says that, “technology is going to improve a lot … [to allow us to] provide quicker quotes, more accurate quotes, better looking quotes so that DMC can work directly with those tour operators.”
Tour operators aren’t exempt either as they have distribution partners of their own – online and offline travel agents – that will be demanding modern booking capabilities. For instance, Tollman told us that The Travel Corporation is, “evolving our APIs to expand and let agents actually get even more content, and more content that’s relevant. Not just dates and rates, but all robust content there too.” Interestingly, he sees potential for APIs to expand the company’s distribution reach even outside the bounds of traditional channels, teasing that “We are also looking at a number of distribution channels, which typically have never sold multi-day tours.”
And although the largest operators in the world are starting to evolve, the reality is that most small and medium sized tour companies lag significantly behind. Here’s a striking fact: Murray Decker, the CEO of multi-day tech vendor Tour Amigo, told us that, “of all the operators we’ve had discussions with, about 95% of them actually don’t have a dedicated multi-day tour [backend] system, or are using a mix of multiple systems that are designed for other travel business (day tours, activities, etc).”
If there is to be a post-COVID gold rush in multi-day tours then these back-end vendors, like Tour Amigo, are selling the pick-axes. Inventory management, content management, and booking engines are part of a standard digital retail tech stack in airlines, hotels, short-term rentals, and most recently day tours. Not only do they allow for operators to keep up with evolving distribution channels, but there is a major book-keeping and business management benefit as well.
Digitizing inventory allows for more advanced sales analytics, quicker account reconciliation, fewer back-end staff, and reduced errors. Murray estimates that at large travel agencies and tour operators the error budget due to manual loading mistakes can run into the millions of dollars.
The path forward is clear to us: DMCs and tour operators alike will need to buy or develop new back-end systems that can deliver live pricing and availability. Intrepid’s Matt Berna reflects that, “I used to talk to product managers and ops directors about how great our products were. Now I talk to data science engineers.”
These backend systems and APIs are increasingly table stakes to participate in the current digital tour operator landscape. But they don’t come cheap and an unfortunate reality is that, especially in the wake of COVID-19, many operators will not have the cash on hand to upgrade these systems, shutting them out of modern tour distribution. We see this creating a class of have and have nots, especially in the more commoditized product offerings. This will drive some to sell out to more sophisticated tech platforms or simply to fall behind and go out of business.
The Impact of COVID-19 on the Multi-Day Tour Sector
Up until this point in the report we have discussed the structure of the industry and how long-term changes in technology are causing tour operator business strategies to evolve. In this section we will discuss the more immediate changes caused by COVID-19. This includes both new trends in the actual tour products being offered, as well as how some industry-wide practices and standards are evolving in the wake of the pandemic.
“We are going through a seismic shift in our world,” says Gavin Tollman, “the fact is we’ve entered just an entire new world.” COVID-19 has caused a dramatic shift in what kind of tours that travelers take. Some of it is due to changing preferences, such a desire for more cleanliness and safety, while other changes are due to government orders such as the closing of borders. Regardless of the reason, tour operators have responded by creating new types of tours for the pandemic era.
Rise in Domestic Tourism
The biggest new trend to emerge from the pandemic is the new emphasis on domestic tourism. At Intrepid Travel, Berna tells us that, “before COVID, about 60% of our customers worldwide came from Australia. … It’s flipped now. The US is our biggest booking market for Intrepid worldwide… 50% now of all travelers are American.”
Tollman of The Travel Corporation concurs. “Our domestic US travel brands [are doing] unbelievably well. Our domestic Australia brands, pre their last shutdown, [were also] unbelievably well… One is really beginning to see whether it’s in South Africa, the U.S., Australia, or the UK, domestic first, near-destination second, and international third.”
Focus on Sustainability
The other major new shift has been towards a more thoughtful understanding of travel’s impact on ourselves and the world around us. “If you said, what is fundamentally changed,” Tollman asks, “it’s going to be sustainability.” His family of tour brands are making significant shifts to be more respectful of the communities they visit and have pledged to be carbon neutral by 2022.
James Thornton, the CEO of Intrepid Travel was emphatic about this point. “Increasingly people want to be purchasing and working for and buying from companies that are truly sustainable, not companies that say that they’re sustainable, but companies that really are and have the independent accreditations to back that up,” he explained. Intrepid Travel is the world’s largest certified travel B-Corp and has been carbon neutral since 2010.
This is not just a COVID shift but a generational one, according to Thornton. “Increasingly millennials and gen Z are wanting the higher standards of environmental and social expectations when they travel. … Younger people are expecting brands to reflect their own values and particularly think about things like climate change.”
The shift towards sustainability doesn’t have to come at the cost of the trip experience, and if executed thoughtfully, can even enhance the overall experience. Thornton gives the example of a trip to Cambodia which would typically have an internal connecting flight. But the airport is a generic and stressful experience. “What we’ve now done,” he explains, “is remove the flight aspect of that trip and introduce a boat trip. One, it’s a more relaxing experience. Two, it’s a more local experience. Three, it emits a tiny proportion of carbon by comparison.”
Thornton also believes that demand for domestic travel can continue due to its climate impacts. “I think there’s going to be more questioning about just jumping on a plane to fly to the other side of the world, to go there for a week,” says Thornton. “I think you’ll see a trend towards people traveling closer to home more frequently, but then when they go for longer trips overseas, those trips will probably be a bit longer in nature to factor in the carbon emissions.”
Small Groups
There has also been a shift towards smaller groups, custom itineraries, and more high-end accommodation. This kind of travel provides extra space, flexibility, and exclusivity which are perceived as cleaner and safer, the ultimate luxuries during pandemic.
But rather than this being a new trend introduced by lockdown, Catherine Prather of the National Tour Association explains, the move towards small groups, “was already happening prior to COVID and that’s really been amplified [by the pandemic]. I think that’s something that’s really just here to stay because people were already wanting to have a smaller group experience, but that was being driven by not only generational changes, but also by people wanting those authentic experiences. It’s easier and better to have that with a smaller group.” She also highlights luxury travel as, “something that was already happening.” But now, Prather says that “People equate luxury with safety and cleanliness and security.”
Active Vacations
Another big COVID-19 winner has been active and outdoor vacations. This was already a fast growing trip type but the perceived safety of the fresh air and the backlash to lockdown really poured a lot of gas onto the fire for these tours.
Tom Hale, Founder and President of Backroads, a leading bike and active tour operator, told Skift that, “demand for active travel was already growing pre-pandemic, and COVID has accelerated the trend with people wanting to spend more time outside in a safe and active environment.” 2022 bookings at Backroads are currently 70% above 2019 levels, its best historical year ever.
Further reinforcing the above domestic trend, Hale spoke to how Backroads quickly pivoted to add domestic capacity, leading to them taking “20% more guests on trips in the US than we ever had before.” Hale sees the trend towards smaller, active trips continuing even as the pandemic fades. “We expect to see huge demand for Europe and other international locations in 2002] … and predict that … 2023 will see unprecedented numbers of active travelers.”
Outside of product offering, another major industry transformation due to COVID-19 that many spoke to us about was a new sense of teamwork and transparency across the industry.
“There has been a lot more collaboration,” says Prather, “hey, this tour can go, but I really need five extra people. Do you have clients who may want to experience or go on this trip?” This is partially born out of a sense of camaraderie brought about by the near-death experience of COVID and a realization that it will be a group effort to keep the sector afloat.
“People are a lot more open,” agrees Matt Berna. “What I mean by that is DMCs will go to the partners and say, ‘Here’s our costs. You can see them, but I need to make 5%.’ … Nowadays, it’s open books. We’re all in this together. We need to all make money, but we also need to see where our costs lie… That trust piece I think that still will continue.”
There is also an element of working together to develop best practices and industry standards in the face of a rapidly shifting disease picture. “There definitely has been a lot more sharing of information,” Prather explains, “How are you dealing with this? Are you asking for proof of vaccination? Are you masking on your tours?”
The final reality of COVID is that despite many operators’ best efforts – all of their cost cutting, pivots to new tours, and industry-wide collaboration – many will not make it through this crisis. There have been far fewer bankruptcy cases than expected, but we believe that this is mostly because of emergency funding, lenient creditors, and forgiving customers. All of this will soon begin to wear out.
Prather warns, “I don’t think we’ve seen the shakeout as much yet in terms of true consolidation because of the PPP loans [A U.S. small business aide loan] and idle loans and things like that, that have helped people survive.” Gavin Delany of TravelStride goes even further, “there definitely is going to be significant consolidation. A number [of tour operators] have already gone out of business, mostly smaller ones.”
Many businesses went into hibernation but may find that restarting is more challenging than expected. For instance, many tour operators’ first trips back will be 2020 tours rescheduled into 2021. And while it must feel good to be operating again, the timing of cashflows can be deadly. There are few new dollars coming in the door as these were mostly previously paid for, but staff salaries and suppliers need to be paid all the same. This further draws down already diminished cash reserves.
Delaney says that, “I’m actually sort of surprised at this point. I would have thought more companies would have gone out of business. So up until this point, they’ve been fairly resilient.” He points out another challenge of coming out of hibernation. “I think part of the challenge is the rebound will actually be slowed a little bit by the fact that [tour operators] cut all these sales staff. So in June, pre Delta variant, we had this surge in interest. People wanted to book trips and there were not enough people to answer the phone and answer questions.” As with seemingly every other industry, tour operators are being plagued by labor shortages and supply chain backups.
There is also a great disparity between the types of services that tour operators provide and the kinds of regions they service. Those with a domestic outdoor focus are obviously doing better than an operator that specialized in international study abroad, which has been totally shut down for the foreseeable future.
On the whole though, revenues are still down dramatically. the ATTA, in a survey of adventure tour operators found that 74% of respondents had seen a 80% or greater reduction of revenue in 2020 compared to 2019. And these are the outdoor operators that are supposed to be doing the best! Prather says that “our members are telling us… It won’t be until 2023 that we will really see a full recovery in terms of getting back to 2019 levels.”
And that’s a long way for a struggling tour operator to make it alone. Add in the investment required to digitize and the scale increasingly needed for effective distribution, and the hurdles become insurmountable for some. In that same ATTA survey, 15% of tour operators surveyed said they are possibly closing down, 3% are definitely shuttering. 28% surveyed were interested in being acquired by or merging with another company.
As bad as things have been for tour operators, we believe that we have yet to see the full wave of bankruptcies and consolidation to come in the multi-day tour industry.
Overall, we believe it is possible to look at how flights and accommodations were transformed in the wake of their digital revolutions in the early 2000s as a road map for the multi-day tour industry.
The flip side of the rise of digital marketing and online booking sites is that, as many an airline or hotel discovered, tour products will become increasingly commoditized. Both OTAs and Google search encourage suppliers to fit their tours into the neat boxes drawn up by online distributors. And comparison search engines necessarily require that the more unique aspects of a tour be minimized in favor of the more standardized feature sets like departure date, price, length, and destination.
Matt Berna, Managing Director, North America for Intrepid Travel told us that, “the reason I say that the price is becoming more important is some of these OTAs.” Berna clarified that, “we like to work with review sites like the TourRadars of the world where [the sort algorithm] goes by customer reviews… whereas [if] we go just to a platform that sells a price only, it’s going to be really, really competitive and it may not be worth the business for us.”
Commoditization, in which the main means of competition becomes price, is exactly what the rise of digital distribution did to airlines, hotels, and alternative accommodations. True, tours are more complex products, and therefore may never become quite as commoditized, but the direction of the trend is clear to us.
Using this as a benchmark, we see four broad paths forward for tour operators to follow in response to the rise of digital channels and online and the commoditization it will bring.
1) Embrace Commoditization : If you can’t beat ‘em, join ‘em, as the saying goes. Rather than try to fight it, some tour operators will choose to compete on price and make up for lower margins with volume. Call it the Walmart strategy.
Sometimes customers just want, “your bread and butter trips” says Berna. Berna explains that Intrepid works very hard to differentiate even these trips based on quality, but admits that, “once you get into that competitive set, we’re all selling the Inca trails… of course, the only way to really compete sometimes is the price.” Intrepid, as one of the largest tour operators in the world, has the scale necessary to run trips like this.
But very few other operators will be able to grow to the size necessary to win at this game. Expect only the largest operators in the world to pursue this strategy. That leads us directly into the next industry shift we expect to see.
2) The Big Get Bigger Through M&A: There’s safety in numbers, and more importantly, operating leverage. We discussed in the earlier online booking section how these sites have a scale advantage in performance digital marketing. The airlines and hotels both found the best way to compete was to consolidate to build this same marketing advantage for themselves. Call it the Marriott/Starwood strategy.
By consolidating, the biggest players broaden their supply choices which makes it easier to drive loyalty program customers who consistently book direct and have higher lifetime values, justifying higher upfront marketing acquisition costs. This makes large-scale businesses better able to compete with booking sites in performance marketing. Plus, with growing name recognition they can invest in brand marketing which drives new customers and makes performance spend more effective.
Consolidated suppliers also have more leverage to negotiate lower commissions with travel agents, both online and offline. Finally, with larger balance sheets comes the ability to control exclusive and/or scarce resources that can only be sold through exclusive first-party channels. By this we mean sources of unique supply like national park permits, private islands, or wholly owned hotels and resorts, which are very expensive to acquire or develop.
3) The Boutique Route: For many, competing on price and volume is a race to the bottom that only the biggest can win. Like with the boutique hotel movement, we think there is a great opportunity for tour operators to de-commoditize their product by providing very high service or specializing in a very specific niche.
The niche for these ‘boutique’ tour operators can be anything from a specific region, a type of tour (e.g., mountaineering or biking), an affinity group (e.g., photography or cooking) or a style of travel (e.g., train travel or sailing). But the key is that it needs to be something where the operator can be differentiated and best in class. By committing to a niche, it precludes growing to a large size, but it means that you can be the world leader in your particular area and attract direct bookings looking for this unique offering. Even better, because fewer other operators commit to any given niche there will be less competition and these boutique businesses can have stronger pricing power.
A good example of this is MT Sobek which has a 53 year pedigree in mountaineering and adventure travel that started in Nepal. Massimo Prioreschi, its CEO, told us that, “[adventure travel is] a tough business to scale… It’s hard to manufacture deep knowledge and excellence in guides.” He explains, “I’ve been at companies before that were very scale driven. And [MT Sobek] isn’t, it’s quality driven, it’s connection driven, it’s relationship driven. And that really, I think that’s why we’re still here.” Prioreschi has turned the slow process of grooming a mountain guide into a competitive moat for his business by embracing the boutique nature of their organization. As a result MT Sobek sees 90% direct traffic and 75% of their business comes from repeat guests or word of mouth.
4) Embrace The Complexity of B2B: In response to an increasingly competitive B2C market, some may drop it altogether and pursue the still largely offline B2B market. Coltur Peru , a local DMC is an example of this. As a result of COVID it reorganized to drop its lower-end consumer offerings. Now Coltur focuses largely on complex custom group tours and special interest itineraries.
“There’s this mass hysteria that everybody has to be with one foot in B2B and one foot in B2C and if you’re not in B2C, then you’re going to die,” says Coltur’s Chief Commercial Officer Enrique Velasco Jr. Dismissing this conventional wisdom, he says that the company is, “trying to focus in market segments that do need the middleman. That segment … might, as a percentage of the whole industry… become smaller. But it’s not going to die.” Velasco sees the challenges incumbent in planning a custom itinerary as a competitive moat, telling us, “the more complex what you’re looking for, the more we stand apart from our competition, that’s what we believe.”
This is akin to the strategies pursued by business travel agencies which, up until COVID-19 hit, had continued to grow by providing high-touch service to large organizations while leisure offline travel agencies shrunk in the face of D2C challengers. There is still a lot of value to be had in planning high-value and complex tours. The addressable market may be smaller than the mass-market D2C opportunity, but those that can successfully hang onto their slice of the pie will be rewarded with stable cash flows.

- Connect with Us
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
All Types of Guided Tour Operations
What kinds of tours are there.
Let's see what the possibilities are. According to the UN World Trade Organization, there are three kinds of tours - domestic, inbound, and outbound - and thus three kinds of tour operators who hire tour directors. Many companies offer both domestic and outbound tours.
Domestic tours involve residents of the given country traveling only within their own country. Tours offered in this country could be national parks tours, Mississippi river boat cruises, autumn colors tours in the Rockies or the northeast, southwestern U.S. tours, Hawaii tours, Alaska tours, Pacific northwest tours, southern hospitality tours, train tours, the options are endless and the income potential for tour directors is substantial. The US is the second most popular destination in terms of people visits, and the most lucrative market in terms of income. TDs who work for domestic tour operators have the potential of wending their way around the country on a variety of tours, or, if repeating the same tour, of watching the different seasons come to a particular area or park with each visit.
Outbound Tour Operators take residents from one country to travel in another country. These tours take travelers all over the world and to every continent. Where do the tours go? The most popular place is Europe, but that's just a start on opportunities. Add to that the South Pacific, China, Australia, Patagonia, Antarctica, worldwide cruising, the Middle East. Where would you like to go?
Inbound Tours involve non-residents traveling in another country. Companies that provide local assistance for tours arriving in their country or town are called Inbound or Receptive Tour Operators. They are commonly used on international trips, particularly where language issues are part of the mix. These companies make the local arrangements for airport pickup and delivery, arrange for activities, hire local guides, attend to all the details of the stay, and help in emergencies. A Receptive Tour Operator could be a ground transportation company, or a Destination Management Company (DMC). If you are working for a Receptive Tour Operator, you likely are a local who is working WITH the inbound tour, not FOR its tour company. If your tour is the Inbound Tour, for example traveling to Argentina, then you work with the local Receptive Tour Operator, who is handling the travel details for you, and can be counted on to speak really good Spanish if you can't. Consider jobs with TrekAmerica if this niche is of interest. They provide tours of the USA!
The Bottom Line: There are Job Opportunities at Home and Abroad!
- Search Thousands of Jobs
- Cruise Industry Career Tips and Proven Strategies to Get Hired!
- Create a Personal Profile
- Use our Advanced Job Search
- Accounting - Finance (233)
- Activities - Fitness (51)
- Administration - Clerical (54)
- Administration - Management (8)
- Advertising - Marketing - PR (121)
- Casino (13)
- Cruise Line - General (651)
- Culinary - Chef - Cook (1,118)
- Deck & Engine (8)
- Engineering (397)
- Entertainment (22)
- Food & Beverage - Restaurant (536)
- Front Desk - Concierge (1)
- Guest Services (147)
- Housekeeping (29)
- HR - Payroll - Training (115)
- IT - Internet (20)
- Landscaping - Grounds (6)
- Mechanic - Maintenance (341)
- Other (243)
- Procurement - Purchasing (28)
- Resort - General (274)
- Retail - Merchandising (24)
- Sales - Reservations (34)
- Salon - Spa (257)
- Security - Surveillance (81)
- Shore Excursion (2)
- Travel - Tourism (23)

Which Type of Tour Operator are You?
Let’s be honest – the tour operator business is highly competitive as companies try to get a large share of the international and domestic markets they operate in. In order to better navigate the landscape, you need to understand where you stand in that market.
We all know that a tour operator is one who packages key components (or all) of a trip, markets it, sells it to a traveler or tourist, and handles the entire tour operation.
But do you know exactly which type of tour operator you are?
Having clarity on this question will help you identify key partners to work with (like DMOs or hotels) and make better business decisions overall. As a result, you’ll be able to curate better tour packages and run your entire tour operation smoothly, efficiently and successfully.
This is why we’ll cover the different types of tour operators below (plus – we’ve attached a handy infographic at the end for your reference).
So, let’s get to it – which type of tour operator are you?
Types of Tour Operators
There are five main categories of tour operators that you could fall into: inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators, domestic tour operators, receptive tour operators, and ground tour operators. Let’s find out which one of these five you fall into.
Of course any tour operator cannot be fully successful without a booking system that will automate all reservation processes and allow them to generate more revenues. If you still haven’t got a booking system, try Regiondo , the most popular booking system in Europe designed to streamline your booking process. Book a demo with Regiondo experts to learn how your business can leverage booking system.

Inbound Tour Operators (AKA Incoming Tour Operators)
Inbound tour operators bring tourists into a country as a group or via individual tour packages. They handle all arrangements in the host country; and the types of tours they curate are specifically for non-residents touring the country.
Let’s look at an example.
If a group of Italian tourists want to explore Germany, then the tour operator in Germany who handles all the arrangements for the tour is known as an inbound tour operator. So, inbound tour operators are locally based and offer tours that cover their own country.
Most inbound tour operators hire local travel agencies for things like airport pick-up and drop-off; form partnerships with local hotels and businesses; and have key partnerships with other types of tour operators (who help them run tours on the ground).
Outbound Tour Operators
Unlike inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators work within their countries to take travelers to other countries. They are tour operators who market their tours for international destinations, either for business or leisure travel.
Let’s say, for example, that a group of Canadian tourists are planning a trip to Italy. Then the tour company in Canada that handles all the ticket reservations and hotel bookings is the outbound tour operator.
To further simplify things, outbound tour operators design and package tours for tourists in their home country to visit an international destination.
Now, most outbound tour operators choose to specialize in specific destinations: either a destination that is “trending” or one in which they have particular expertise and distribution partners. They often work with other tour and activity providers in the destination when designing their travel packages.
Domestic Tour Operators
Domestic tour operators are those that put together inclusive tour packages and sell them to domestic travelers. In other words, they are tour operators who provide travel packages and tours within a tourist’s native country.
Domestic tours usually involve residents of a specific country traveling within that country. They can visit national parks, scenic areas, hospitality tours, city tours , train tours, etc. Since there are many options that tourists can choose from, domestic tour operators often combine several tourist components into an inclusive package that they can sell to travelers within the boundary of the country.
Domestic tour operators form key partnerships with other tour and activity providers in order to attain a larger share of the domestic tourism market.
Receptive Tour Operators (RTOs)
Receptive Tour Operators (RTOs) provide tourism products to tour operators in other markets (as a business-to-business relationship).
Specifically, RTOs sell tourism products, whether they are sold in a tour package or alone, to tour operators and/or travel agents . They are essentially wholesalers and they don’t sell directly to the public.
So how do they make money?
They add a percentage rate (or fee) to the final price that the tour operator is selling the product or service for. When a travel agent buys the tour product, they incur the RTO’s fee in the final price. In that sense, RTOs do not charge commission. They simply market the tourism product and add their fee to the final product price.
Another key characteristic of RTOs is that they are experts in the region they operate in; and know much more than just the hotels and types of tourism activities that are offered in the region. As such, RTOs to help other tour operators identify things like hotels, services and design itineraries in regions they are not familiar with.
Ground Tour Operators
Ground tour operators operate domestically. They are however different from domestic tour operators in that they organize tours for incoming tourists on behalf of an inbound tour operator (and sometimes, outbound tour operators).
Let’s look at an example to better understand the role they play.
Italy will be the destination in this example. So, here’s how it works:
An inbound tour operator designs and promotes beach holidays, adventure, and heritage tours in different parts of Italy. Problem: the inbound tour operator doesn’t have offices across Italy. The inbound tour operator also doesn’t have close contacts or partnerships with suppliers and key agents in certain parts of the country. So, they consult with ground tour operators.
It is the ground operator that will handle the incoming tourists at those various destinations around Italy. They oversee land arrangements; negotiate with and contract local vendors; coordinate arrivals and departures; plan and put together local tour packages; escort tourists; provide market data; and cost and price tour packages. Overall, it is their duty to ensure that the entire trip goes smoothly based on the package tours and agreements.
You may know ground tour operators as “handling agencies” because they organize tours for incoming tourists on behalf of overseas tour operators.
Wrapping Up
Back to the question we asked at the very beginning: which type of tour operator are you? Now that you’re better informed to answer that question, you can also start thinking about ways to improve your distribution and marketing channels based on that answer.
The next step is to figure out who your key partners are and strike up deals to propel your business forward.

Stay updated with Regiondo by signing up for our Newsletter
Get a personalized demo or create your free account now
Take your business to the next level with Regiondo - it's free to get started and you don't need a credit card.

Who is a Tour Operator? Know Roles and Responsibilities
If travel destinations and tourist places are something that interest you or fill you with enthusiasm, probably then, you must know about a tour operator. Tour operators advise customers about different travel options. They organize tours for individuals or different groups of travelers. As professionals, they prepare tour itineraries, and tour packages and coordinate with vendors for your holidays.
In this write-up, we delve into a tour operator’s roles and discuss the necessary skills, roles, and education qualifications for the job.
Who is a Tour Operator?
A tour operator is someone who belongs to the hospitality industry. He organizes tours and helps customers during trips so that they have positive reviews. Advising customers on different tour packages based on their budget and interests, and handling all logistics of a tour, such as booking tickets and accommodations, are some basic roles assigned to them.
Tour operators generally work for travel agencies or tour companies A tour guide will accompany tourists on their trips, but tour operators are solely available to answer their questions. They provide detailed information about tourists’ itineraries.
Types of Tour Operators
Here are some types of tour operators who can help you plan your holidays better and make them memorable!
1. Domestic Tour Operators
Domestic tour operators provide tours and travel services within their own country. They serve tourists who desire to explore different regions or attractions within their country.
2. Inbound Tour Operators
These operators serve foreign tourists visiting their country. They plan and organize tours within their own country, and provide services such as transport, accommodation, guided tours, and activities.
3. Outbound Tour Operators
Outbound tour operators organize tours for residents of one country traveling to another country or countries. They arrange the trip, including flights, accommodations, transportation, and activities at the travel destination.
4. Special Interest Tour Operators
These operators specialize in planning tours catering to specific interests or hobbies, such as wildlife safaris, culinary tours, photography tours, adventure travel, or cultural immersion experiences.
5. Wholesale Tour Operators
Wholesale tour operators sell pre-packaged tour products in bulk to travel agencies or retail outlets. They often provide discounted rates to travel agents. Travel agents usually earn a profit by reselling the tours to clients.
6. Incentive Travel Companies
These companies organize travel experiences for corporate groups or organizations as rewards or incentives for employees or clients. They often tailor trips to meet the guided objectives and preferences of the organization.
Tour operators design and organize pre-packaged tours or holiday packages while the Travel agents help clients in booking individual travel components.
What is the Role of a Tour Operator?
Tour operators play a wide array of roles when it comes to planning holiday packages and dealing with tourists.
1. Planning Tour Packages
These professionals design and schedule travel packages for individual travelers or groups of tourists. They coordinate with their clients to discuss their likes and dislikes and then suggest a range of attractions, accommodations, and transportation options to enable the clients to select the tour packages that meet their preferences.
2. Negotiating Rates
Often the tour operators can try to book a group of room /blocks in a hotel for their bigger group. This leads to lower rates for the tourists.
3. Arranging Travel
Tour operators ensure that passengers have their train tickets to travel between the cities or even book a car rental to help customers visit the attractions according to their schedule.
4. Providing Customer Support
A tour operator offers travelers with the technical assistance that they may need before a trip. For example, they may reply to customer questions about a trip they are planning, tell them about currency exchange rates, or notify them if there are any changes in their itinerary.
5. Preparing Tour Budgets
A tour operator comes up with different price options with sample itineraries and counsels customers on the kind of lodging and attractions that are within their budget.
6. Researching Travel Options
Tour operators are specialists who gather and study data on traveling patterns to suggest itineraries to tourists about where they should go, where they will stay, and where they can eat on their trips.
They read articles and browse online for details about travel trends and popular tourist spots that they can use to stay updated with what is trending currently.
Educational Requirements for a Tour Operator
To become a tour operator you need a high school diploma or equivalent. Some employers, particularly tour companies or travel organizations, may prefer to hire candidates with a bachelor’s degree.
Tour operators need a degree in tourism and travel services management or hospitality management. Many colleges and universities offer these undergraduate programs, and it typically takes four years for students to complete their degree. You can also consider doing short-term courses in the following streams.
- Hospitality finance
- Foundations of tourism
- International hotel management
- Tourism information technology
- Hospitality management strategies
- Sustainable tourism planning
- Revenue management
- Service technology
- Event planning
- Human resources management
- Hospitality sales and marketing
Difference between Travel Agent and Tour Operator
Tour operators and travel agents both play important roles in the tourism industry, but they have distinct functions and responsibilities. Let’s differentiate between the two.
Travel Agent :
A travel agent is an individual or a company that acts as an intermediary between travelers and travel service providers. They may specialize in certain types of travel, destinations, or services.
Travel agents typically earn commissions from the travel suppliers they book with, rather than charging clients directly for their services.
They assist clients in planning and booking the trip, including flights, accommodations, transportation, and activities.
Tour Operator :
A tour operator is a company that designs, organizes, and sells pre-packaged tours or holiday packages to travelers. Tour operators handle all aspects of the tour, including accommodations, transportation, meals, guided tours, and activities. They often work with travel agents to sell their tour packages to clients.
They may specialize in specific types of tours, such as adventure tours, cultural tours, luxury tours, or eco-tours. Tour operators also offer customized tour packages tailored to the preferences and needs of individual clients or groups.
Wrapping Up
The profile of a tour operator is special as it blends creativity, expertise, and impact. Tour operators have the privilege of turning travelers’ dreams into reality by crafting unique and immersive travel experiences tailored to specific interests and preferences.
They have an extensive knowledge of travel destinations, coupled with strong connections with local suppliers. This enables them to offer better service and access to exclusive travel opportunities.
Check also: Best Places to Visit in Kashmir
Moreover, tour operators play a crucial role in promoting sustainable tourism practices as they support local communities, and preserve cultural and natural heritage. Although they may face challenges such as changing rules and unforeseen circumstances, tour operators show professionalism in ensuring the safety and satisfaction of their clients.
A tour operator designs organizes, and sells pre-packaged tours or holiday packages to travelers. They plan and coordinate all aspects of the tour, including accommodations, transportation, meals, guided tours, and activities.
They also negotiate contracts with travel suppliers such as hotels, airlines, transportation companies, and tour guides. A tour operator promotes tour packages to attract clients.
Moreover, they assist and support to travelers before, during, and after the tour. They also ensure compliance with safety regulations and provide a high-quality travel experience.
While both tour operators and travel agents are involved in the travel industry, they have separate roles and functions.
A tour operator specializes in designing and organizing pre-packaged tours or holiday packages for travelers. They handle all aspects of the tour, from transportation and accommodations to planning activities and excursions.
On the other hand, a travel agent acts as an intermediary between travelers and travel service providers. They assist clients in planning and booking various aspects of a trip, such as flights, accommodations, transportation, and activities.
Travel agents may work with tour operators to sell their tour packages to clients, among other services.
A tour operator designs and creates pre-packaged tour itineraries tailored to specific destinations or themes. They negotiate contracts with hotels, airlines, transportation companies, and other travel suppliers to secure competitive rates and check availability.
They handle all logistics related to the tour, including booking accommodations, arranging transportation, and organizing guided tours and activities.
They market and promote tour packages to target audiences through online platforms, travel agencies, and promotional events.
A tour operator provides assistance and support to travelers throughout the tour, including addressing any issues or concerns that may arise.
Finally, they ensure compliance with safety regulations and industry standards to ensure the well-being and safety of travelers.
Last but not least, a tour operator continuously evaluates and improves tour offerings based on customer feedback and market trends to improve the overall travel experience.
Sign Up For Daily Newsletter
Be keep up get the latest breaking news delivered straight to your inbox..

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Stay Connected
Latest posts.

Travel Photography Tips: How To Take Good Travel Photos?

Top 10 Famous Tourist Places In Bastar, Chhattisgarh

How to Plan a Family Summer Vacation & Places to Visit

How to Make Travel Reels That Stand Out on Social Media?

Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Tour Operators: Types, Functions, Importance, Difference
- Post last modified: 19 January 2023
- Reading time: 18 mins read
- Post category: Uncategorized
What is Tour Operator?
Tour operators are sometimes called wholesalers but this is partially true because a wholesaler buys goods or services in bulk at his own account to prepare a tour package and then retails it through the travel agencies or directly to the clients.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Tour Operator?
- 2.1 Inbound Tour Operators
- 2.2 Outbound Tour Operators
- 2.3 Domestic Tour Operators
- 2.4 Destination Management Companies
- 3.1 Planning a Tour
- 3.2 Making Tour Package
- 3.3 Arranging a Tour
- 3.4 Travel Information
- 3.5 Reservation
- 3.6 Travel Management
- 3.7 Evaluate the Option Available
- 3.8 Promotion
- 3.9 Sales and Marketing
- 3.10 Taking Care of Glitch
- 4 Importance of Tour Operators
- 5.1 Tour Packages Creation
- 5.2 Make Travel Arrangements in Advance
- 5.3 Tour Operations Budgeting
- 5.4 Providing a Relaxed and Safe Tour
- 6 Difference between Travel Agent and Tour Operator
However, a tour operator who has his own one or more tourist product components formulates a new tourist product for example ‘inclusive tours’. Tour Operators generally offer a variety of package tours to cater to the needs of different kinds of travellers.
An organization, firm or company which buys individual travel components, separately from their suppliers and combines them into a package tour, which is sold with their own price tag to the public directly or through middlemen is called a tour operator.
More precisely, tour operators are mainly responsible for delivering and performing the services specified in a given package tour. They can provide these services themselves as some have their own cars and coaches, hotels and other travel-related services or can obtain these from other suppliers. That is why they are called manufacturers of tourism products.
Types of Tour Operators
Following are the types of tour operators explained briefly:
Inbound Tour Operators
Outbound tour operators, domestic tour operators, destination management companies.
These are also known as incoming tour operators. Technically, the operators who receive guests, clients/tourists, and handle arrangements in the host country are called inbound tour operators.
For example, a group of American tourists coming through TCI to India and the company makes arrangements and handles the group in India, then TCI is called an inbound tour operator. Incidentally, the inbound traffic to the country for the last two decades has been decreasing.
Essentially, tour operators need to adopt innovative marketing strategies and should introduce special interest tours to cater to the special needs of foreign tourists.
Tour operators, who promote tours to foreign destinations, maybe business tours or leisure tours are called outbound tour operators. Indian outbound tourist traffic is growing at a rate of 10 percent annually and this makes India the second-largest country in the world with regard to the travelling population.
However, India’s outbound tourism is not only holiday-oriented but it is business-oriented too. There are many travel companies that offer outbound packages such as SITA, TCI, Thomas Cook etc.
Domestic tour operators are those who assemble and combine tourist components into inclusive tours and sell them to domestic travellers. In general, these tour operators provide travel services within the boundary of the home country and offer package tours to travellers viz. domestic inclusive tours or independent tours.
These are commonly known as handling agencies and their main function is to organize tour arrangements for incoming tourists on behalf of overseas operators. When a tour operator himself promotes beach holidays, wildlife holidays, wildlife tours, heritage tours, cultural tours at different places, difficulty arises.
It is the ground operator who handles the incoming travellers in the same season but at different places and ensures that the entire operation is according to the package tours or agreements.
Sometimes when a handling agency is at a prominent tourist place, for example, Delhi and it has to make arrangements to Goa, then it contracts (if it has no office of its own) with a local operator (known as an excursion agent) to handle the arrangements on his behalf.
Functions of Tour Operator
A tour operator is like a service provider, providing the most convenient option for tourists to stay, visit, as well as leave the city. A tour operator owns a high volume of travel services across carriers, services, and accommodation. Some most important functions of the tour operators are following:
Planning a Tour
Making tour package, arranging a tour, travel information, reservation, travel management, evaluate the option available, sales and marketing, taking care of glitch.
The most important function of the tour operators is planning a tour. Tour operators plan a tour and make a tour itinerary that contains the identification of the origin, destination and all the stopping point in a traveller’s tour.
A prospective tour operator also gives advice to intending tourists in various types of tour programmes, which they may choose for their leisure or commercial travel.
Tour operator buys individual travel components, separately from their suppliers and combine them into a package tour. Tour operators make tour package by assembling various travel components into a final product that is called a tour package which is sold to tourists with their own price tag. Making tour packages is also an important function of the tour Operator.
Tour operators make tour package and also arrange a tour according to tourist demands. Tour operators arrange the tour package and various tourists activities to provide the best experience to tourists/travellers.
Whatever the size of tour operators, it has provided necessary travel information to the tourists. This task is utterly difficult and very complicated. A tour operator must give up-to-date, accurate and timely information regarding destinations, modes of travel, accommodation, sightseeing, immigration, health and security rules about various permits required to travel in a particular area etc.
It is a very important function of all types of tour operators and travel agencies. Tour operators make all the reservations by making linkages with the accommodation sector, transport sector and other entertainment organizations to reserve rooms, and seats in cultural programmes and transportation.
Tour operators manage tours from the beginning to the end of the tour. A tour operator has the responsibility to look after the finer details of a vacation or tour such as hotel, accommodation, meals, conveyance etc. Tour operators provide travel guides, and escorting services and arrange all travel-related needs and wants.
Tour operators evaluate all available options to provide a unique or unforgettable travel experience to tourists during their journey. Tour operators evaluate the various options available for a tour package and provide the best of them to tourists.
Tour Operators makes tour packages and promote them into various tourists markets at domestic as well international level. Tour operators promote a travel destination to attract a large group of tourists at the domestic as well as international level.
In the promotion of tourist destinations, tour operators play a key role. Travel agencies or tour operators are called image builders of a country.
Tour operators do sales and marketing of tourist products. Tour operators buy individual travel components, separately and combine them into a tour package, which is sold with their own price tag to the public directly. Tour operators do the marketing of tourist destinations and tourism products to attract the attention of tourists/travellers.
Tours operators are also called handling agencies that handle tour package and take care of all the glitches and problems that arise during a tour package. Tour operators fix the glitches and provide the best available alternative to tourists during their journey.
Importance of Tour Operators
- Tours operators play a key role in the tourism sector. Tour operators create tourist product, promote them and finally sold them to tourist.
- Tour operators provide the best and competitive price to the tourist. Tour operators negotiate with suppliers of tourism product such as hotels, airlines and provide the best possible price to the tourist.
- Tour operators buy tourist product in bulk and get huge discounts from suppliers. So that they can provide tourist’s products at cheap price.
- Tour operators organized a tour in the best way. They personalize and make sure each and every component of the tour is well-taken care. Tour operators provide best travel experience during a tour. Tour operators save tourist’s times and money.
- Tour operators provide immediate support system at host country as well as foreign land. When tourists travel to a foreign land and things get uncertain, maybe it’s a health or loss of documents and need to return back or change of travel plan. A qualified tour operator takes care of all these unseen events with efficiency.
- Tour operator caters to the needs of tourists on the based on their taste of travel. Tour operator provides all the best available option according to tourist needs and demands.
Role of Tour Operators in Tourism Business
Tour packages creation.
The tour operator is in charge of developing and maintaining guests’ tour packages. The preparation of activities that appeal to the specific visitors embarking on the trip is part of tour package management. When and how to adjust a tour package to best adhere to the group or individual’s goals should be covered by the tour operator.
Make Travel Arrangements in Advance
In most circumstances, tour operators are responsible for making travel arrangements for the touring group. This covers transportation from one location to another, as well as ensuring that all members of the group arrive at their next destination. Tour operators frequently assist with flight tickets and collaborate closely with hotels to recommend lodging reservations, sightseeing alternatives, and other activities to group members.
Tour Operations Budgeting
Tour operators work hard to build tour packages that provide users with great service at a lower cost than if they booked each commodity separately, while still running a profitable business. Tourists purposefully seek out the assistance of a travel agent or tour operator in order to get more value for their money. Before finalising a tour package, tour operators should take the time to evaluate pricing.
Providing a Relaxed and Safe Tour
A tour should fulfil all of a traveller’s expectations and beyond. A tour operator should be skilled at putting together an experience that will leave guests with lifelong memories.
It’s just as crucial to providing a meaningful, good experience as it is to keep your passengers safe throughout the journey. Some tour activities may represent a possible risk to travellers, putting the tour organisation at risk. As a tour operator, you should encourage your visitors to purchase travel insurance. Insurance will give you and the tourists peace of mind as they go on once–in–a–lifetime experiences. Travel Agency & Tour Operators Roles & Responsibilities
Difference between Travel Agent and Tour Operator
There is a lot of confusion about the difference between tour operators and travel agents what exactly makes them different. The main difference between a Travel agent and a Tour operator are following as:
- A travel agent is a person who has a full knowledge of tourist product – destinations, modes oftravel, climate, accommodation and other areas of the service sector. He acts on the behalf ofthe product providers/principals and in return get a commission.
- Tour operator is an organization, firm or company who buys individual travel components,separately from their suppliers and combines them into a package tour, which is sold withtheir own price tag to the public directly or through middlemen.
- Tour operators are like wholesalers and travel agents are the retailers.
- A tour operator makes the package holidays up and the travel agents sell them on.
- Tour operator taking up the bulk of the responsibilities and his fee is obviously much greaterthan a travel agent.
- A tour operator has the responsibilities to look after the finer details of a vacation or tour suchas hotel, accommodation, meals, conveyance etc.
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window X
- Opens in a new window Facebook
- Opens in a new window Pinterest
- Opens in a new window LinkedIn
- Opens in a new window Reddit
- Opens in a new window WhatsApp
You Might Also Like
Communication skills in customer service, what is sauce importance, thickening agents, mother sauces, what is breakfast types, table setting, cover, order of service, best resorts in the world, food and beverage service: department, outlets, manager, customer retention: in marketing, measures of customer, recruitment, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- North America Tours
- Tour Operators
Top Tour Operators and Travel Agencies in USA 2024/2025
Top Tour Operators and Travel Agencies in USA. Below you will find 29 of the best tour operators and travel agencies in USA offering in total 335 tours and holidays through-out USA. Combined they have received 173 customer reviews and an average rating of 5 out of 5 stars. The top tour activities offered in USA are: Adventure and sport, Wildlife, landscapes and nature & Sightseeing, attractions, culture and history.
- Tours in USA
- USA Travel Guide
- 12 Things to do in the USA
29 Tour Operators in USA with 173 Reviews

Infinite Adventures
- Address 809 W Riordan 100-325, Flagstaff, USA
- Response Rate 100%
- Response Time 2 hours

- Address 2461 FM 778, Mineola, USA
- Response Rate 95%

- Best-in-Class Top 5% of companies
- Excellent Service Top 10% of companies
- Superior Service Top 15% of companies

Expat Explore
- Address 10 Merryweather Place, London, England
- Response Rate 90%
- Response Time 1 hour

Omega Tours
- Address 142 Westmount Avenue, Toronto, Canada
- Response Rate 94%
- Response Time 3 hours

Intrepid Travel
- Address 380 Lonsdale Street, Melbourne, Australia

World Expeditions
- Address 1B Osiers Road, Wandsworth, London, England
- Response Rate 82%

- Address Picquet House, St Peter Port, Guernsey, London, England

The Coyote Trip
- Address 182 Mayall Road, London, England

Luxury Gold
- Address 33 Kern Road, Toronto, Canada
- Response Rate 60%

Doctor Gumbo Tours
- Address 823 Decatur St, New Orleans, USA
- Response Rate 50%

Indus Travels
- Address 233, 11951 Hammersmith Way, Richmond, Canada
- Response Rate 98%

Adventures Abroad
- Address 2148-20800 Westminster Highway, Richmond BC, Canada

- Response Rate 88%

- Address Nelson House, 55-59 Victoria Rd, Farnborough, England
- Response Rate 96%
USA Tour Reviews
- Ms. Rachel T.
- Mrs. Deena M.
- Ms. Melanie P.
- USA budget tours
- Eco tours in USA
- USA guided tours
- USA family tour packages
- USA luxury tours
- USA private tours
- USA self-guided tours
- USA small group tours
- USA solo trips
- USA tailor-made vacation packages
- USA tours for senior citizens
- USA tours for young adults
- USA group tours
- USA last minute deals
- USA travel deals
Popular Destinations
- San Francisco Tours
Upcoming Departures
- Spring 2024/2025
- Summer 2024/2025
- Winter 2024/2025
- August 2024
- September 2024
- October 2024
- November 2024
- December 2024
- January 2025
- February 2025
- August 2025
- September 2025
Best price guaranteed - No booking fees
Free cancellation on most trips
Sign-in to unlock instant trip discounts. Create wish lists and save up to USD 1,500.
What is a Specialist Tour Operator?
A specialized tour operator provides unique and niche travel experiences. You can think of food tours, cooking classes, wine tastings, and hiking tours. Any tour provider that offers services in a niche is a specialized tour operator.
In recent years, there has been a rising interest in specialized tourism. For example, 2021 data shows that 68% of travelers are shifting towards sustainable tourism. Also, the Global Wellness Institute reports that 64% of travelers want wellness vacations. In addition to these, food tourism is constantly growing. In the U.S. alone, 95% are looking for 'some kind of unique food experience', and the numbers are growing globally.
In this blog, we'll learn more about specialized tour operations. If you are a travel agent or tour provider looking for a fresh marketing approach in 2024, this is for you. Below are 5 ideas on how to curate specialized travel experiences that meet travelers' demands.
1. Niche Expertise

Specialist tour operators have in-depth knowledge and expertise in specific travel niches or themes, such as adventure travel, wildlife safaris, cultural immersions, or culinary tours.
Did you know that some specialist tour operators specialize in niche markets like "dark tourism," offering tours to historically significant but often somber places such as battlefields, prisons, or disaster sites?
Tips for tour operators:
- Know Your Stuff : Really get to know everything about the special travel area you're focusing on, like history and interesting facts.
- Tell Great Stories : Make your tours interesting by telling cool stories. Work with local people who know a lot about the place to make it more real.
- Listen and Change : Pay attention to what your travelers like and don't like. Use their feedback to make your tours even better.
2. Customized Experiences

They often have travel agency to offer customized or tailor-made itineraries to cater to the unique interests and preferences of their target audience, allowing travelers to personalize their journeys.
Many specialist tour operators provide travelers with the opportunity to design their own itineraries, offering a level of personalization that can include specific activities, accommodations, travel arrangements, or even dietary preferences.
- Offer Tailor-Made Options : Give your travelers the chance to create their own itinerary. This could mean letting them pick specific activities, choose their own accommodation, or even request special meals.
- Ask for Preferences : Before the trip, ask your travelers about their interests, what they want to see and do, and any special needs they might have. Use this info to make their experience more personal.
- Flexible Scheduling : Allow some flexibility in your itinerary. This way, travelers can spend more time on the activities they enjoy most or explore additional sites that catch their interest during the tour.
3. Destination Specialization

Some specialist tour operators concentrate on specific destinations or regions, becoming experts in those areas and offering comprehensive experiences within them.
Other specialist tour operators focus exclusively on regions with unique natural wonders, like the Galápagos Islands, where they specialize in eco-friendly and sustainable travel experiences.
- Be a Local Expert : Learn everything about the specific region or destination you focus on, including its culture, history, and natural wonders. This knowledge will help you create in-depth, engaging tours.
- Highlight Unique Features : Showcase what makes your destination special, like unique natural attractions or cultural experiences. For example, if you specialize in the Galápagos Islands, emphasize eco-friendly tours that highlight the unique wildlife and ecosystems.
- Sustainable Practices : If your destination is known for its natural beauty, like the Galápagos, prioritize sustainable and eco-friendly travel practices to preserve the environment. This is not only good for the planet but also appeals to eco-conscious travelers.
4. Exclusive Access

They may provide package tours with exclusive access to attractions, accommodations, or activities that are not readily available to mass-market tour operators, enhancing the uniqueness of the tours.
Specialist tour operators might arrange exclusive access to archaeological sites before or after regular opening hours, allowing travelers to explore these historic treasures without the crowds.
- Arrange Special Visits : Work to get special access to popular sites, like arranging visits to archaeological sites outside of normal hours. This lets travelers enjoy these places without the usual crowds.
- Unique Experiences : Offer activities or experiences that aren't usually available to the general public. This could be anything from a private tour with a local expert to exclusive access to certain areas.
- Build Relationships : Develop good relationships with local attractions and accommodation providers. This can help you arrange special access or unique experiences for your travelers.
5. Passionate Guides

Specialist tour operators often employ passionate and knowledgeable tour guides who are experts in the niche or destination, ensuring travelers receive a high level of expertise and engagement during their journeys.
In the world of birdwatching tours, specialist operators often employ ornithologist guides who are not only experts in bird identification but also passionate advocates for bird conservation, enriching travelers' experiences with their deep knowledge and enthusiasm.
- Hire Expert Guides : Look for guides who are not just knowledgeable but also passionate about the niche. For example, in birdwatching tours, hire ornithologists who are experts in bird species and conservation.
- Train for Engagement : Ensure your guides are trained not only in factual knowledge but also in engaging storytelling and interaction with travelers. This enhances the overall experience.
- Focus on Special Interests : Match guides with specific interests or expertise to relevant tours. A guide's enthusiasm for their specialty, like bird conservation, can greatly enrich a traveler's experience.
Key Takeaways
As we wrap up our exploration of specialized tour operators, it's clear that this niche-focused approach in the tourism industry is not just a trend, but a growing sector meeting diverse traveler demands.
From the increasing interest in sustainable tourism and responsible travel, to the rise of wellness vacations and unique culinary experiences, the opportunities for specialized tour operators are vast and varied.
To stand out in this competitive market, here are three key actionable tips that you, as tour and activity providers, can implement:
- Embrace Your Niche : Whether it's eco-tourism, culinary experiences, or wellness retreats, dive deep into your niche. Know your audience and tailor your offerings to their specific interests and needs.
- Prioritize Authentic Experiences : Travelers are seeking genuine, immersive experiences. Collaborate with local communities and experts to offer authentic and unique tours that cannot be found elsewhere.
- Leverage Technology and Innovation : Utilize the latest technology, like AI for personalized itinerary planning or virtual reality previews of tours, to enhance the customer experience and streamline operations.
By focusing on these areas and continually adapting to the evolving desires of travelers, you can create memorable and distinctive experiences that not only meet but exceed the expectations of your clientele. Remember, in the world of specialized tourism, it's all about delivering uniqueness, authenticity, and quality.
Our Happy Specialized Tour Operators
TicketingHub has worked with specialized tour and activity providers for years now. Some of them are now renowned for their food tours, city tours, and special events. Read our case studies below and see what helped them succeed in this rising market.
- The Secret Food Tours
- Egypt's Sound and Light Show
- Belfast City Tours
People Also Ask:
1. why is online booking software helpful for specialist tour operators.
An online booking software is a game-changer for specialist tour operators. This type of software streamlines the booking process, making it easier for travelers to secure their spots on specialized tours.
For the operator, it simplifies managing reservations, tracks customer preferences, and automates tasks like sending confirmations and reminders.
Online booking systems offer efficiency and personalized service, particularly for specialist operators who deal with customized and niche travel packages. It saves money and time, both for the tour operator and the traveler, enhancing the overall experience.
2. What is a specialist tour operator?
Specialist tour operators are tour operators in the travel industry who focuses on offering specialized and niche travel experiences. Unlike mass market tour operators who cater to broad, general travel demands, specialist tour operators offer in-depth expertise in specific areas.
These can range from eco-tourism, adventure travel, cultural tours, to specific country or regional focuses. They provide tailored package holidays and tours that cater to specific interests and often offer more personalized service than other tour operators.
3. What is a specialized tour?
A specialized tour is a travel package designed to cater to specific interests or themes. Unlike general tour packages offered by many travel agencies, specialized tours delve deep into a particular area, offering unique experiences such as eco-tourism adventures, culinary tours in specific countries, or in-depth exploration of national parks.
These tours are usually crafted by specialist tour operators who possess deep knowledge and passion for the niche, ensuring an enriching and authentic experience for the traveler.
4. What are the main three types of tour operators?
The three main types of tour operators in the travel industry are inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators, and domestic tour operators.
- Inbound Tour Operators : These operators specialize in arranging tours and travel packages for travelers coming into a country. They work closely with hotels, airlines, and ground operators to provide a comprehensive travel experience in the destination country.
- Outbound Tour Operators : These receptive tour operators organize trips for travelers stepping out of their home country to visit other destinations worldwide. They often work with airlines, hotels, and travel operators in different countries to arrange all travel components.
- Domestic Tour Operators : They organize tours for domestic travelers within their own country. They specialize in knowing the best local spots and experiences that appeal to domestic travelers, including hotels, transport, and leisure travel activities.
Each type of tour operator plays a crucial role in the tourism ecosystem, catering to different segments of holidaymakers and travelers. It offers varied services like transport, accommodation, and travel packages.
5. What types of niche travel experiences do specialist tour operators offer?
Specialist tour operators offer a wide range of niche experiences, including wildlife safaris, cultural immersions, adventure travel, culinary tours, and more. They cater to specific interests and passions, providing travelers with unique and customized journeys.
6. Are specialist tour operators more expensive than regular tour companies?
Specialist tours can cost widely depending on niche and customization. While some specialist tours may have a premium price due to exclusive access or unique experiences, others can be competitively priced. It's essential to compare options and assess the value of all arrangements and experiences offered.
Get the latest news and stay in touch with the industry secrets.
By clicking "Subscribe", you agree to our Privacy Policy and the data we do collect.

What to Look For in the Best Online Booking Software?

Online Travel Booking Tool: How Magic Link is Solving the Rebooking Problem
.webp)
FareHarbor vs Rezdy vs TicketingHub: Honest Tour Booking Software Comparison Guide

Why Online Reputation Management Is Important for Tour Operators
Keep Reading

Discover the role of specialized tour operators. From wellness to food tours, gain insights in how they create authentic travel experiences.
How Can Tour Operators Contribute to Sustainable Tourism?
Explore how tour operators contribute to sustainable tourism, with eco-friendly strategies and community support tips.
- Transportation
- Single & Multi-Day Tours
- Museums and Attractions
- Destination Marketing Organizations
- Google Things To Do
- Zaui Marketplace
- System Status
- Case Studies
- API Documentation
- Reseller Signup
The Ultimate Guide to working with Tour Wholesalers and Operators
By: Marium Farooq
March 3, 2023
Table of Contents
Tips and Tricks to establish partnerships with Tour Wholesalers and Intermediaries
As you grow your business and find ways to optimize your revenue, you will be intrigued to work with Tour Wholesalers and Operators. But it can be challenging to understand the pros and cons of working with them to ensure the relationship affects your business positively.
Here is everything you need to know about working with Tour Wholesalers and how to make the most of this amazing opportunity:
What is the difference between a Tour Operator and a Tour Wholesaler?
The terms are often used interchangeably but have different meanings. A Tour Wholesaler creates packages by combining multiple activities, most likely, transportation and other services, and sells them via a sales channel. A Tour Operator is an organization or a firm that combines components from different travel suppliers and sells directly to the public.
Why are tour operators and wholesalers important?
Tour Operators and Wholesalers can help you sell bookings in bulk which can help you grow and increase your profit. A sizeable segment of travellers are searching for all inclusive travel packages with the ease of booking. By building a relationship with tour wholesalers and operators, you can add an additional revenue stream to your business. It can also be a valuable distribution channel to scale your business and ensure that travellers have access to your activities and services.
What are the 3 main types of tour operators?
The three main categories of tour operators are Domestic Tour Operators, Inbound Tour Operators, and Outbound Tour Operators.
- Domestic Tour Operators create inclusive tour packages specifically for domestic travellers. To simplify things, they are tour operators who provide travel packages within the traveler’s native country. They typically combine multiple tourism components to create packages e.g. a transport service and a set of activities to sell to travellers within the country boundaries. Domestic tour operators form relationships with other travel service and activity providers to create unique experiences for travellers in order to attain a larger share of the Domestic Tourism market.
- Inbound Tour Operators or Incoming Tour Operators handle all activities and arrangements for the tourists in the host country. The packages are created specifically for Groups and Individuals who are non-residents of the country traveling to the host country for leisure or business. An inbound tour operator typically works with local travel agents and businesses to curate a tour package or packages that covers their own country.
- An Outbound Tour Operator or Outgoing Tour Operator handles all travel arrangements and activities for International destinations. To simplify it further, the packages are created to take travellers to other International Destinations from their home country. They are tour operators who market their tours for international destinations, either for business or leisure travel. Typically, an outbound travel operator will work or partner with businesses, destination marketing organizations and online travel agencies in the destination country to design a tour package for their customers. Most Outbound tour operators specialize in particular destinations based on tourism trends, their distribution partners and their expertise in the destination country.
Tips for working with Wholesalers and Tour Operators:
Here are all the secret ingredients you need to form successful travel partnerships with Tour Wholesalers and Operators:
Research to Find the Right Fit
Every Travel Wholesaler and Operator is different. They have their unique distribution systems and they cater to different markets. You want to make sure that there is a connection between their offerings and yours, especially in terms of the market they are targeting and the tourism services they offer.
Start off by conducting research and compiling a kit consisting of their product fact sheets, pricing information, distribution channels, terms and conditions and any unique information that you might require to set you off on the right foot. This information is instrumental in creating a long-term mutually beneficial partnership with Tour Wholesalers and Operators.
Sell Unique Activities and Experiences
One of the most important pieces of the puzzle is to make your activities attractive for the Wholesalers and Operators. It is most likely that you will be working with multiple tour operators and wholesalers, and you want to make sure they find your offerings attractive and unique to add to their itineraries.
Having authentic and unique experiences will not only increase the demand for your activities and bookings but will also appeal to Travel Operators to promote it better, more so than your competitors. According to recent research , the demand for unique experiences is on the rise and travellers all around the world are willing to pay a premium price for unique experiences. Adding an extra element to your offering to make it stand out might go a long way for your business to generate more revenue by putting you in a position to negotiate higher prices with the tour wholesalers and operators.
Prepare to Manage Bookings in Advance and in Real-Time
Managing Bookings while working with Tour Wholesalers and Operators can be a huge challenge. First and foremost, an Online Booking Software is essential to attract Tour Operators to work with you. It will simplify the booking process and will help your partners automatically earn their commissions. It will take away the mundane tasks of constantly emailing and calling to manage bookings and will replace it with a system that updates in real-time and makes everything effortless.
Working with wholesalers and operators can put you in unique situations which will go beyond simple bookings and commissions. One of these cases is to create bookings in advance and then manage real-time bookings as they happen with time. There are many factors that might come into play, which is why you should invest in an online booking engine that can help you customize your Online Booking System and make it a seamless experience for yourself and other stakeholders.
For instance, a software like Zaui with 20 years of experience can help you connect with the best partners all around the world, allowing them to book instantly with zero human interaction. You will ultimately save time and make more money.
Build Personalized Partnerships and Track Performance
What works in one country might not work in the other, the same is the case with Wholesalers and Operators since they can be located in different parts of the world and operate in different types of travel communities. Building personalized partnerships will help optimize your bookings and create custom marketing strategies to make better-informed decisions.
It is equally important to keep track of how each partnership is performing for your business. Tracking the performance will determine the next steps for your Marketing Plan and Communication. Additionally, it will provide insight into each market and ultimately boost bookings.
One of the ways to achieve your goals and maximize your performance is to choose an Online Booking Software that can help you connect with the best distribution agents all around the world and track their performance.
Zaui Online Booking Software offers a Channel Manager platform and Reporting Dashboard that can help you connect with distribution partners and optimize growth. Request a Free Personalized Demo from our support team to help maximize your Bookings and Revenue!
You can also have a look at our website to hear our customer success stories or check our Buyer’s Guide as you search for the best online platform to work with Travel Wholesalers and Operators.
Get a Personalized Demo
Inside Zaui: Product News, Tips & Tricks
- Tips & Tricks
- Tours & Activities
How to Write a Tour Booking Confirmation Email: 8 Types with Great Examples
How to Write a Tour Booking Confirmation Email: 8 Types with Great Examples Confirmation email templates offer a valuable means...
Top 7 Travel Review Sites for Tour Operators in 2024
Top 7 Travel Review Sites for Tour Operators in 2024 Your customers are the initial guides for your tour and...
11 Tips on How to Increase Sales in a Tour Company
11 Tips on How to Increase Sales in a Tour Company In today’s dynamic travel industry landscape, tour companies face...
Curabitur nec nunc ut augue tincidunt interdum quis a diam. Suspendisse vel justo vitae mauris sodales commodo. Nullam dapibus nisi mi, id lobortis urna scelerisque ac. Duis auctor enim sit amet quam lacinia malesuada.
Outbound generally relates to anything moving or traveling away from a certain place. When speaking of travel, outbound tourism means leaving one’s country of residence to visit a different country for a period of less than one consecutive year for leisure, business , or other purposes.
Outbound tour operators are travel companies that organize trips to international destinations (other tour operator categories include inbound , domestic , and ground ).
An outbound flight is one departing from an airport to a point of destination, as opposed to inbound flights which arrive at the airport.

Recommended content for you
Video: how supersonic flights might finally return, experiential travel explained: players, distribution landscape, and opportunities, video: ai in tours & attractions, tour operator software: itinerary creator, booking engine, and other handy technologies, video: seasonal travel and why we may want to reduce it.
Our website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. By browsing the website you agree to our use of cookies. Please note, we don’t collect sensitive data and child data.
To learn more and adjust your preferences click Cookie Policy and Privacy Policy . Withdraw your consent or delete cookies whenever you want here .
Get in Touch
Yes, I understand and agree to the Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Outbound tour operators contribute significantly to the destination country's economic growth. The majority of outbound tour operators choose to focus on a specific destination. This may be a destination that is currently popular or a destination in which they have special expertise and distribution partners. Most outbound tour operators ...
An outbound tour operator is one who facilitates outbound tourism. The aim of an outbound tour operator is to send tourists out of a particular country or countries. Outbound tour operators will often collaborate with foreign travel agencies and transport operators to facilitate travel arrangements for their customers.
What is an Outbound Tour Operator? While inbound tour operators bring tourists into a country, outbound tour operators market to travellers in their own country and offer tours in international destinations. When creating tour packages, outbound tour operators usually focus on specific countries, destinations or regions of the world, and also ...
Outbound Tour Operators. Tour operator who promote tours for foreign destinations, maybe business tour or leisure tour is called outbound tour operators. For example a group of American tourists going to a trip of India and Thomas Cook handle arrangement in America like as ticket reservation, hotel booking etc. then Thomas Cook is called ...
An outbound tour operator is responsible for arranging travel plans for people traveling outside of their home country. They collaborate with airlines, hotels, and transportation providers to create all-inclusive travel packages, handle visa applications and logistics, and aim to provide a stress-free and pleasurable experience for their ...
As per the requirement, there are different types of tour operators in the travel industry. Some of these include inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators, domestic, specialist among others. Let us explore them one by one. 1. Inbound Tour Operators. Inbound tour operators organize and sell travel packages for visitors coming into the ...
Tour operators play a pivotal role in the tourism industry. They create and organize tour packages, catering to both business and leisure travelers. These packages simplify travel arrangements, offering hassle-free travel. Tour operators are the key architects of memorable trips, ensuring travelers can explore various destinations easily.
Outbound Tour Operators: Outbound tour operators are those who market trips to overseas locations, whether they be for business or pleasure. For instance, if Thomas Cook handles bookings for a group of French tourists traveling to India, Thomas Cook is referred to be an outbound tour operator in the context of France.
Outbound Tour Operators: Outbound tour operators orchestrate travel packages for individuals venturing beyond their home country. They craft detailed itineraries & liaise with local partners in ...
The tour operator is an integral component of tourism, yet many people are unclear about what a tour operator actually is or or what they do. In this video I...
As per the requirement, there are different types of tour operators in the travel industry. Some of these include inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators, domestic, specialist among others. Let us explore them one by one. 1. Inbound Tour Operators. Inbound tour operators organize and sell travel packages for visitors coming into the ...
Tour. This is a catch-all term that implies a type of travel experience that takes place over time, generally visiting multiple sights. It could last 1 hour or 30 days, and be done as a walk, or in vehicle. It could be a solo traveler or a group of 50 people. Other words might be used to describe the same thing: tour, experience, journey ...
Outbound Tour Operators. While inbound tour operators bring tourists into a country, outbound tour operators market to travellers in their own country and offer tours in international destinations. When creating tour packages, outbound tour operators usually focus on specific countries, destinations or regions of the world, and also partner ...
2. Outbound tour operator An outbound tour operator creates and markets international tours for people within their own country. Outbound tour operators usually focus on destinations, countries or regions they know well. They partner with businesses based in host countries to give their customers a high-quality, value-for-money tour experience. 3.
Outbound Tour Operators: These tour operators service international travelers. They typically focus on a single origin market but often service multiple overseas destinations. Outbounds specialize in the market that travelers purchasing a tour are departing from and can provide native language marketing, sales, and customer support. They also ...
According to the UN World Trade Organization, there are three kinds of tours - domestic, inbound, and outbound - and thus three kinds of tour operators who hire tour directors. Many companies offer both domestic and outbound tours. Domestic tours involve residents of the given country traveling only within their own country.
Types of Tour Operators. There are five main categories of tour operators that you could fall into: inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators, domestic tour operators, receptive tour operators, and ground tour operators. Let's find out which one of these five you fall into. Of course any tour operator cannot be fully successful without ...
Tour Operator: A tour operator is a company that designs, organizes, and sells pre-packaged tours or holiday packages to travelers. Tour operators handle all aspects of the tour, including accommodations, transportation, meals, guided tours, and activities. They often work with travel agents to sell their tour packages to clients.
Outbound Tour Operators. Tour operators, who promote tours to foreign destinations, maybe business tours or leisure tours are called outbound tour operators. Indian outbound tourist traffic is growing at a rate of 10 percent annually and this makes India the second-largest country in the world with regard to the travelling population.
World Expeditions. of 636 reviews. Address 1B Osiers Road, Wandsworth, London, England. Response Rate 82%. Response Time 3 hours. Certificate of Best-in-Class. World Expeditions has over 40 years of experience operating authentic and unique adventure holidays with a genuine focus on the paths less travelled.
The three main types of tour operators in the travel industry are inbound tour operators, outbound tour operators, and domestic tour operators. Inbound Tour Operators: These operators specialize in arranging tours and travel packages for travelers coming into a country. They work closely with hotels, airlines, and ground operators to provide a ...
An Outbound Tour Operator or Outgoing Tour Operator handles all travel arrangements and activities for International destinations. To simplify it further, the packages are created to take travellers to other International Destinations from their home country. They are tour operators who market their tours for international destinations, either ...
Outbound tour operators are travel companies that organize trips to international destinations (other tour operator categories include inbound, domestic, and ground). An outbound flight is one departing from an airport to a point of destination, as opposed to inbound flights which arrive at the airport. Share. Share:
As of April 2024, 62% of outbound travelers were female, with a significant portion between the ages of 18 to 29. Spontaneous and Online Bookings: Chinese travelers are researching and booking ...